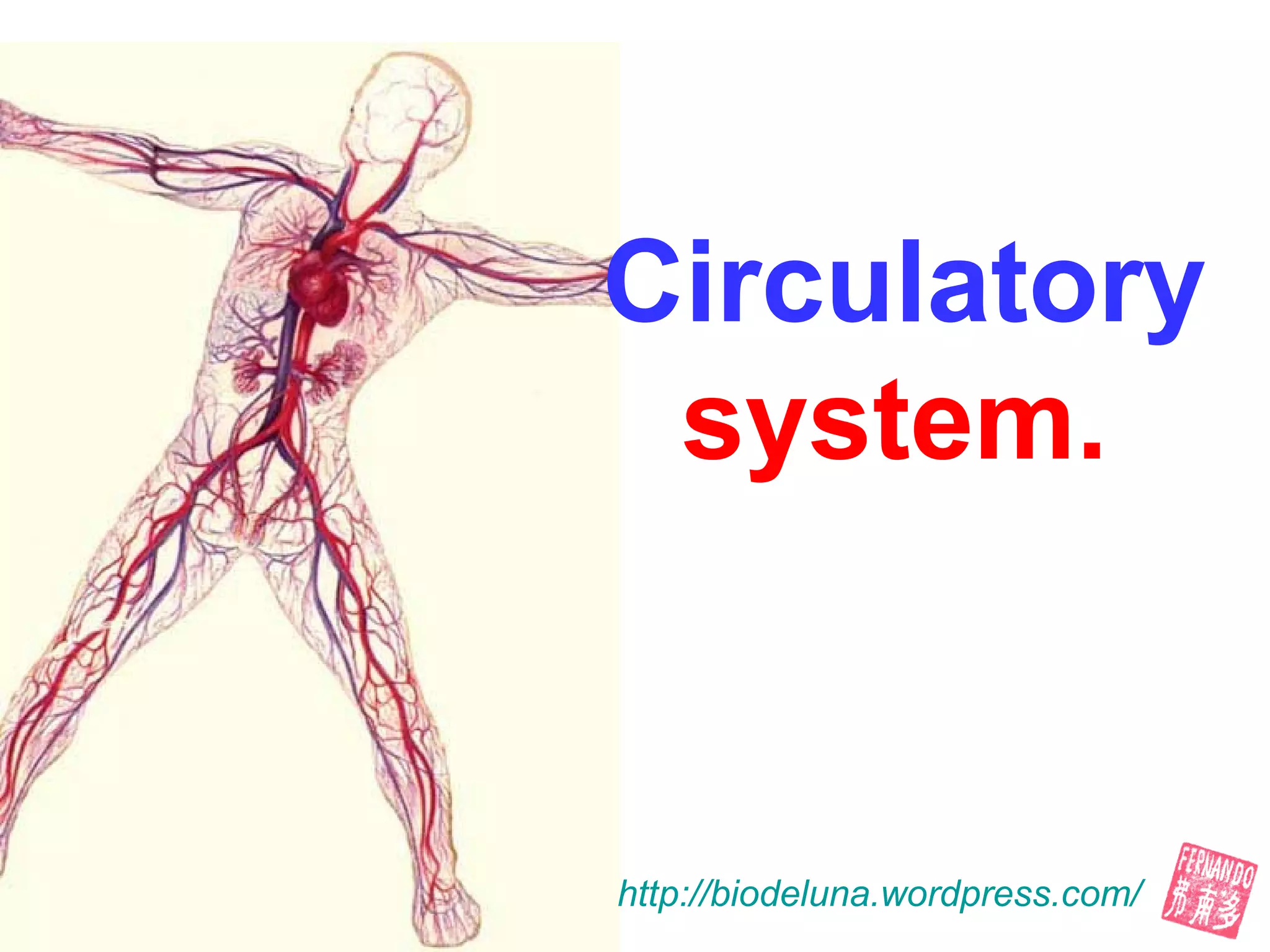
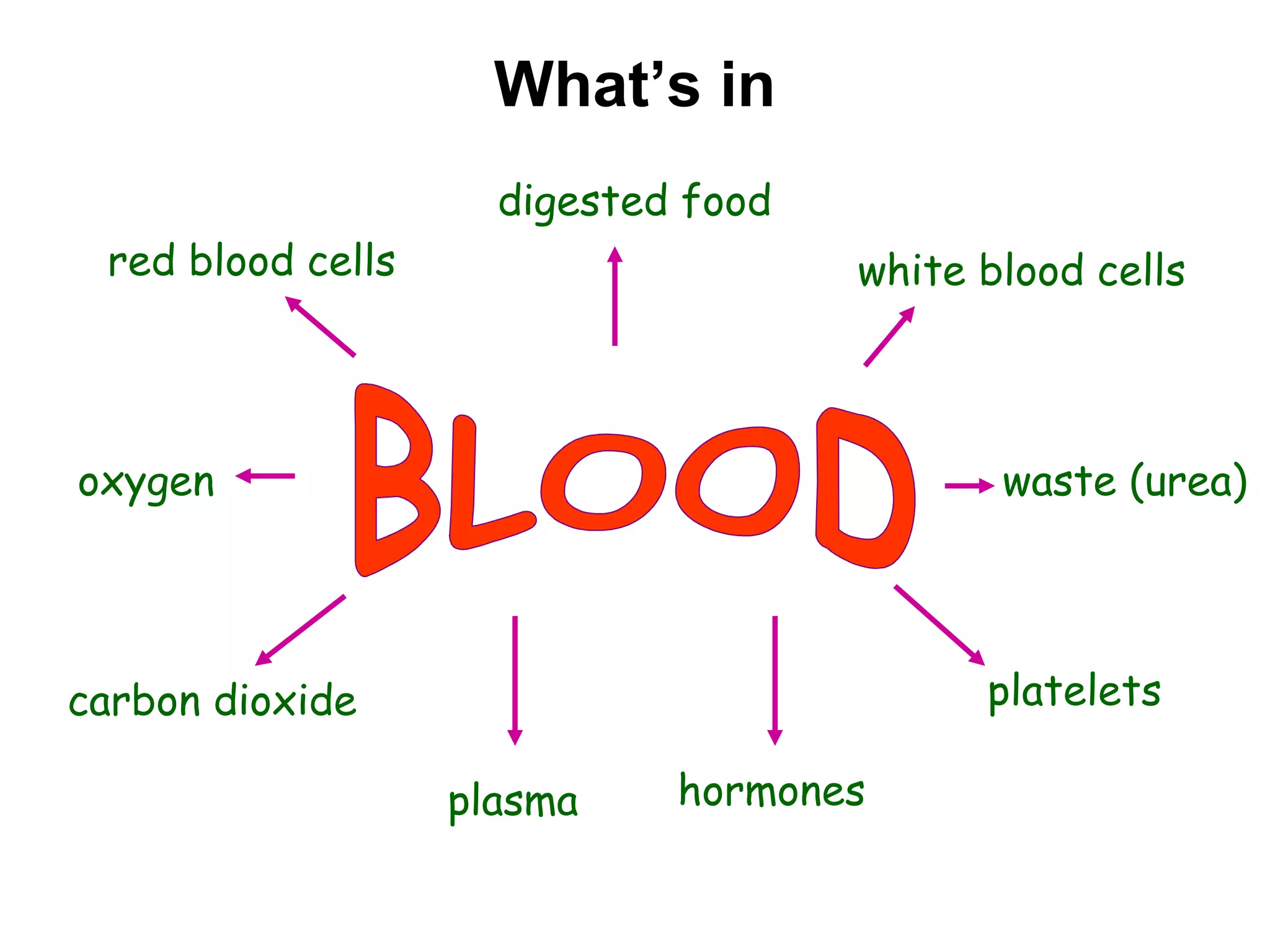
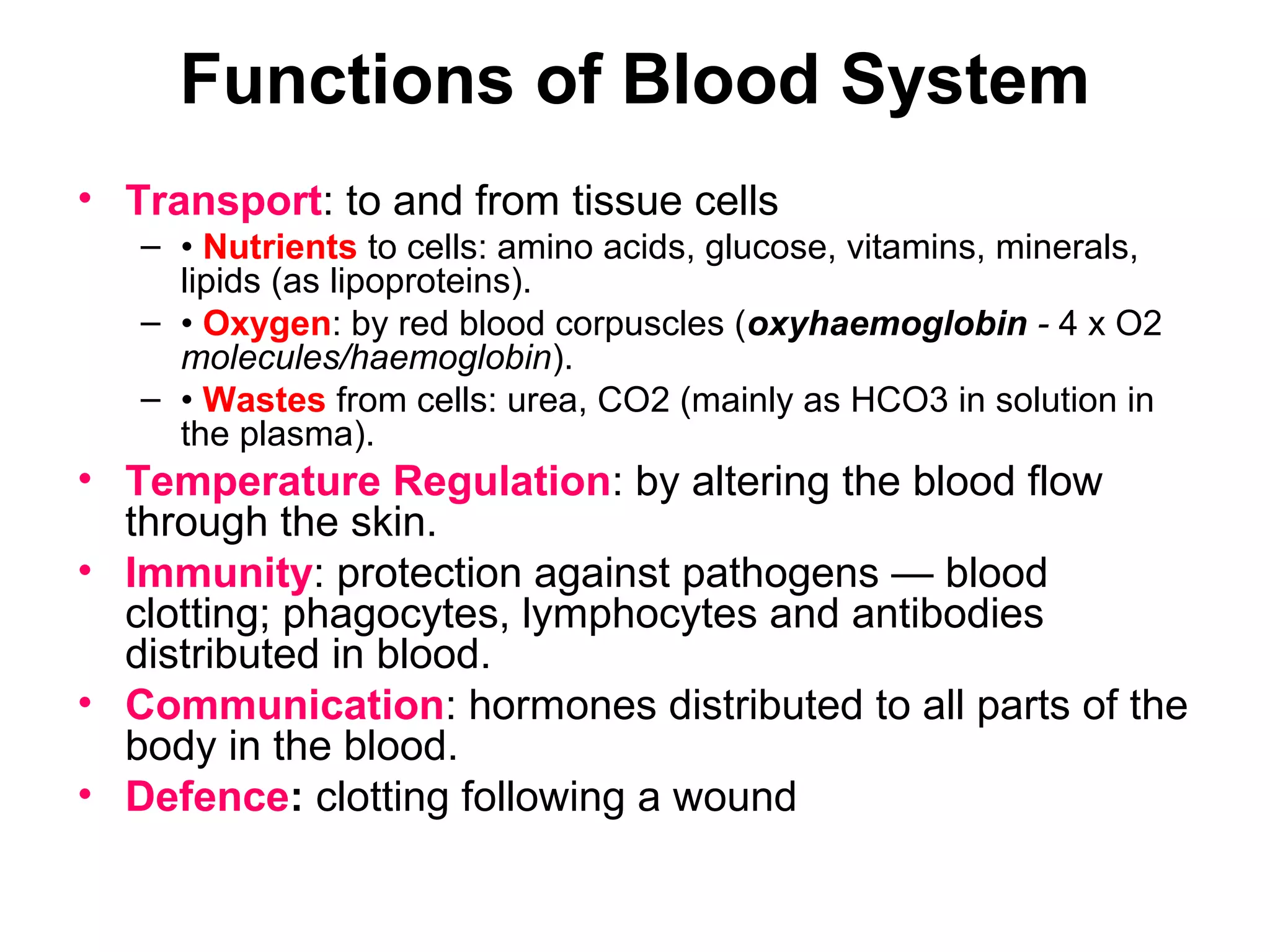
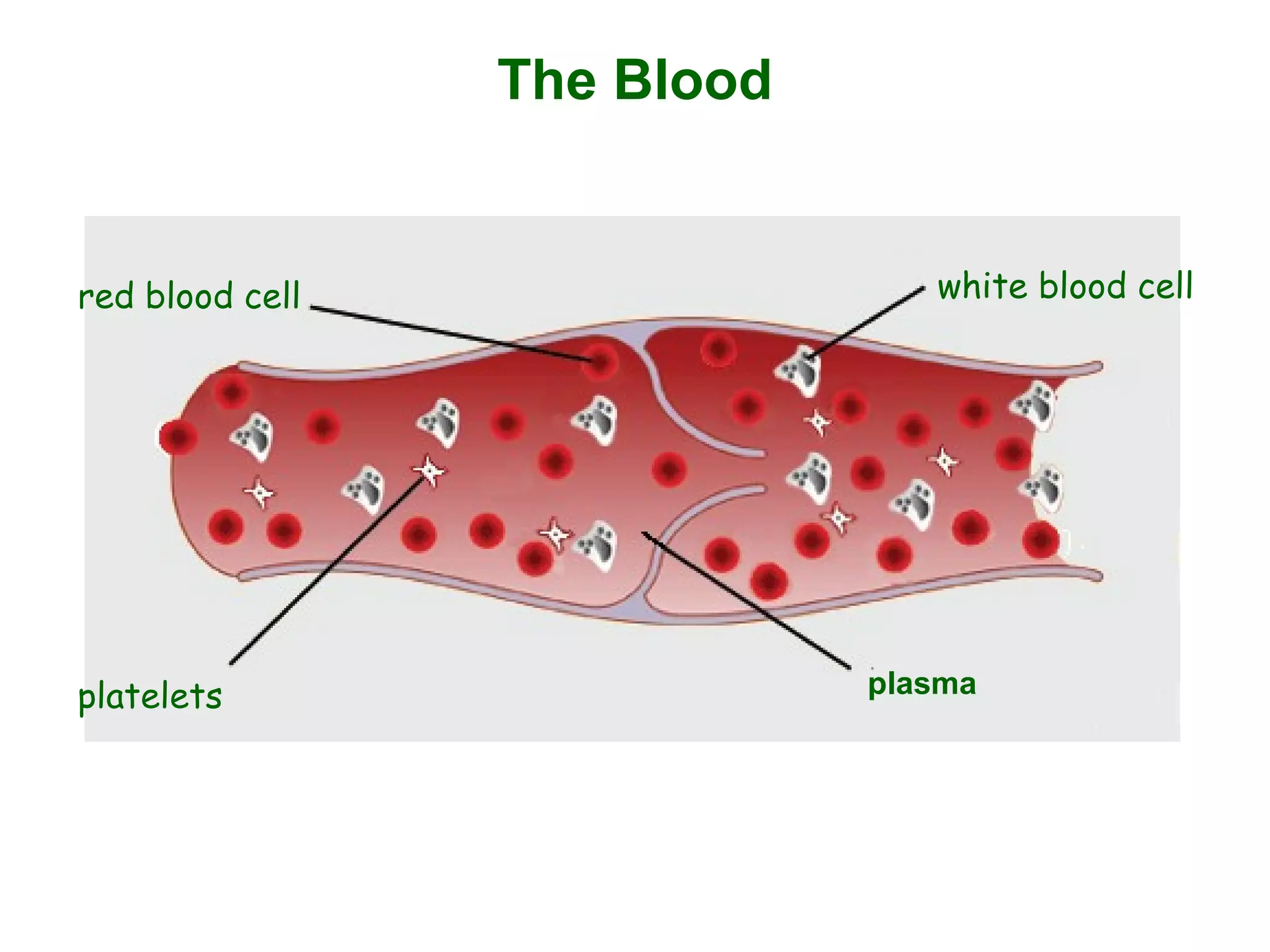
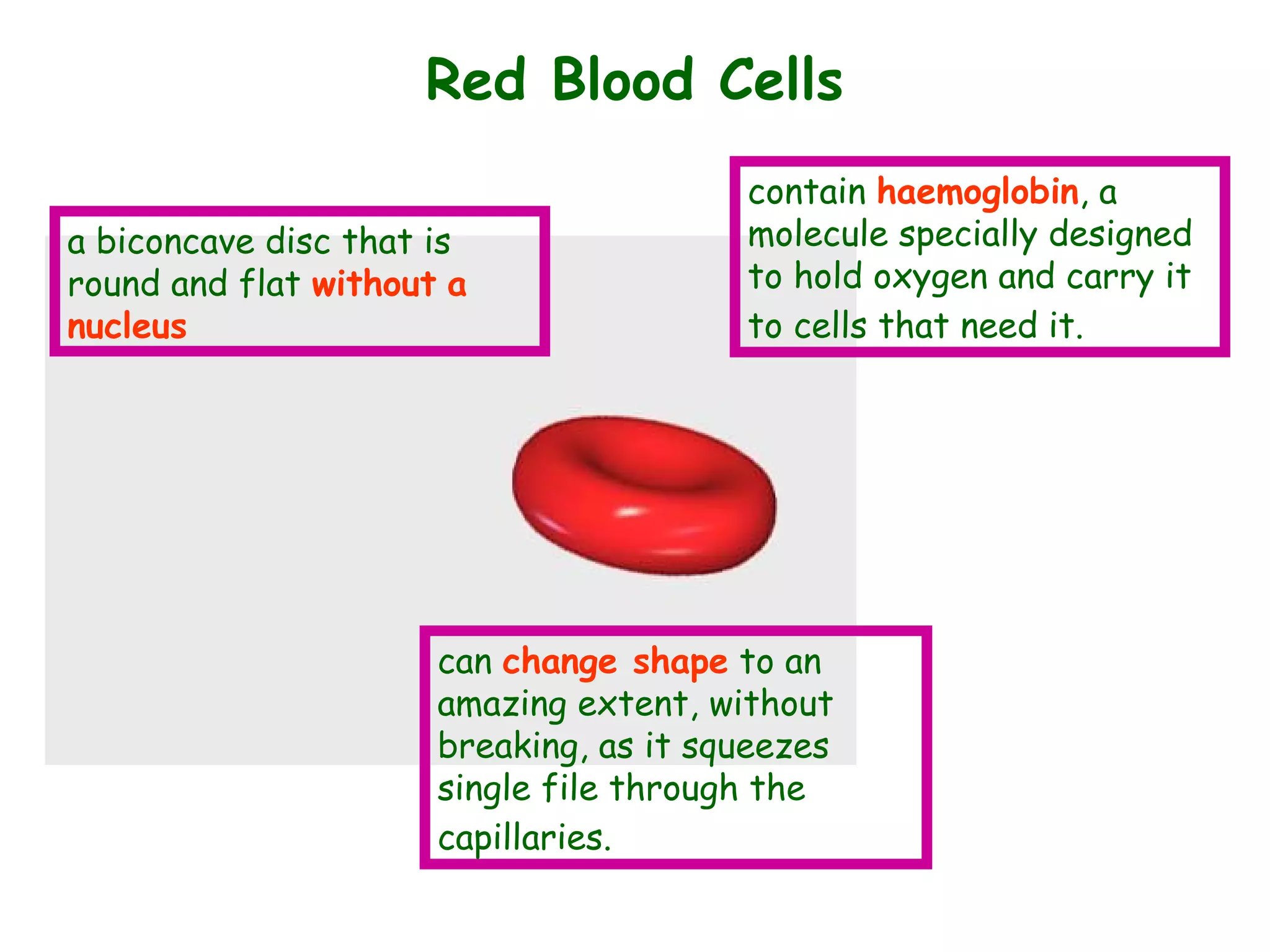
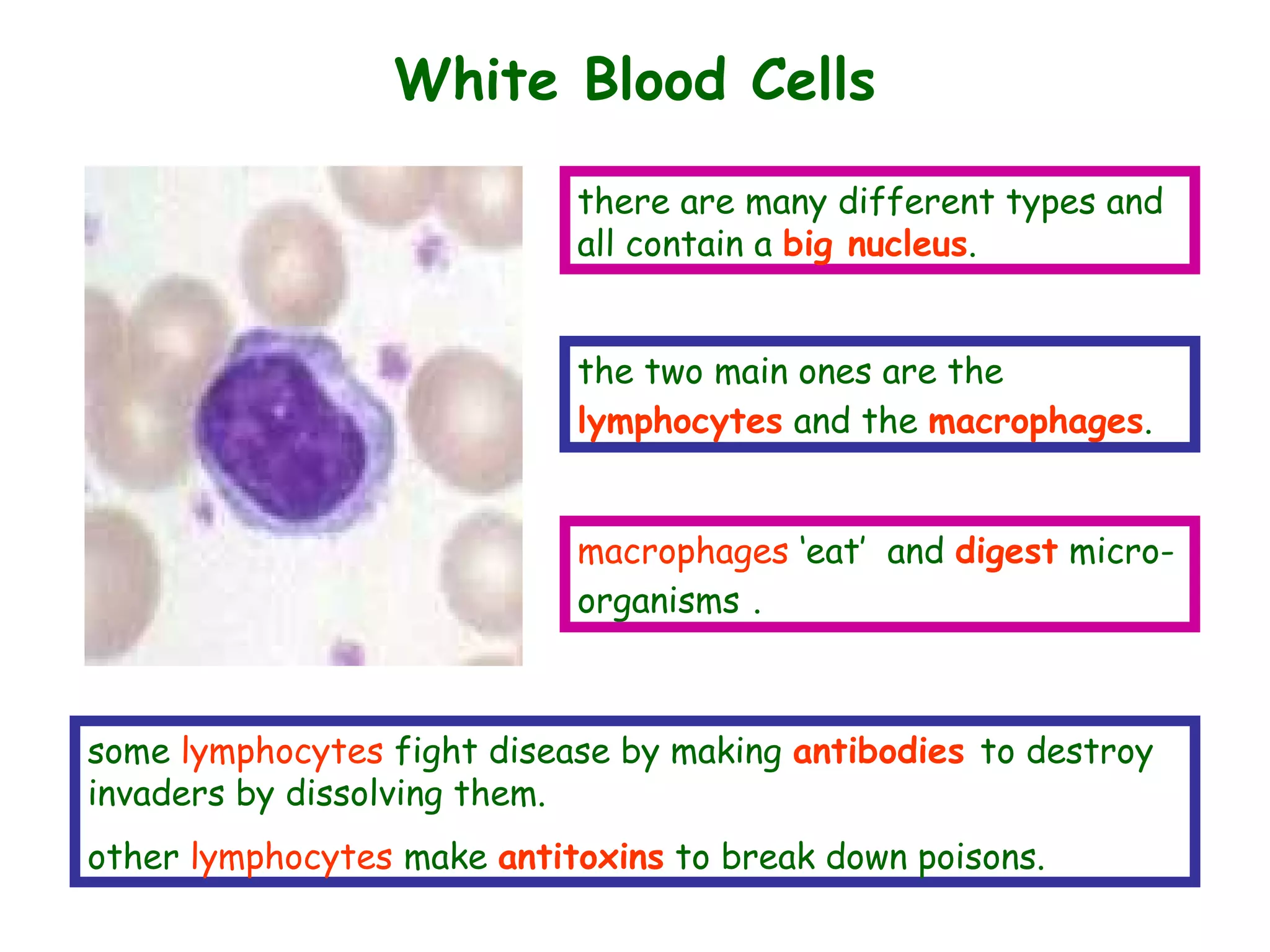
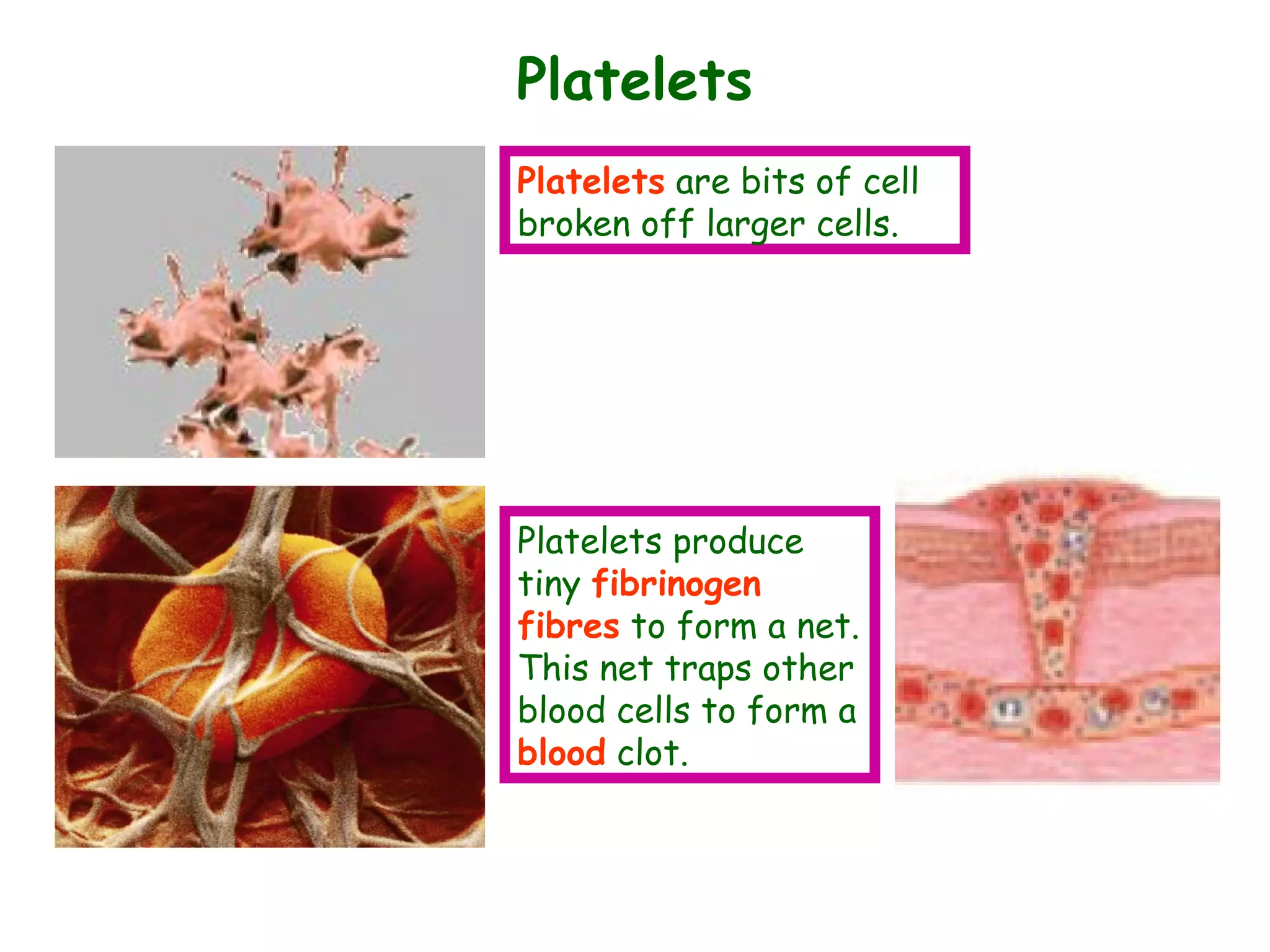
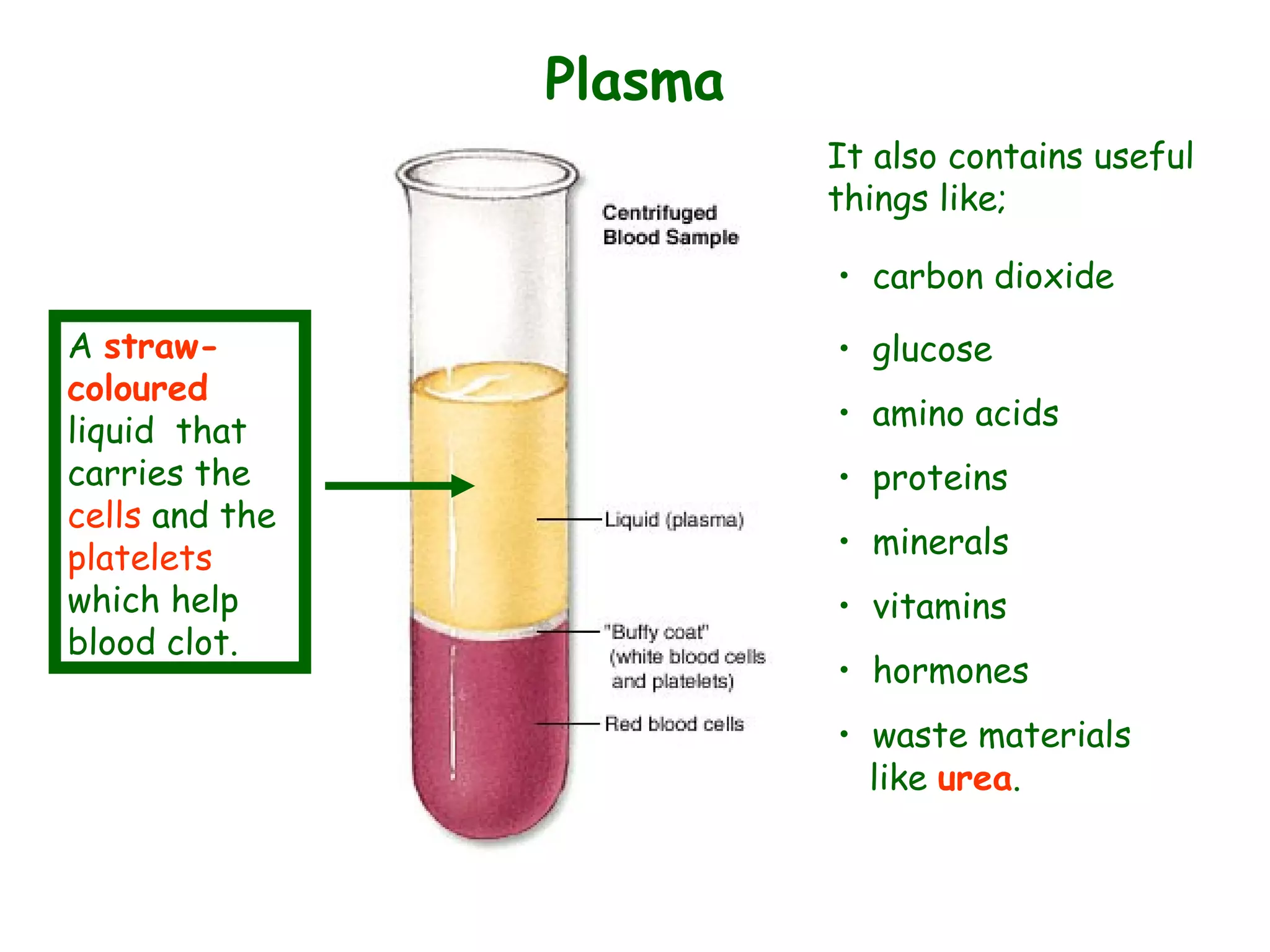
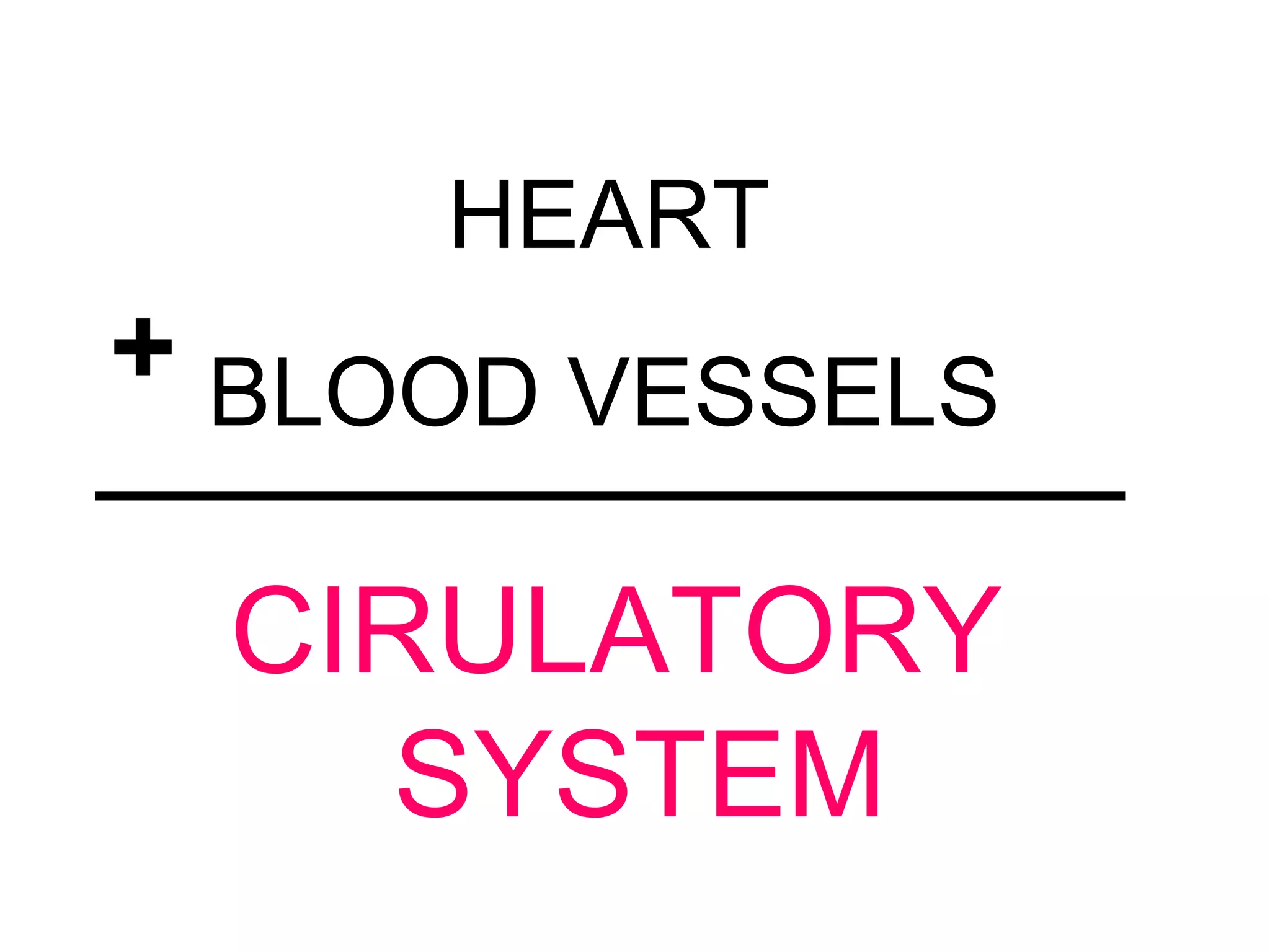
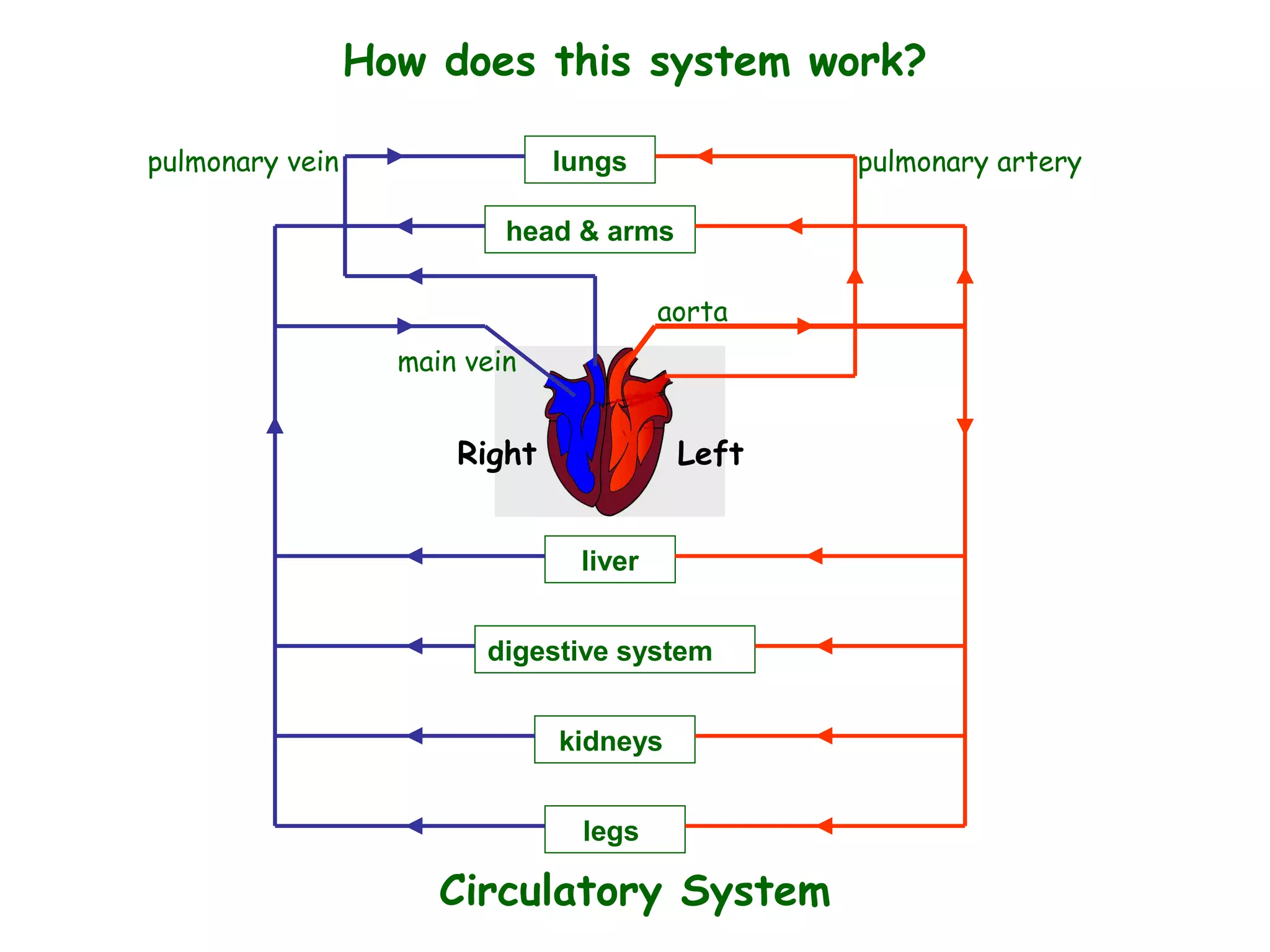
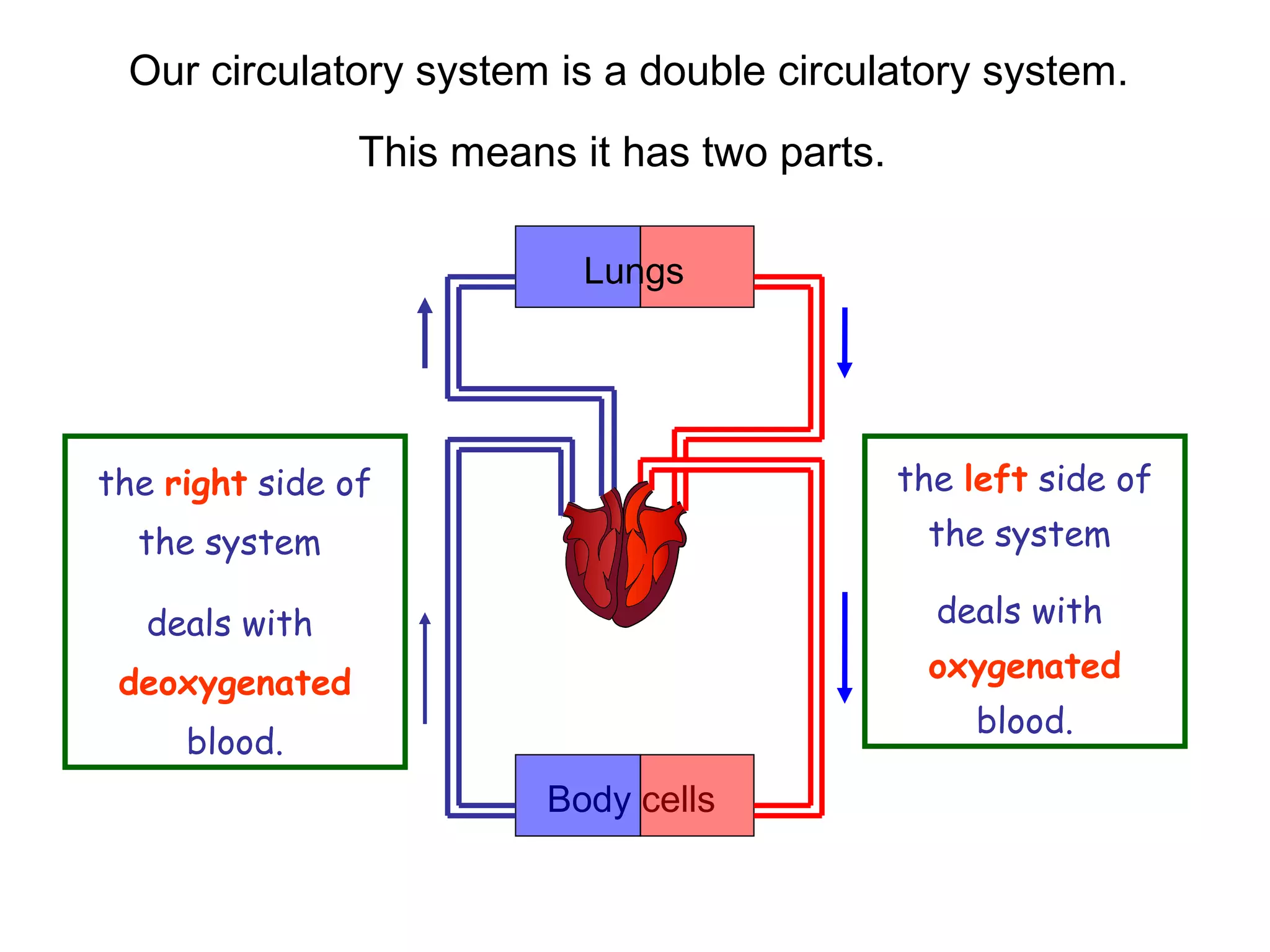
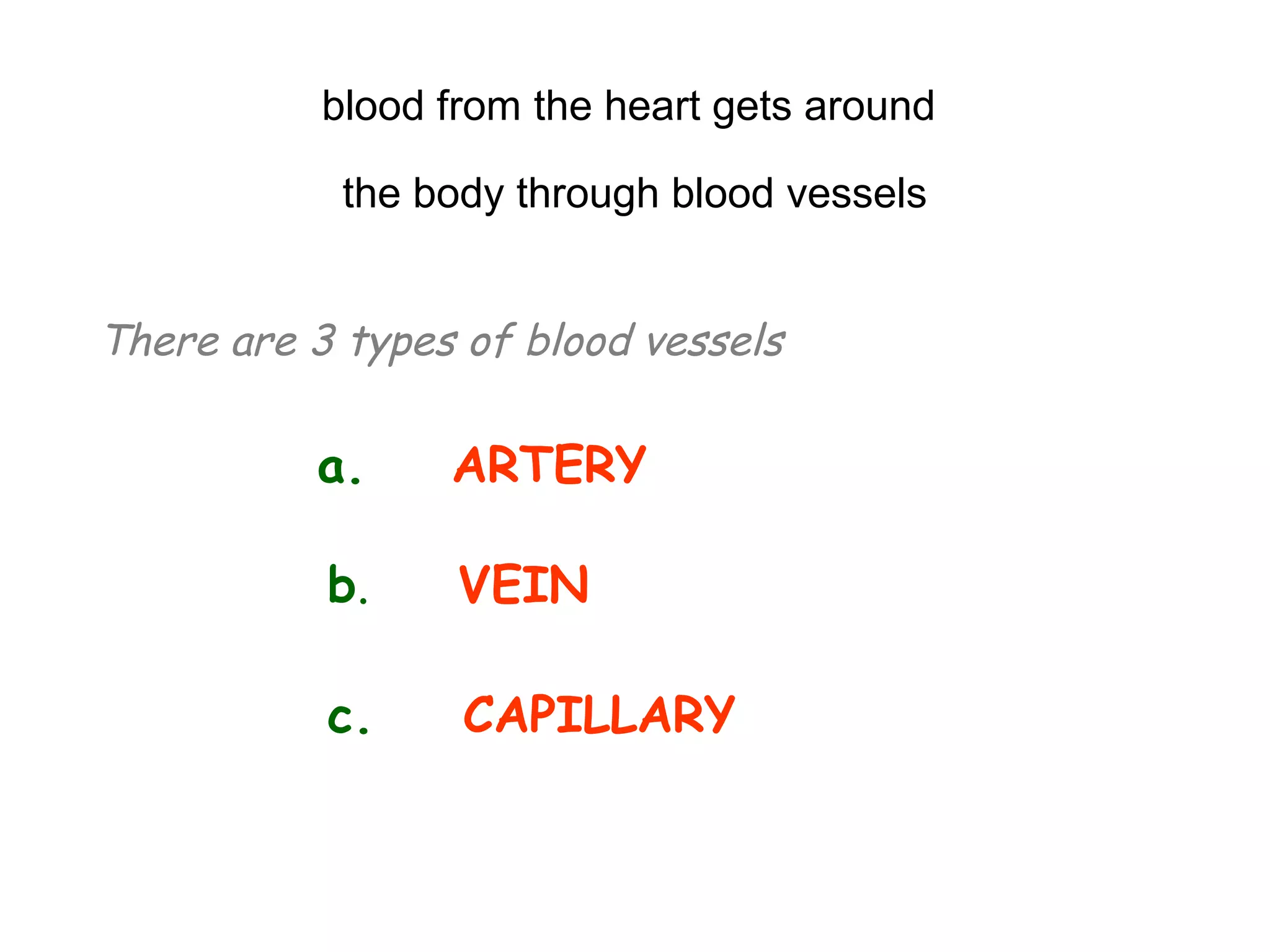
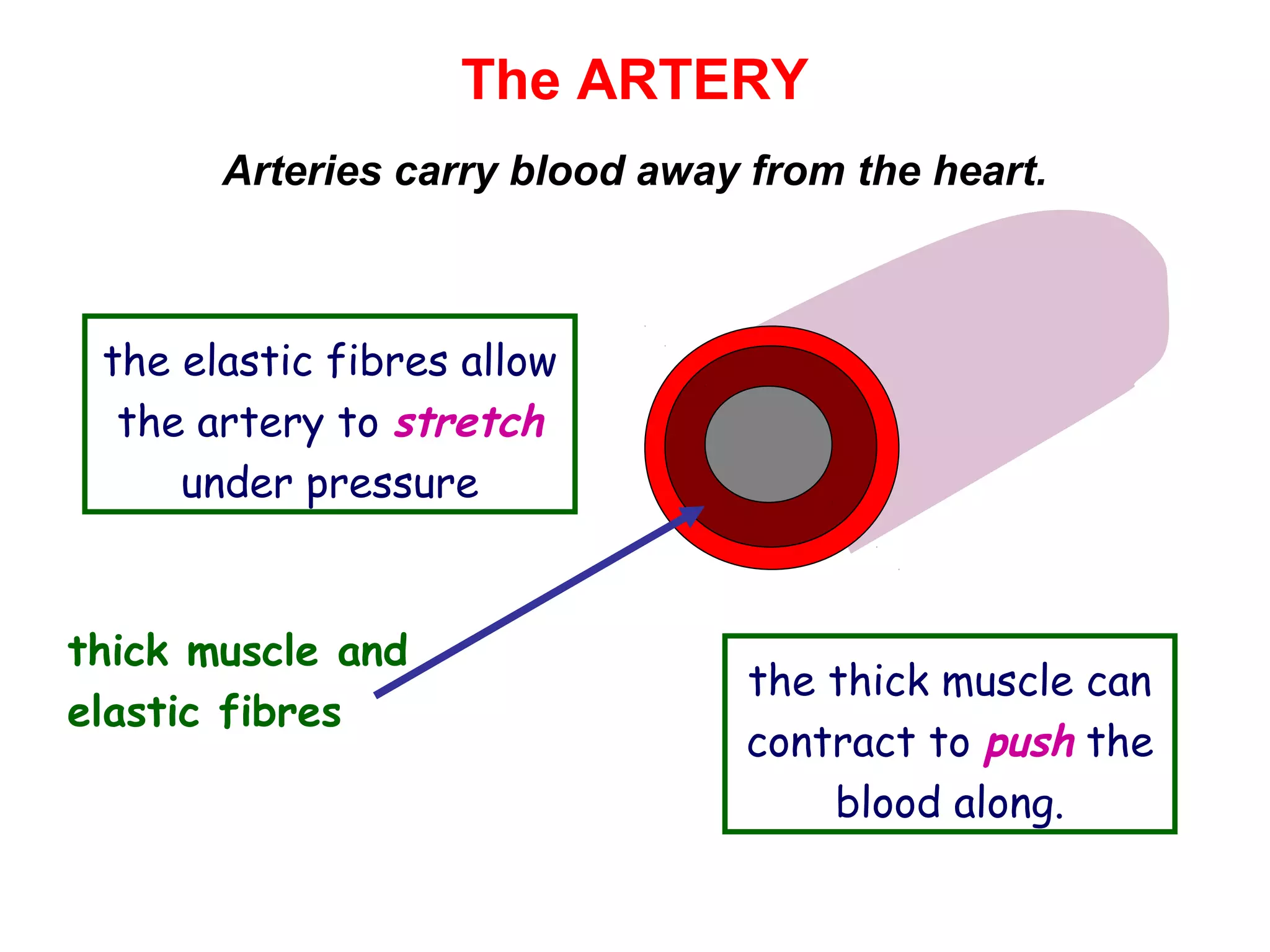
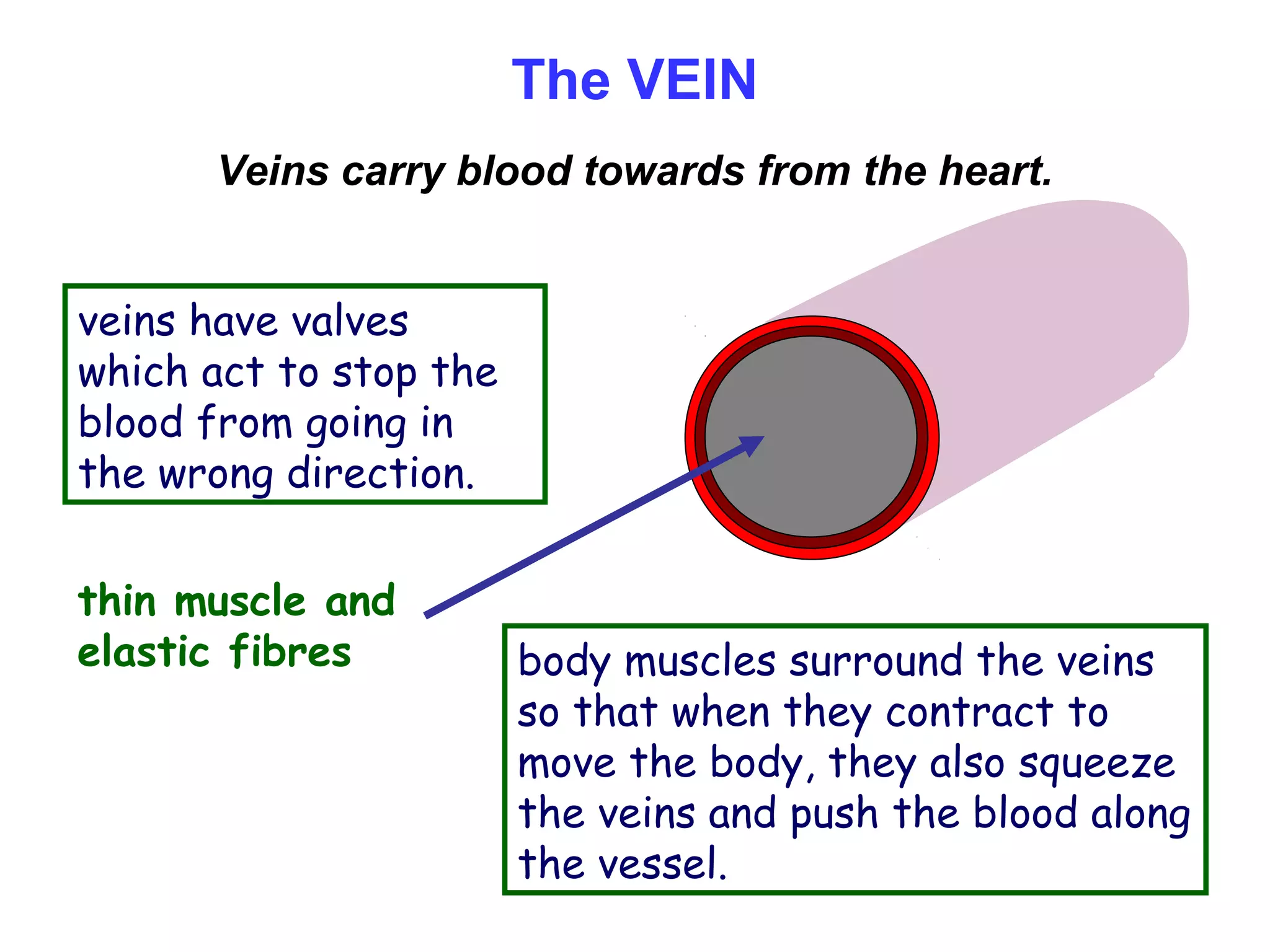
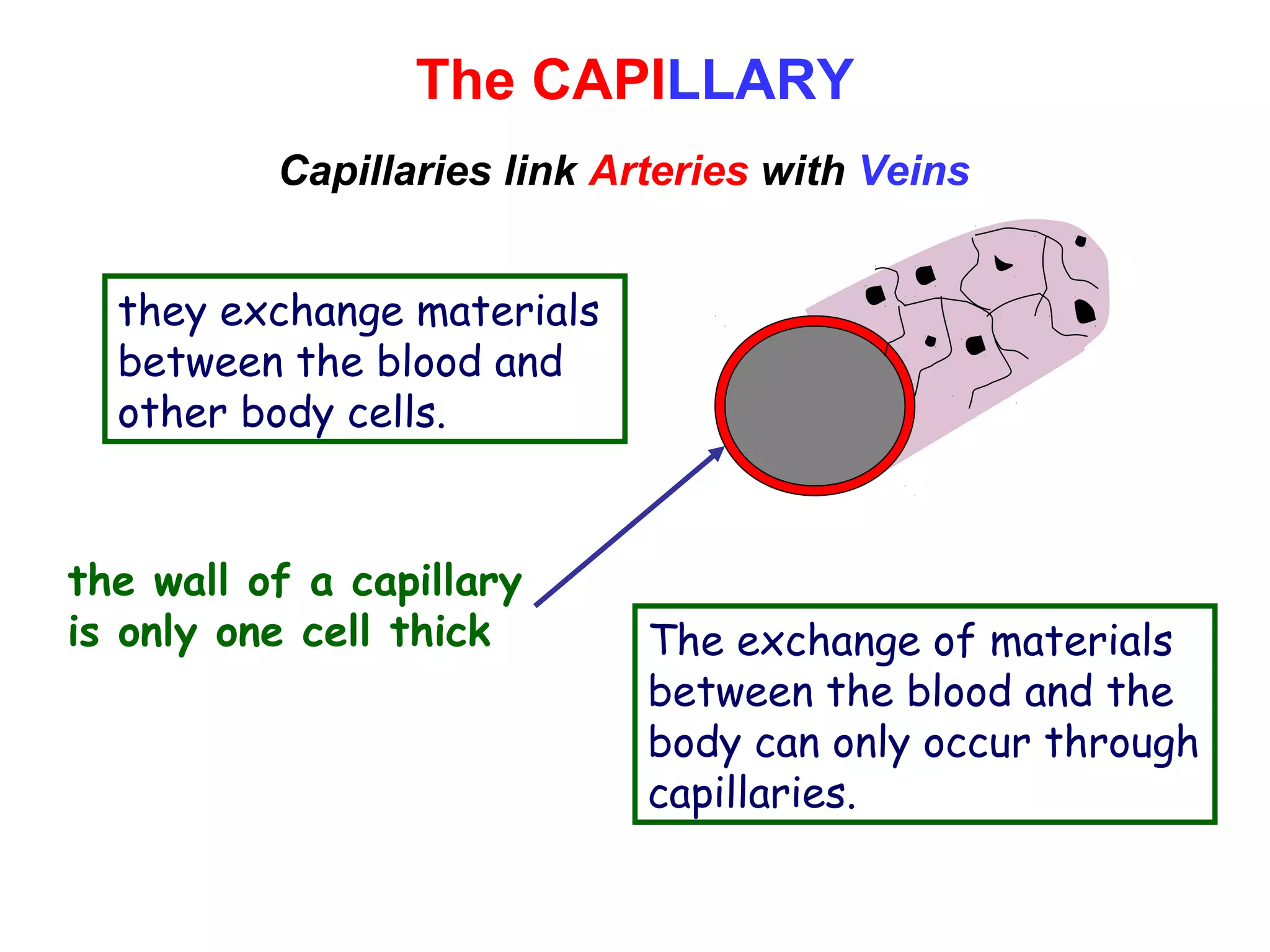
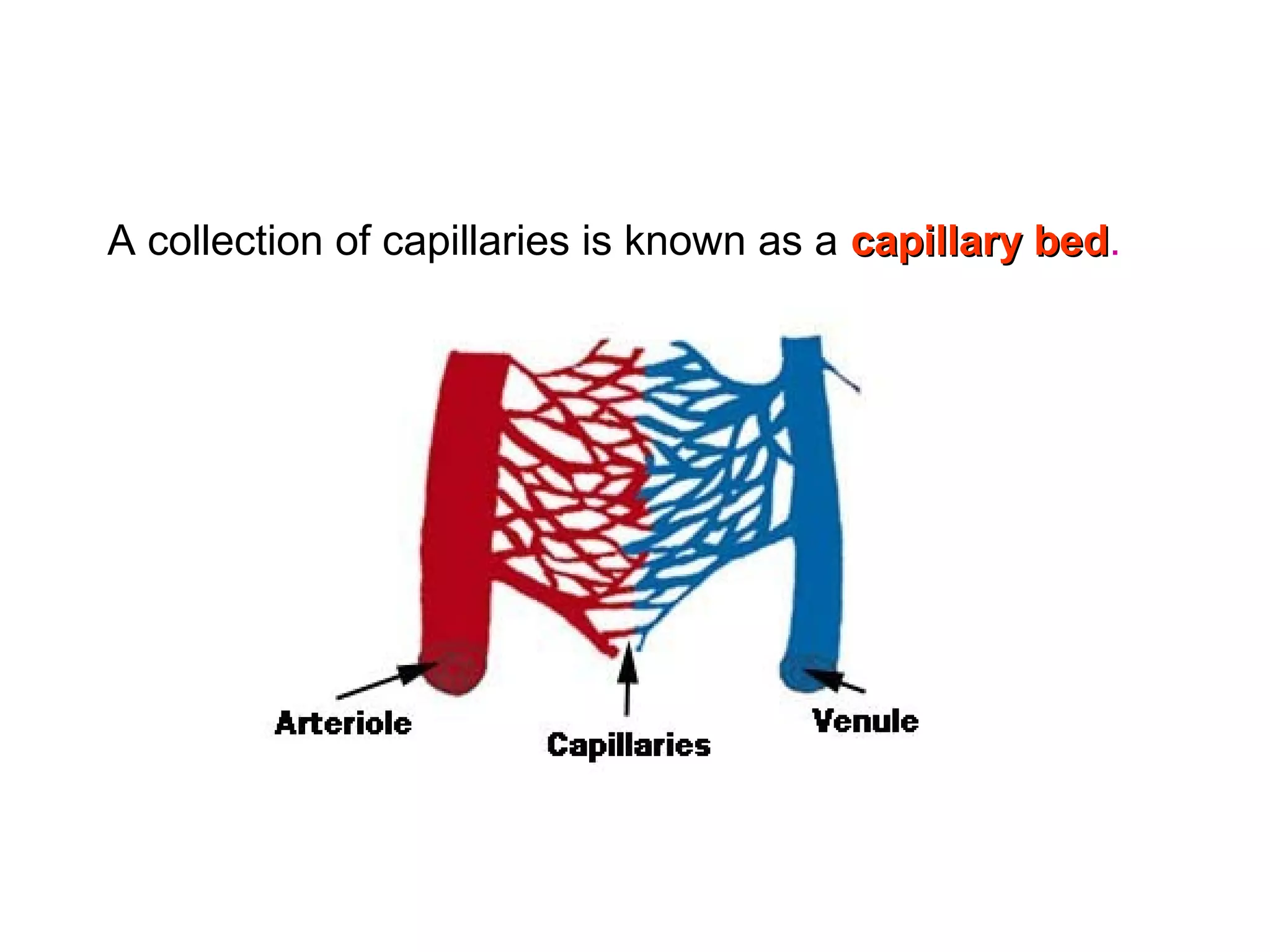
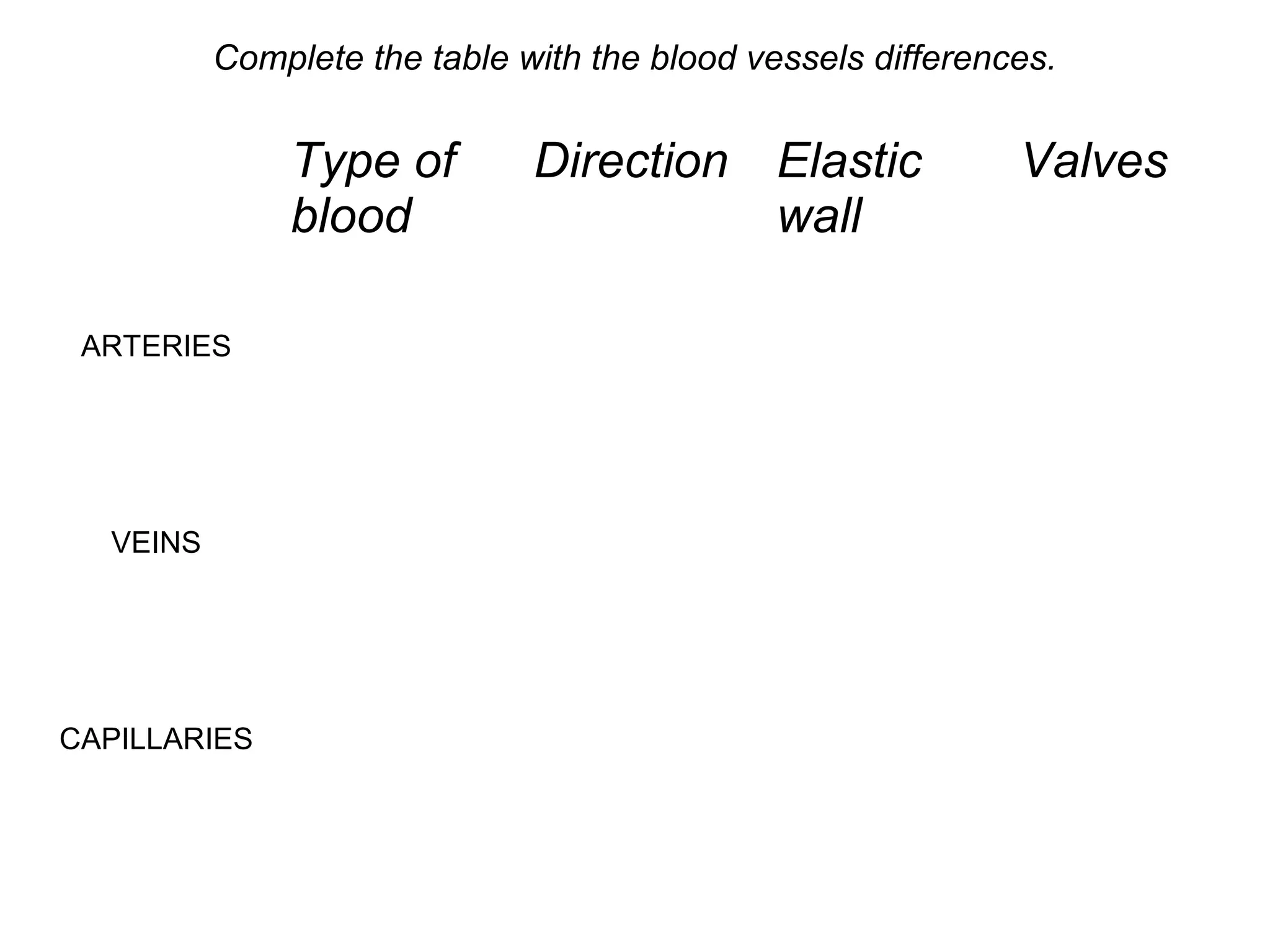
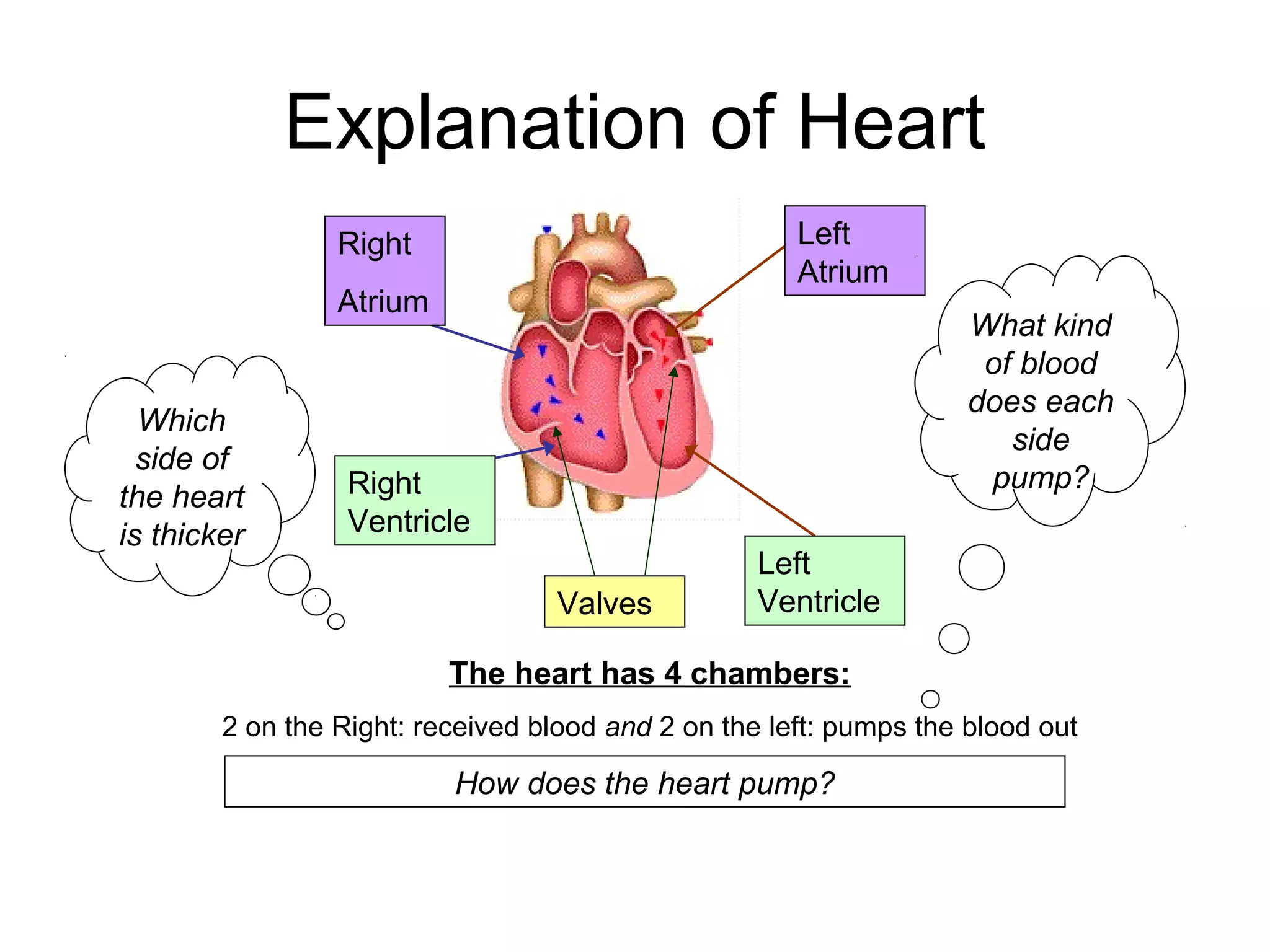
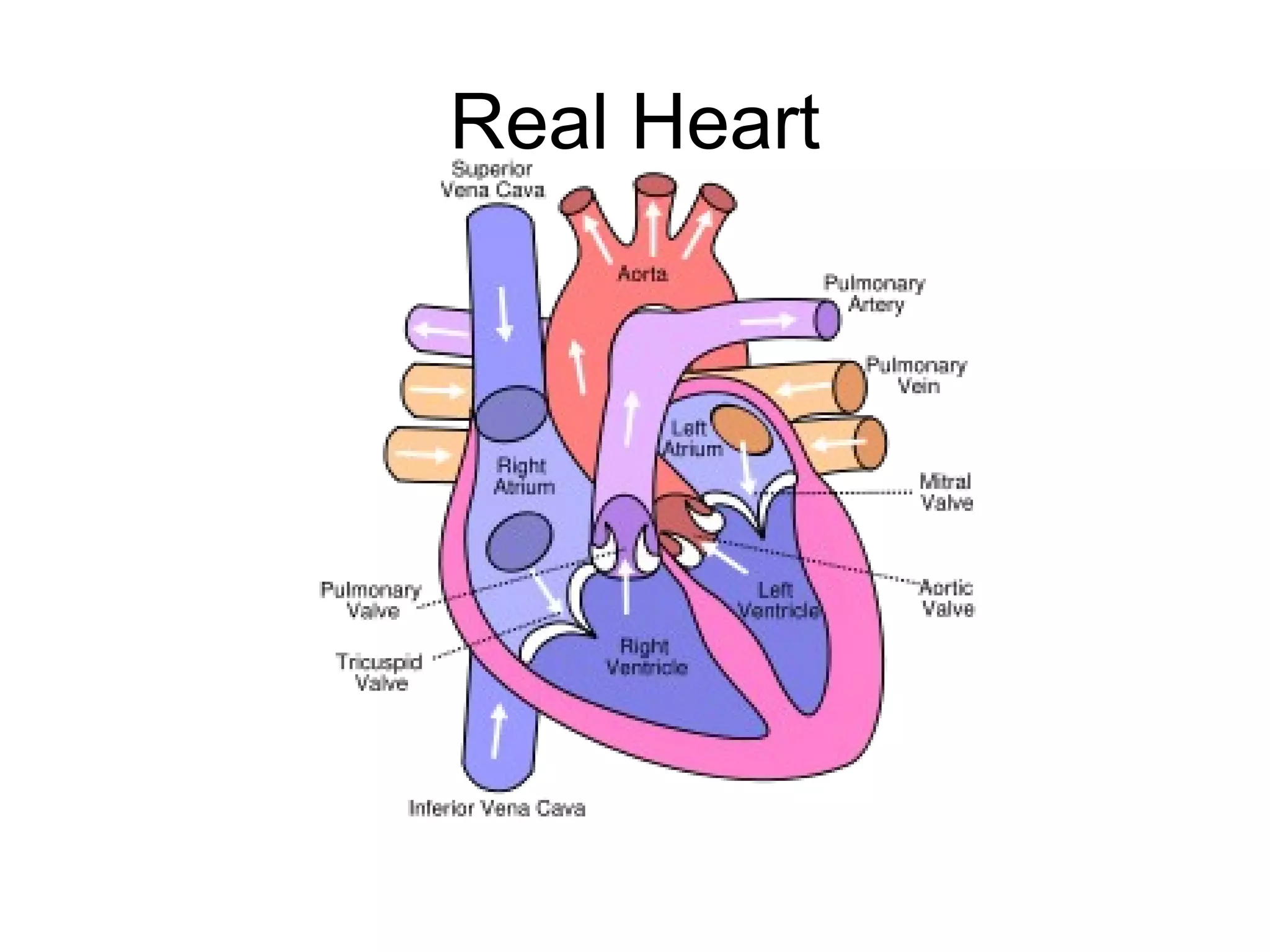
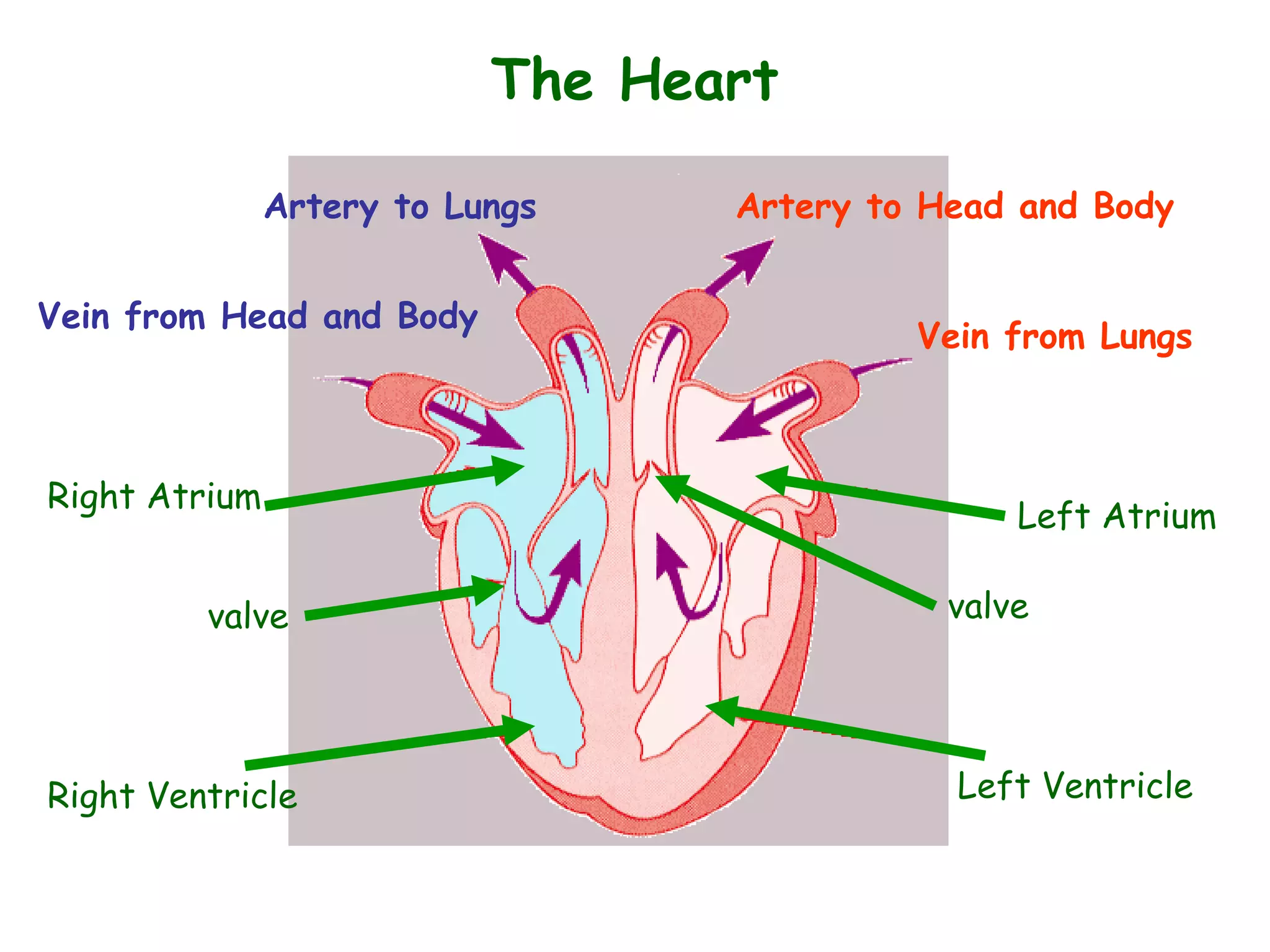
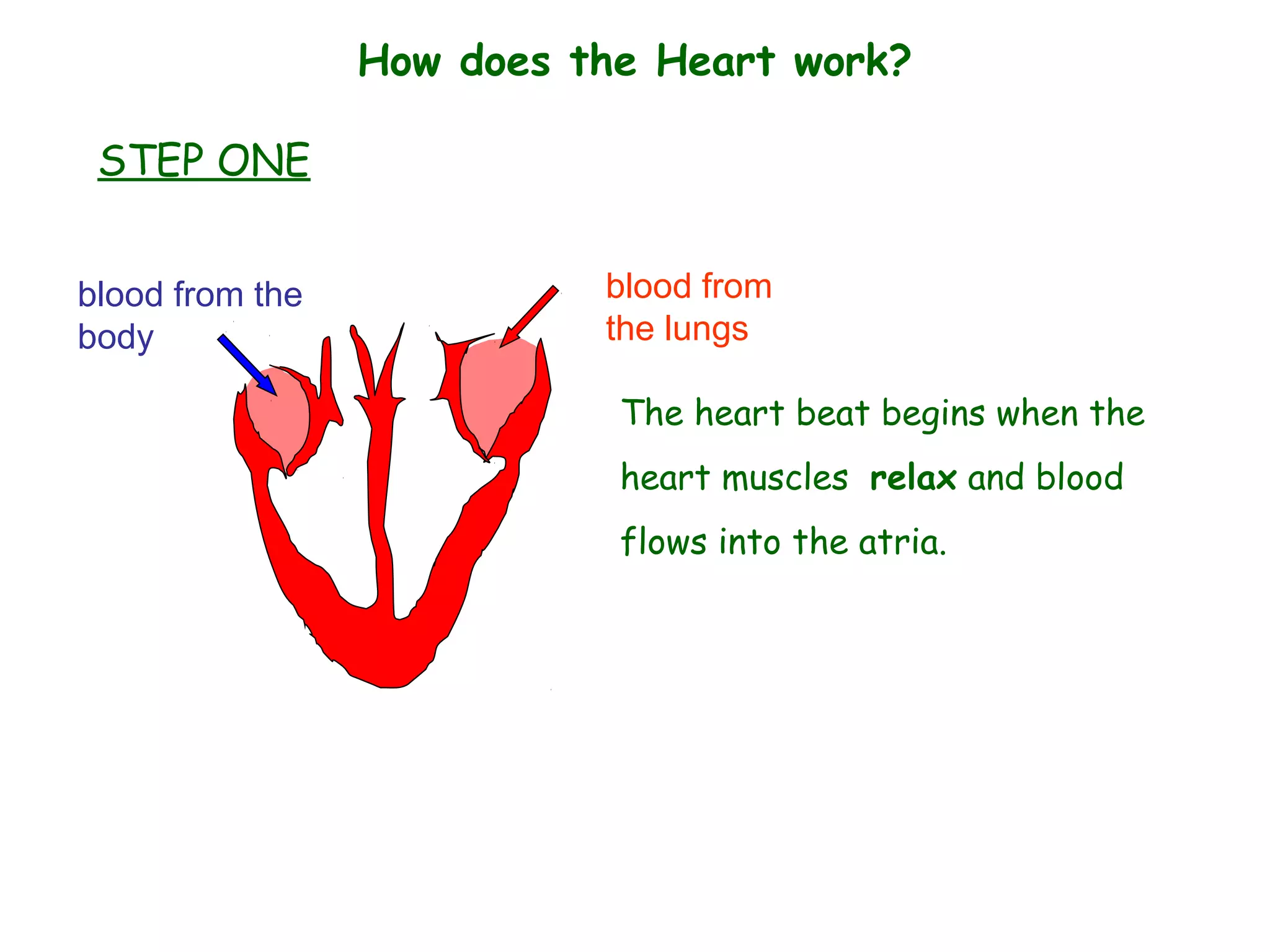
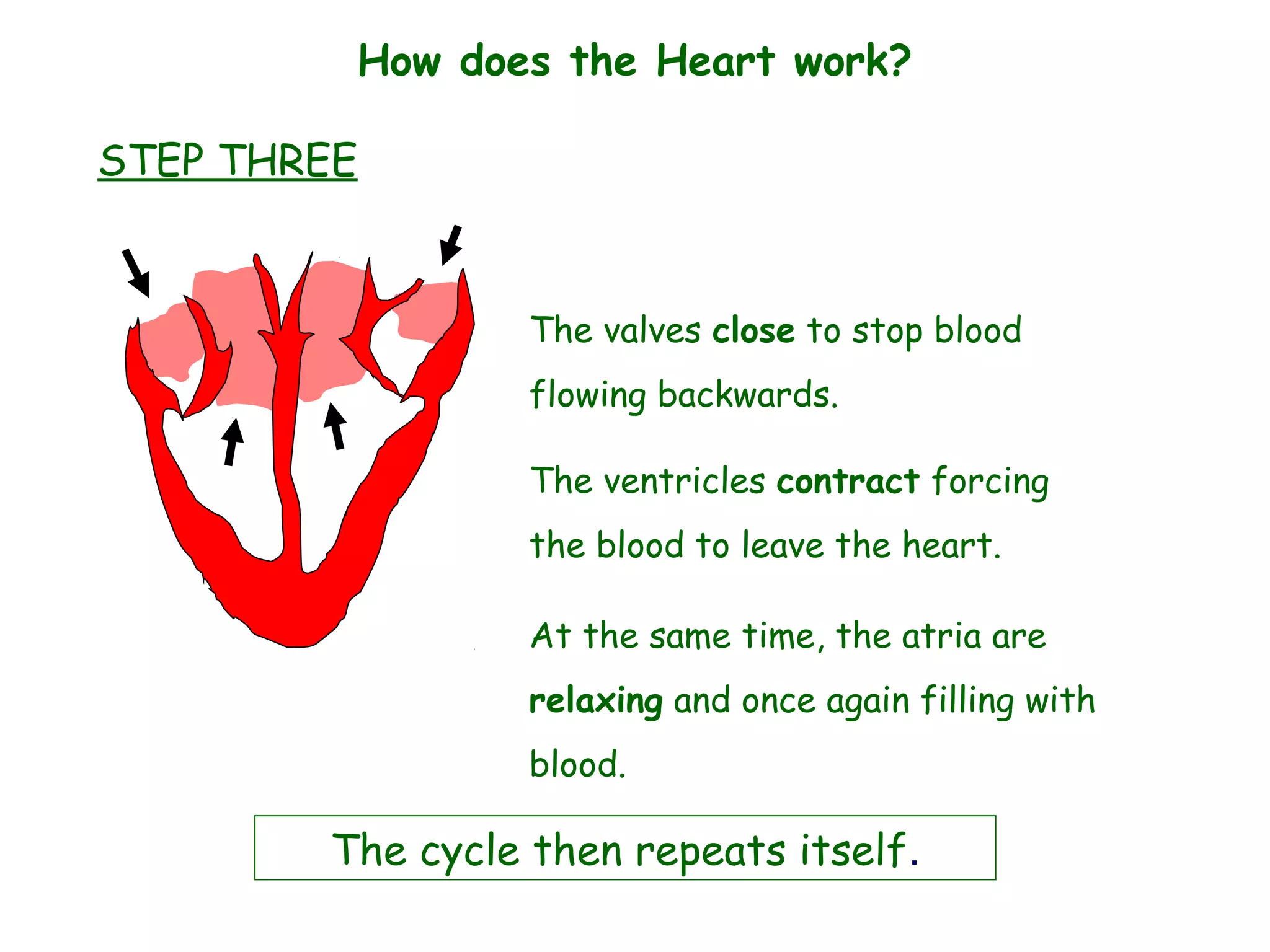
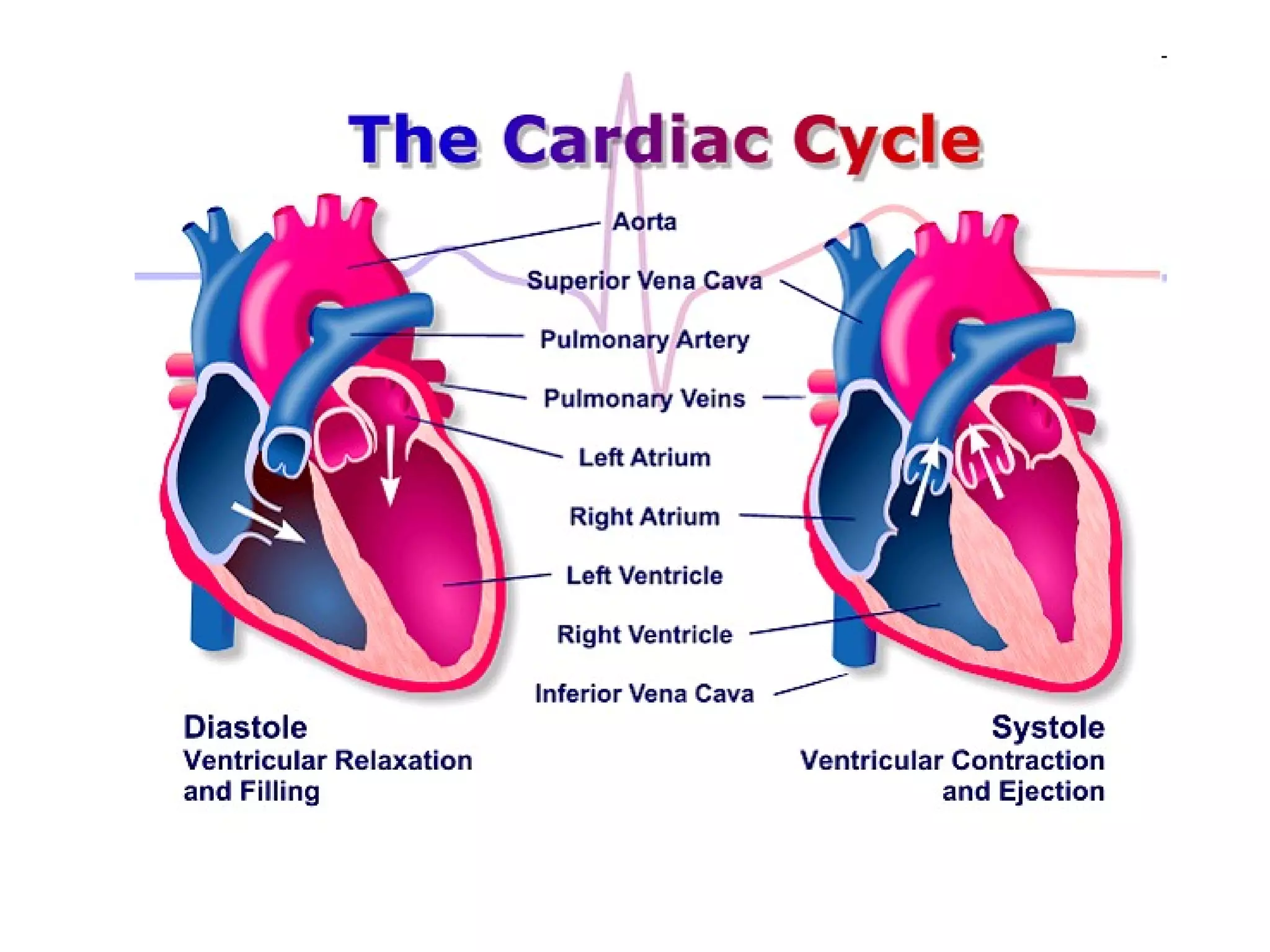
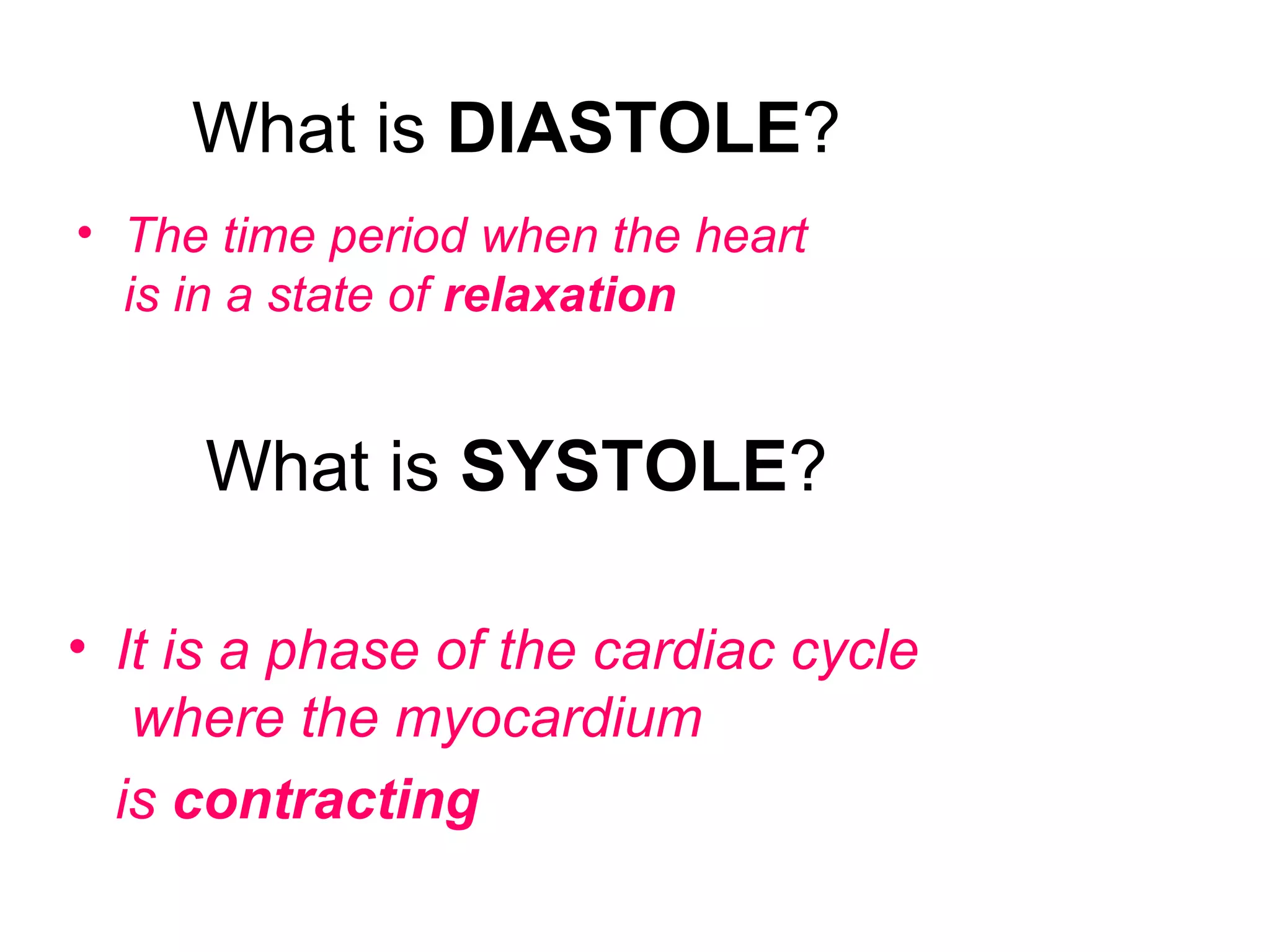
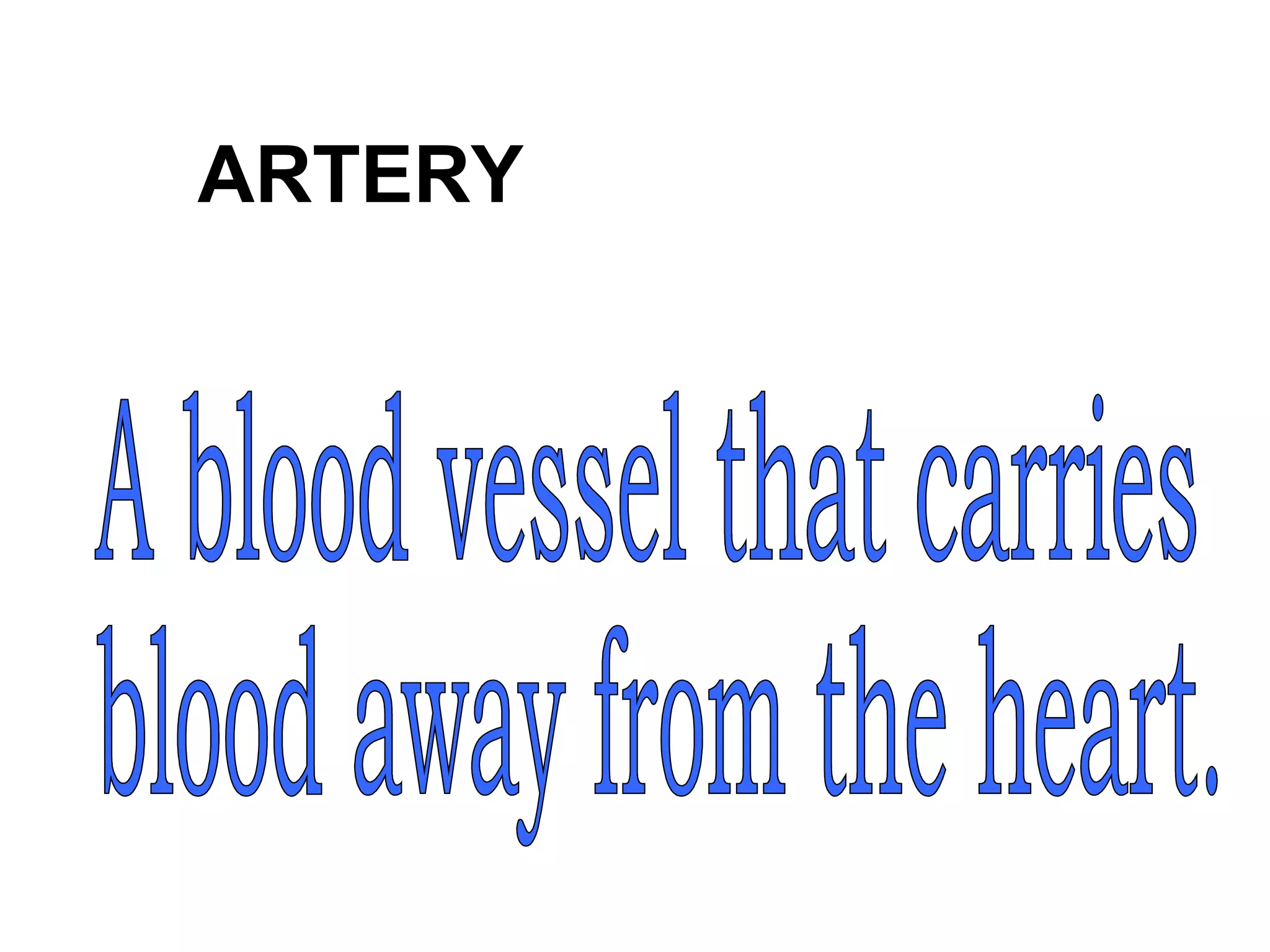
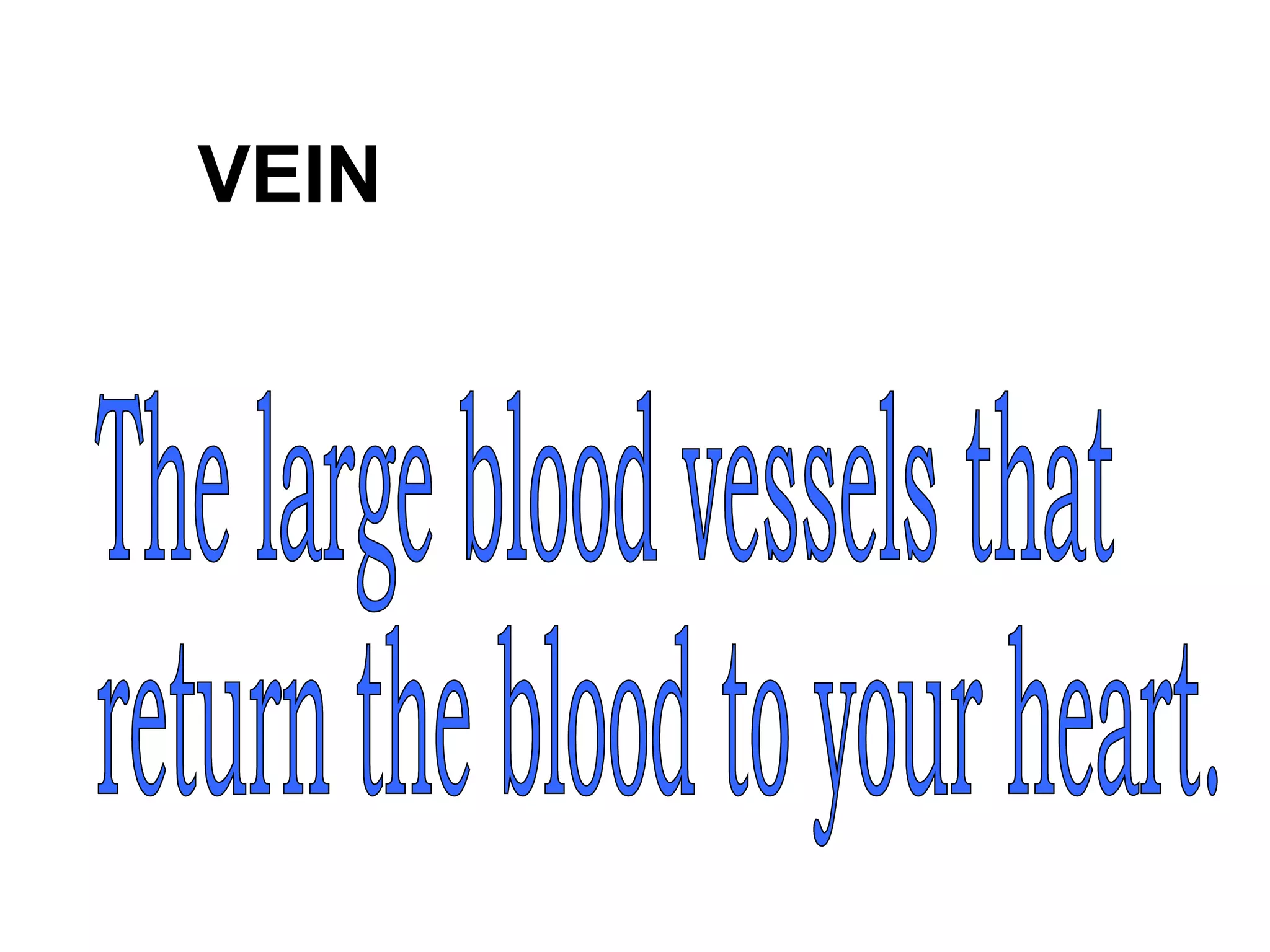
The document describes the human circulatory system, detailing its components, functions, and the processes involved in blood circulation. It explains the roles of red and white blood cells, platelets, and plasma, along with the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Additionally, it outlines how the heart operates to pump blood and the significance of diastole and systole in the cardiac cycle.