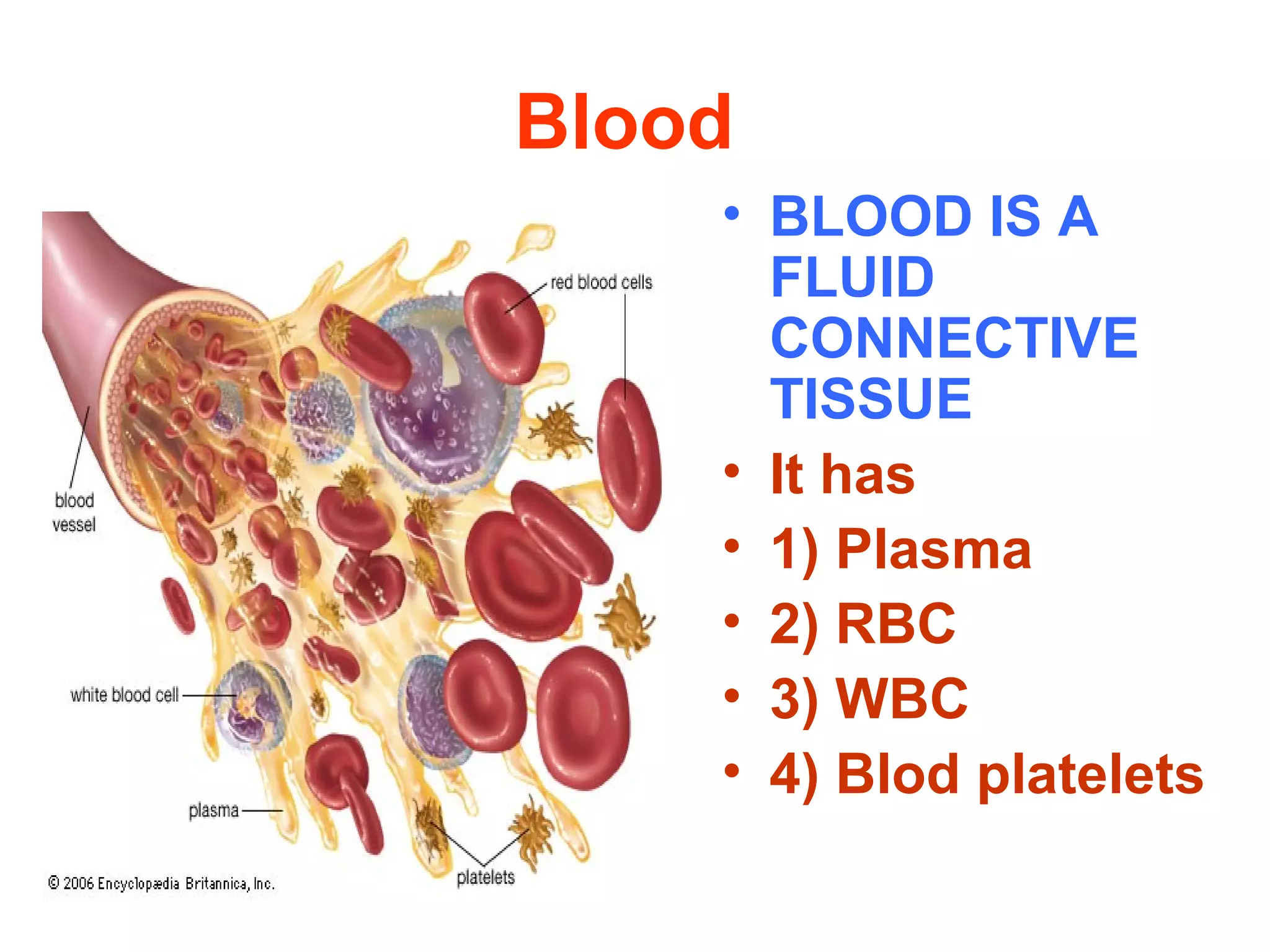
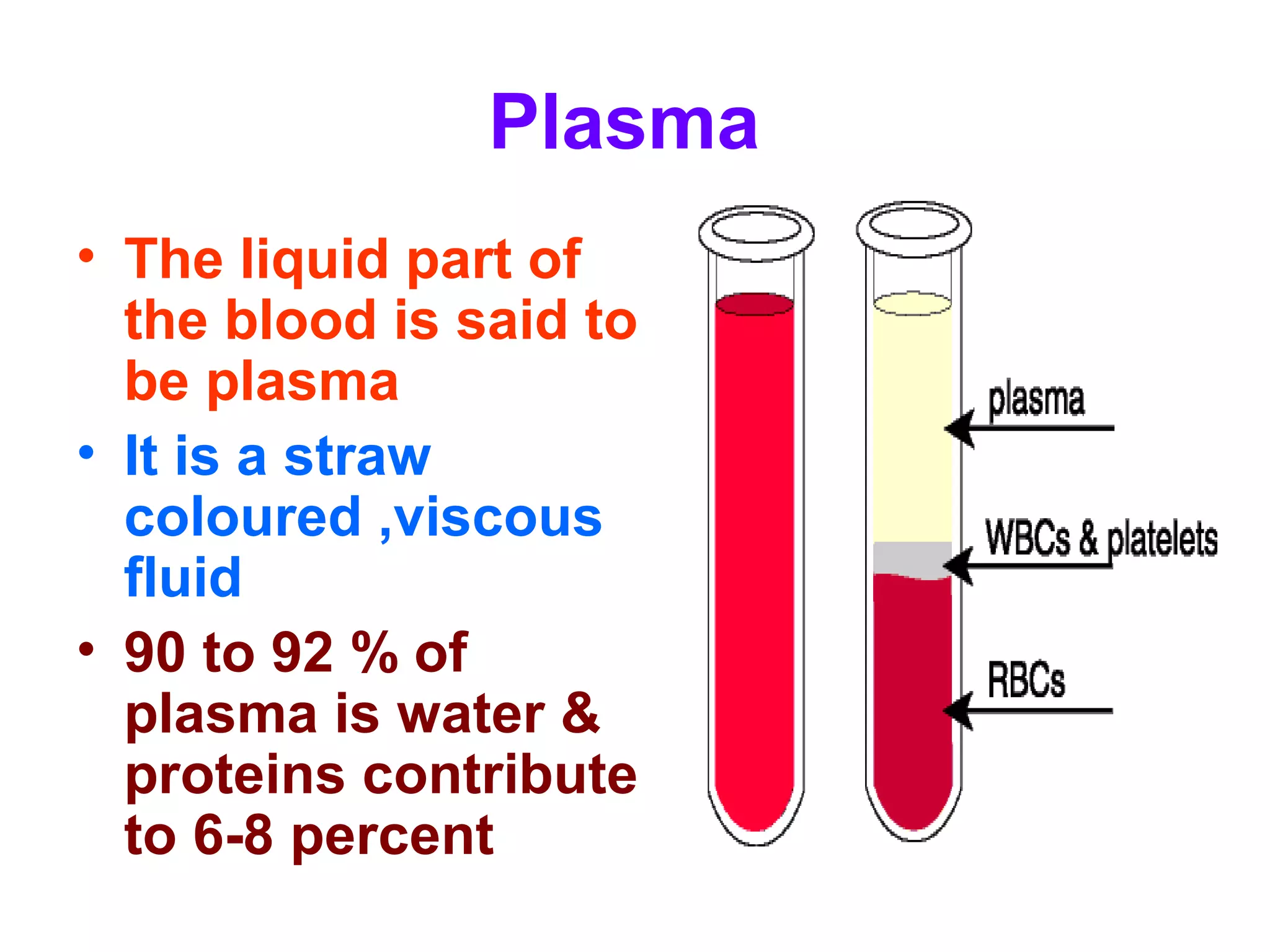
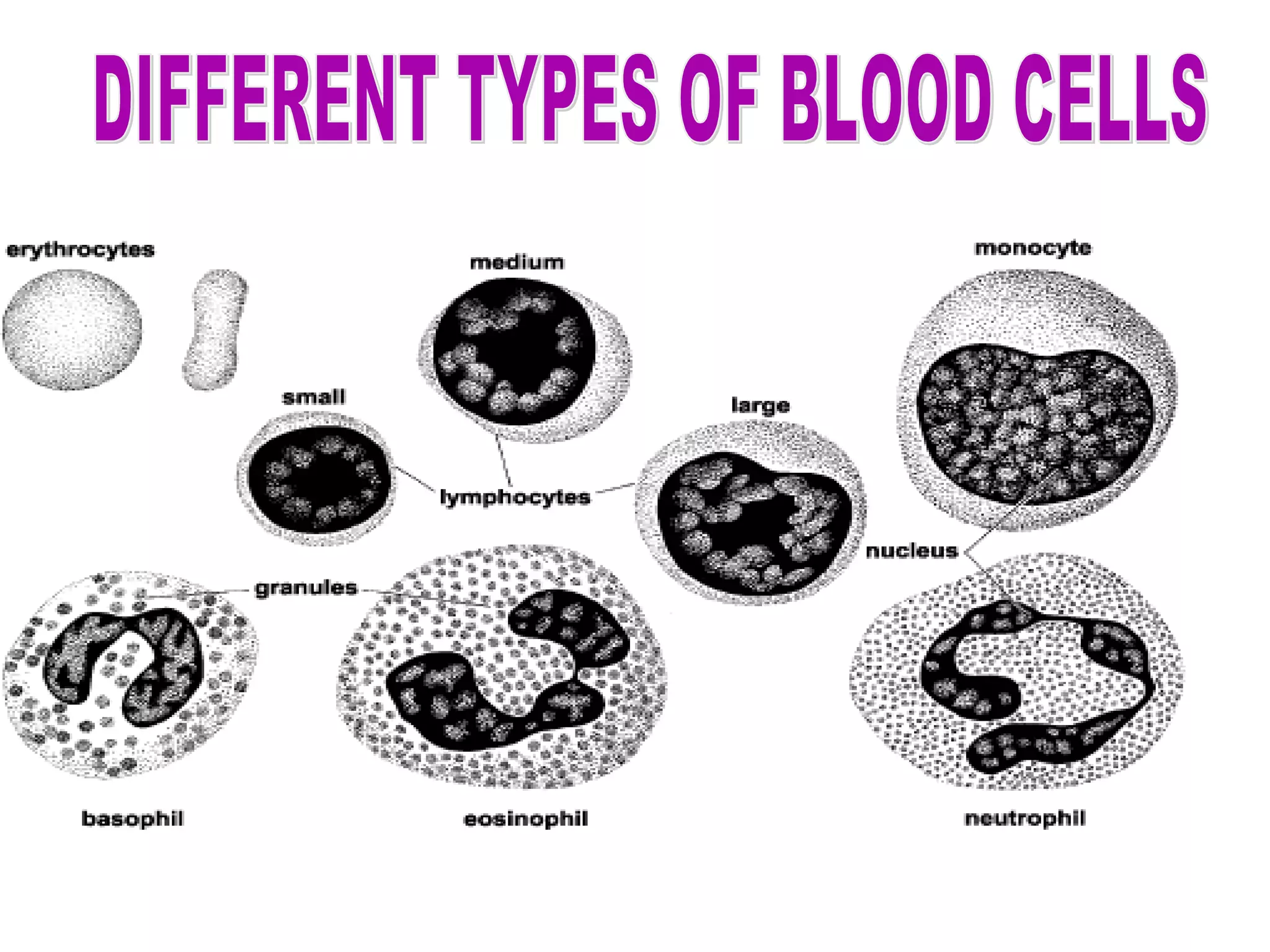
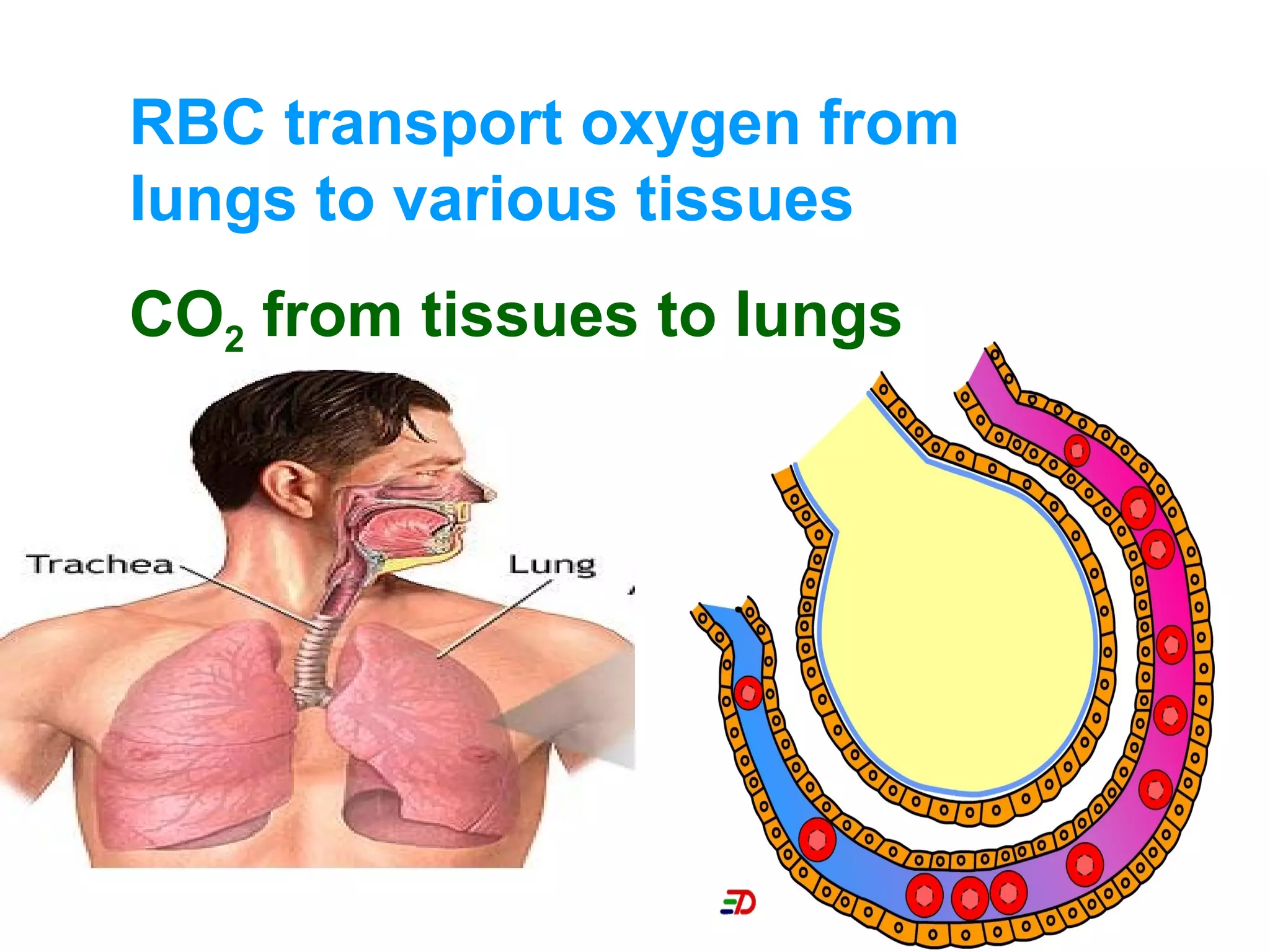
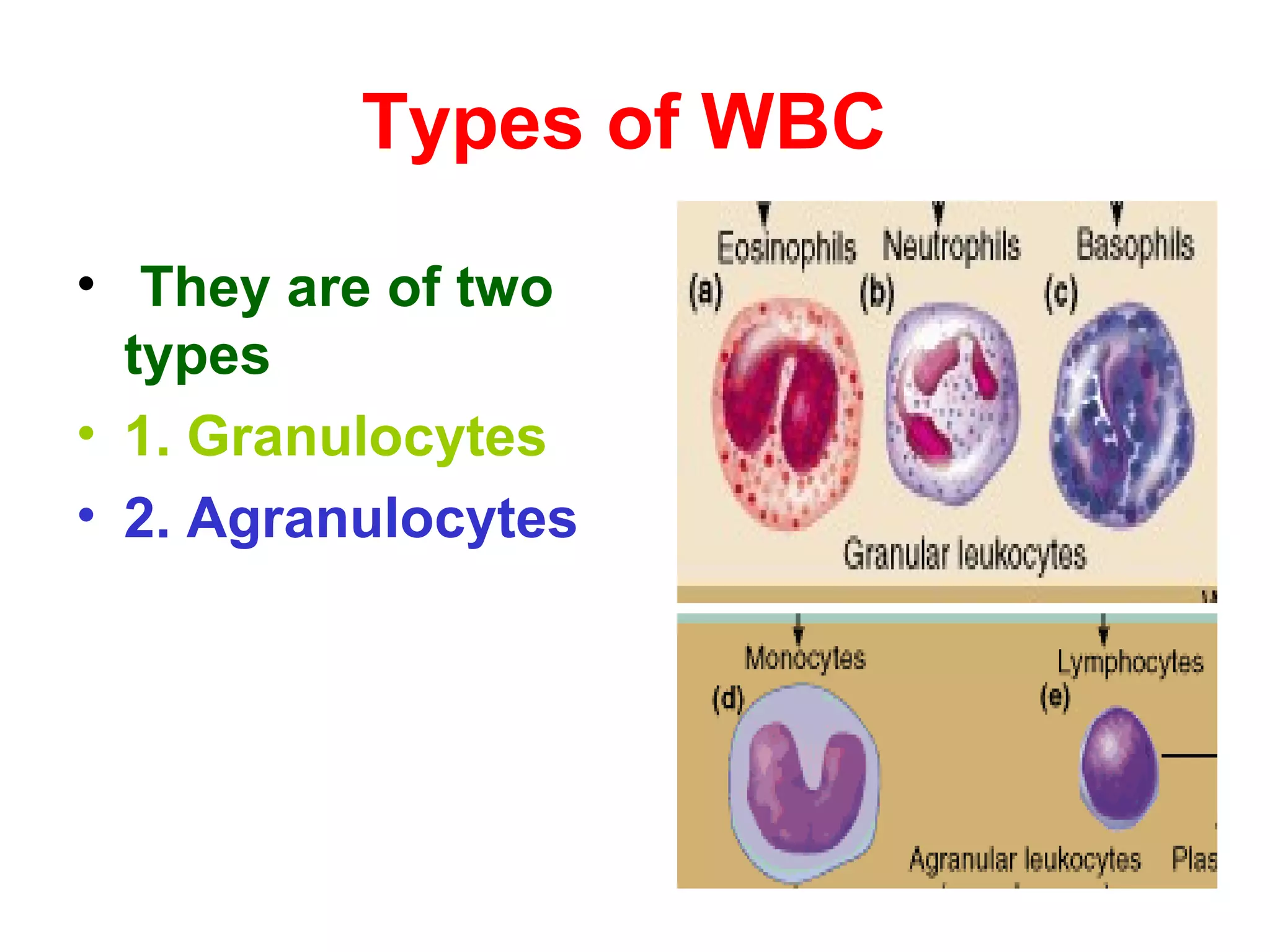
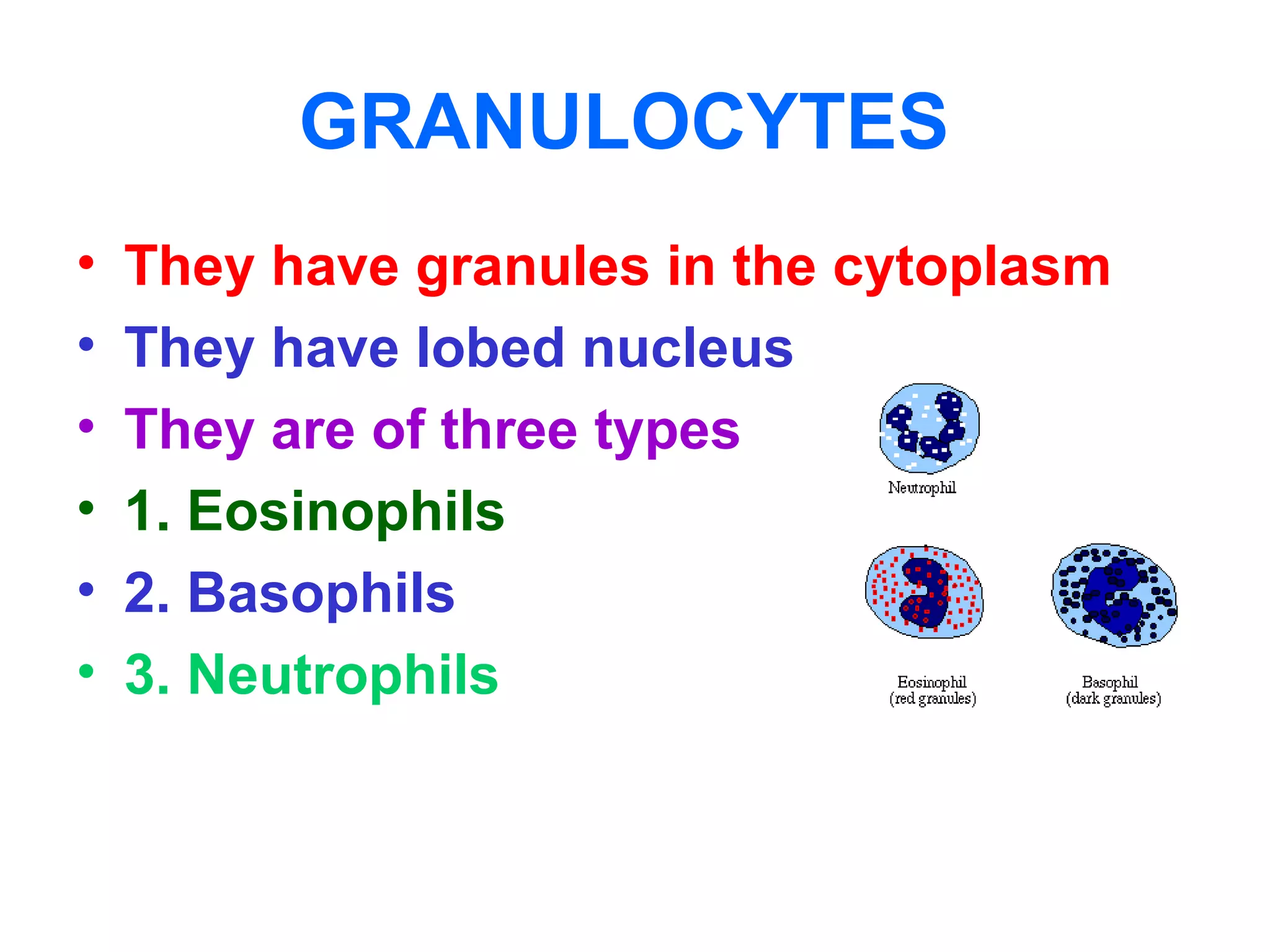
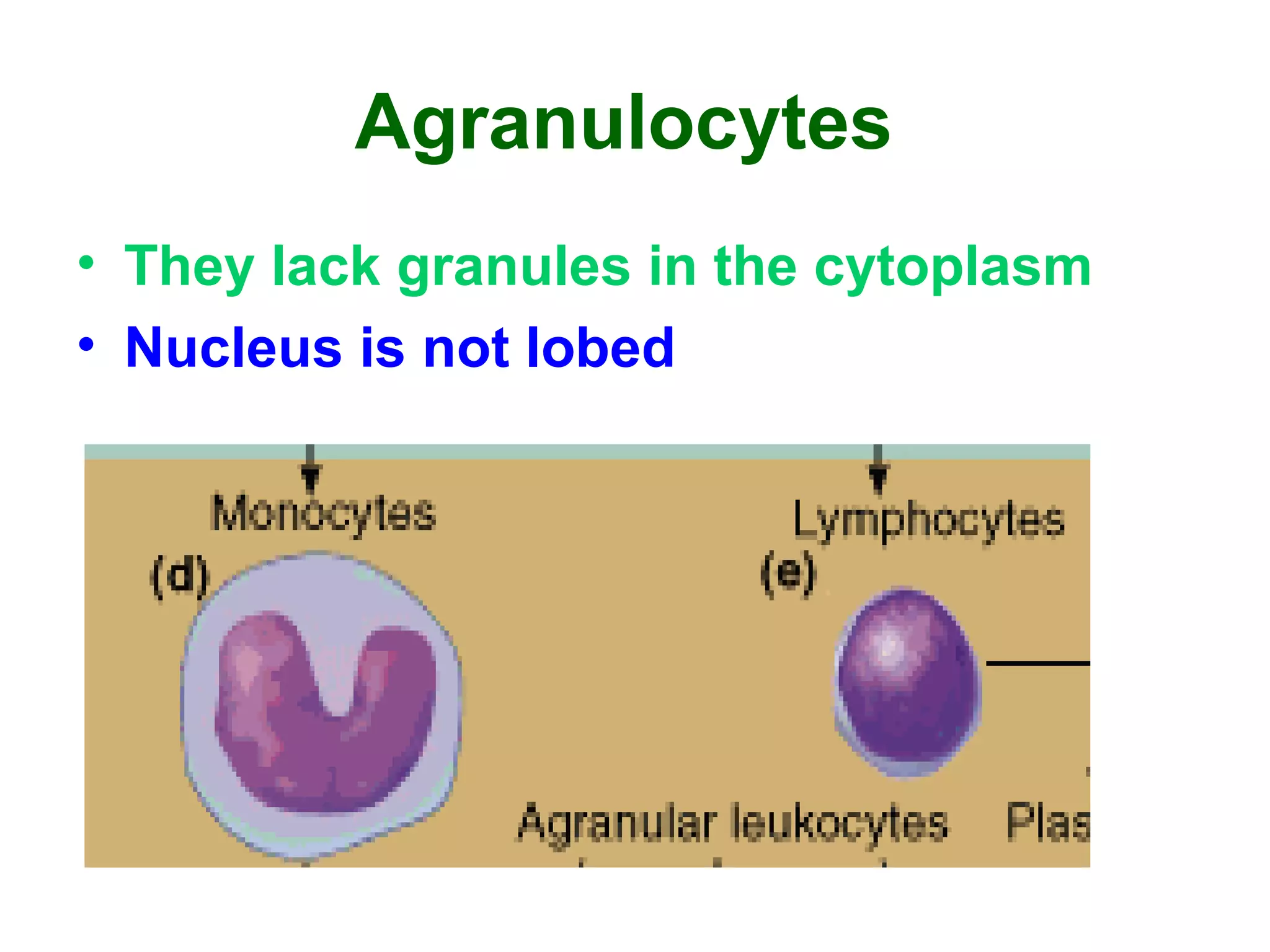
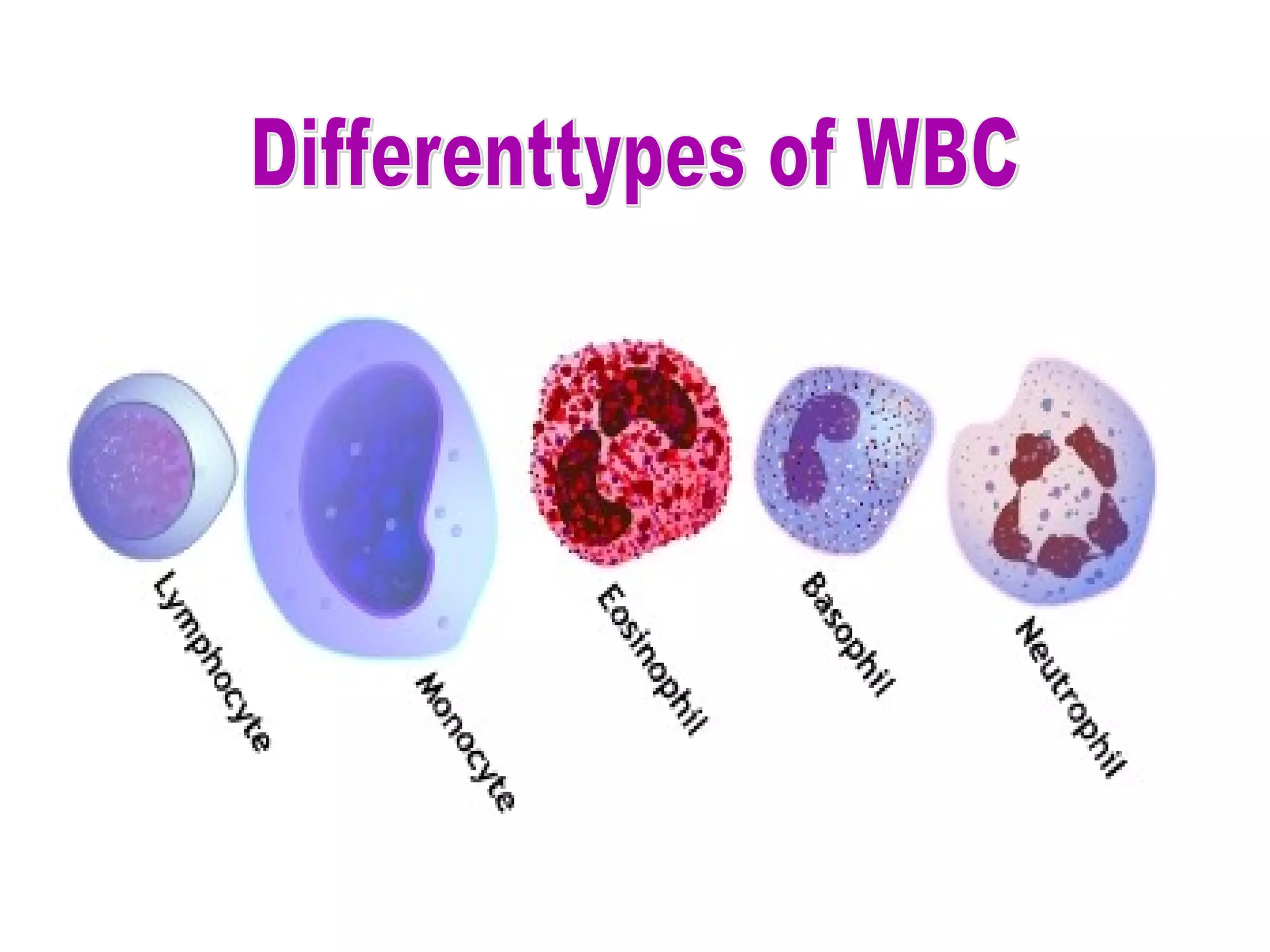
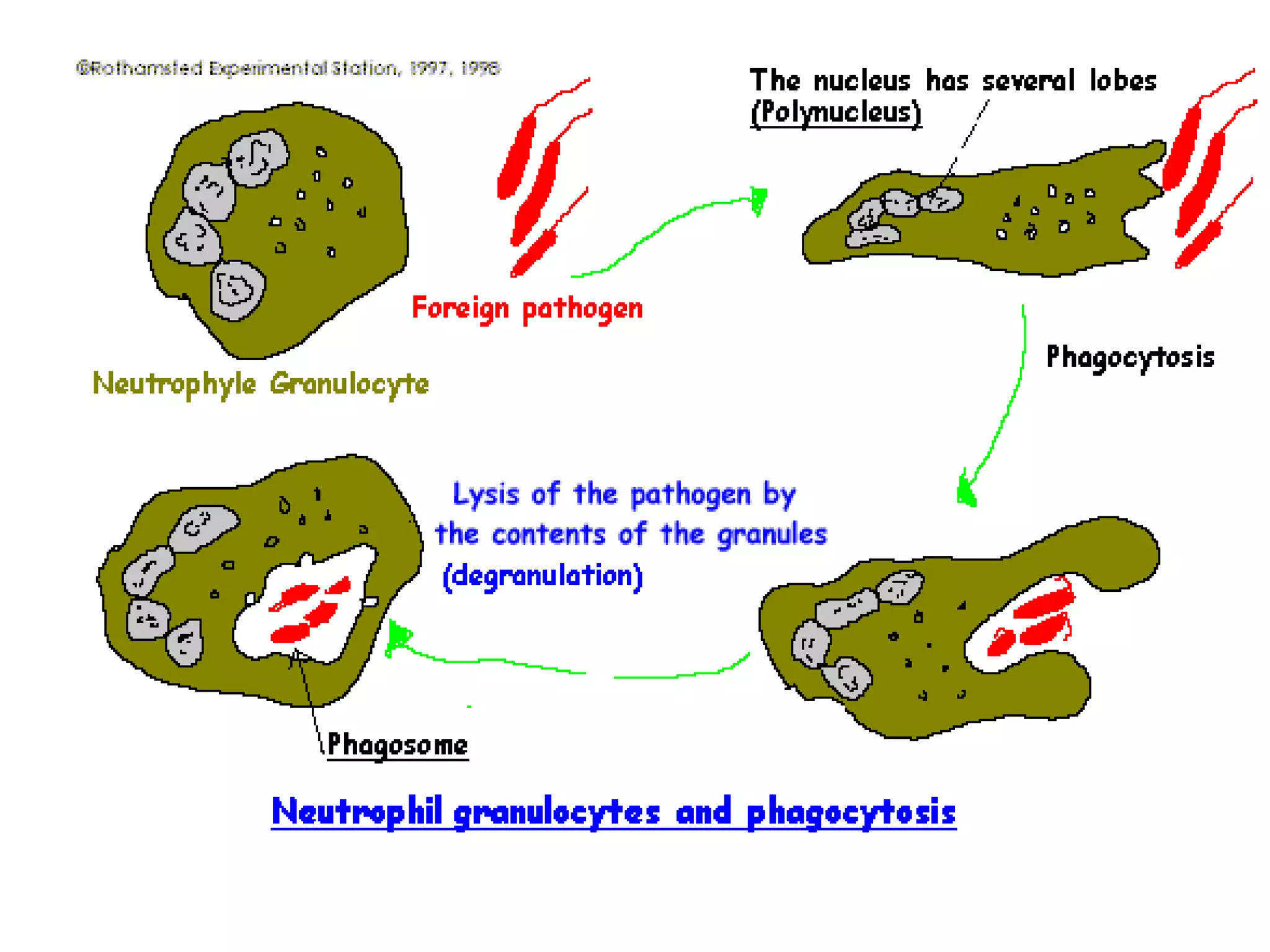
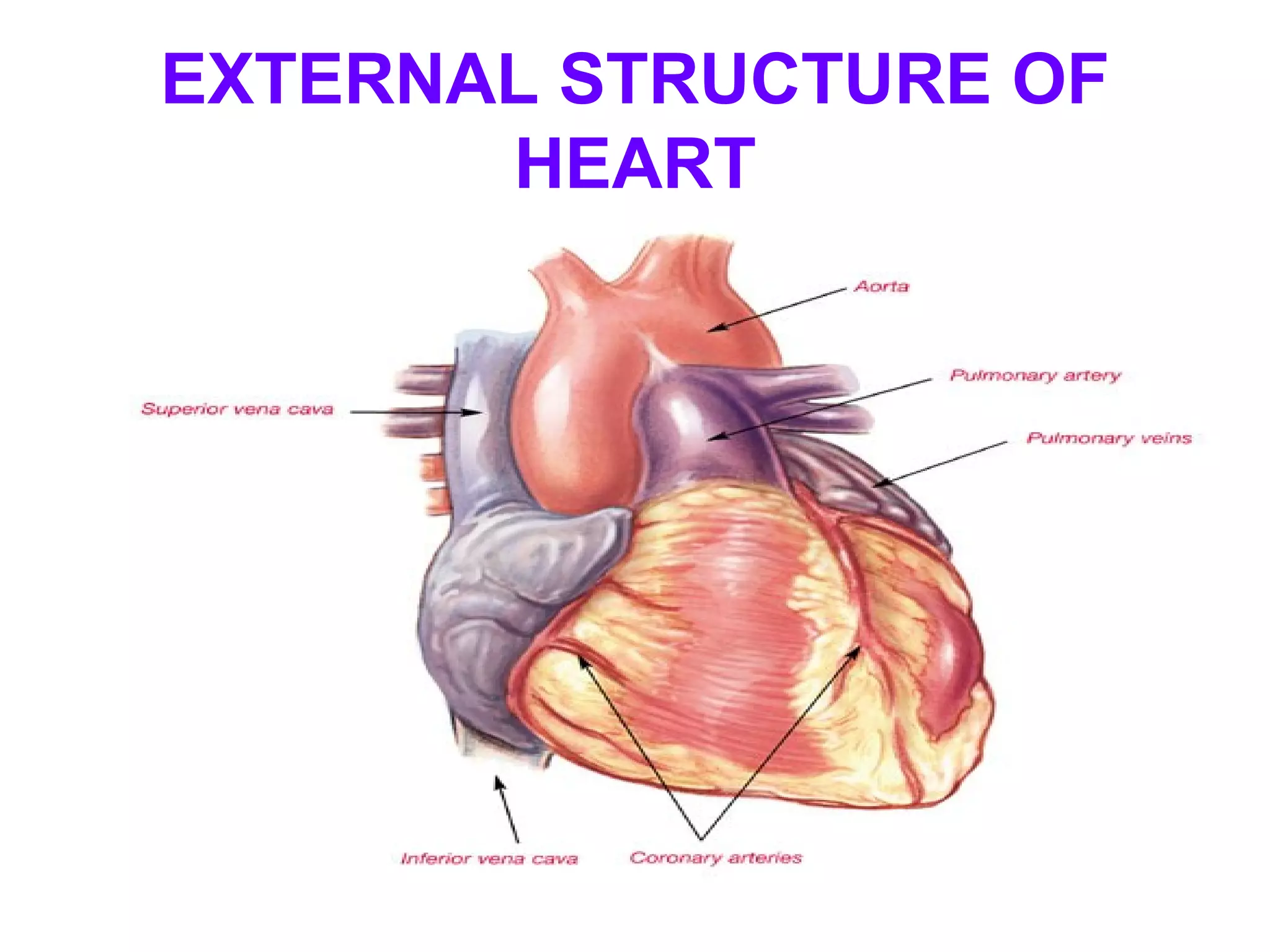
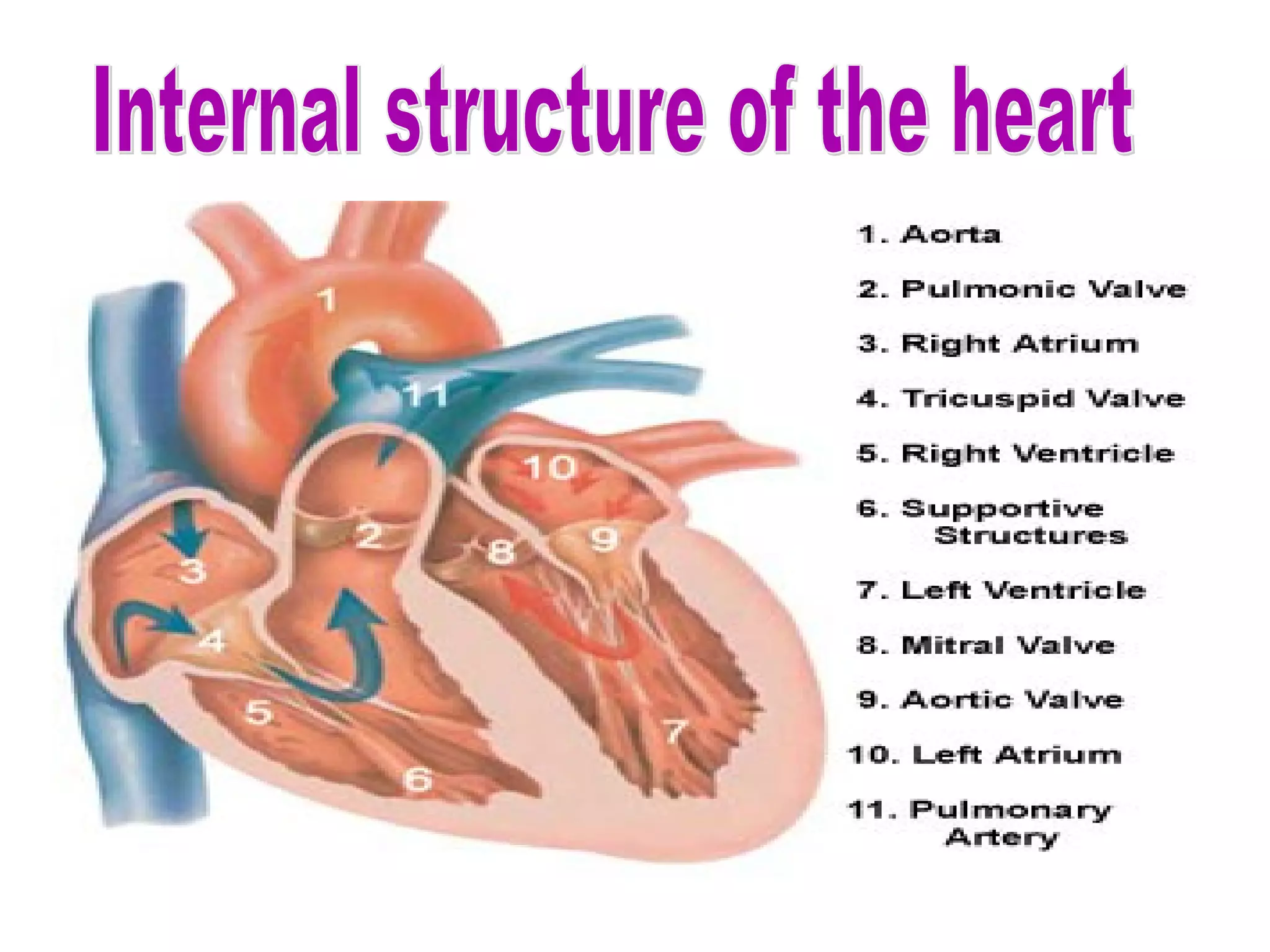
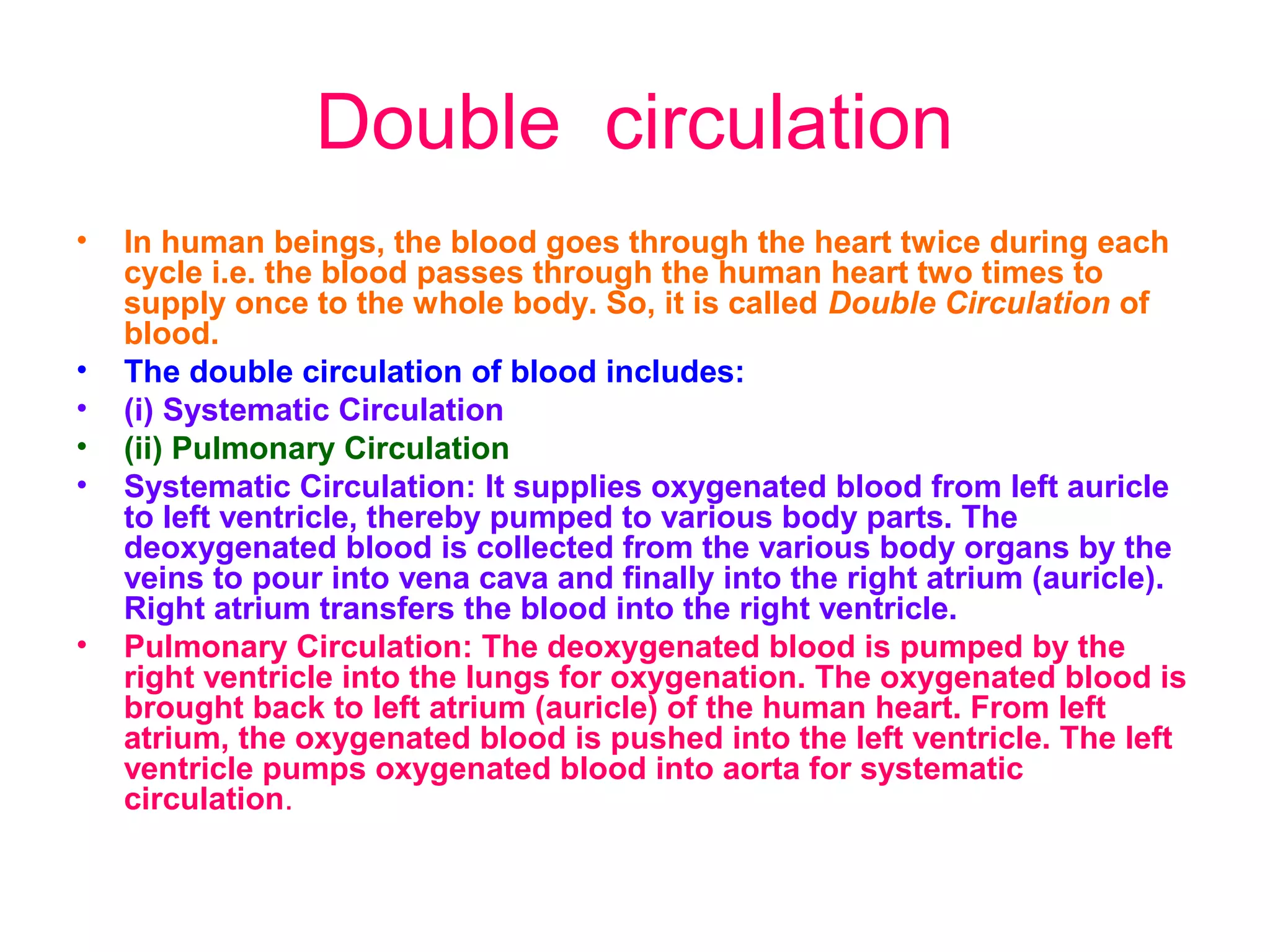
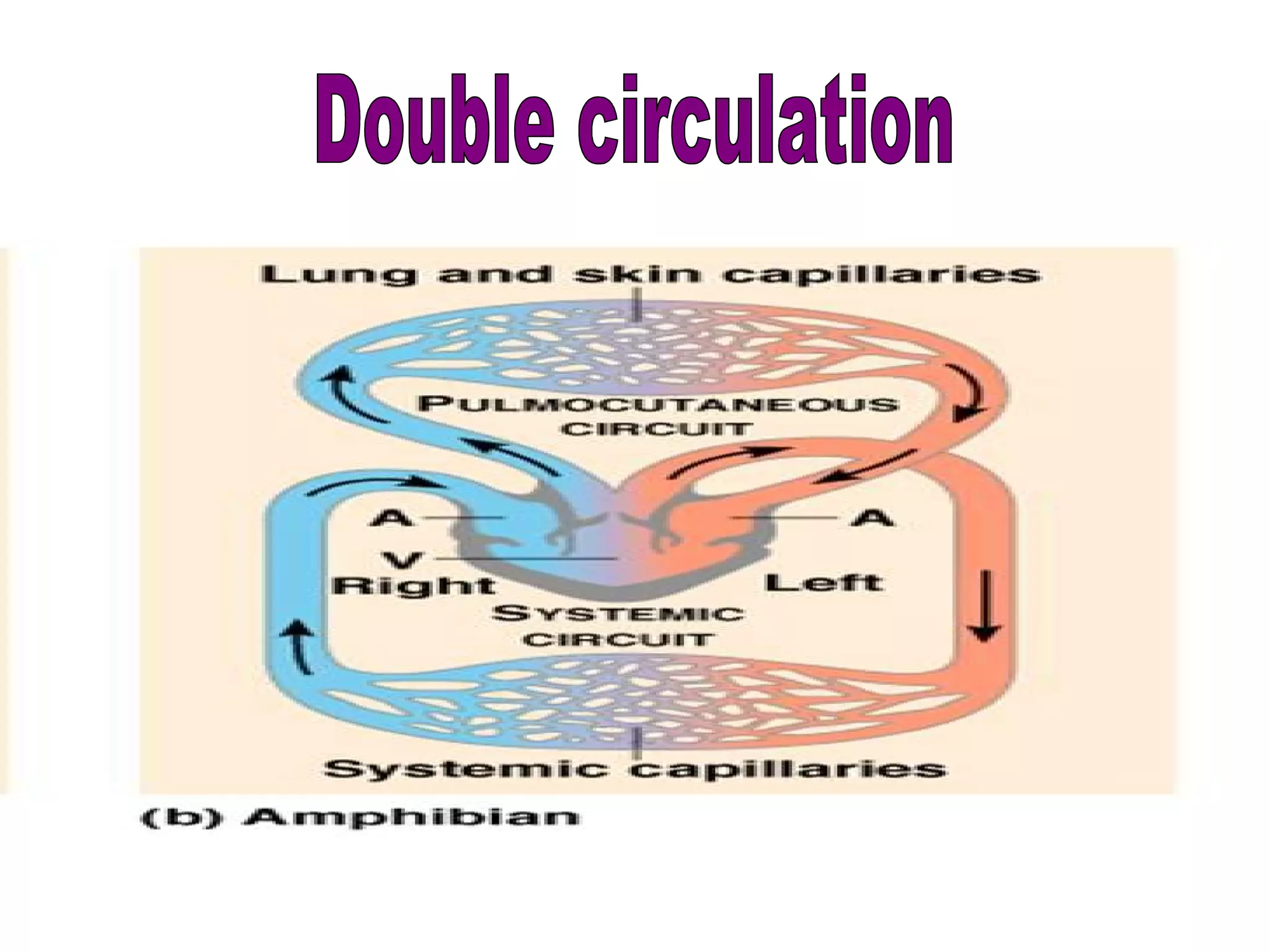
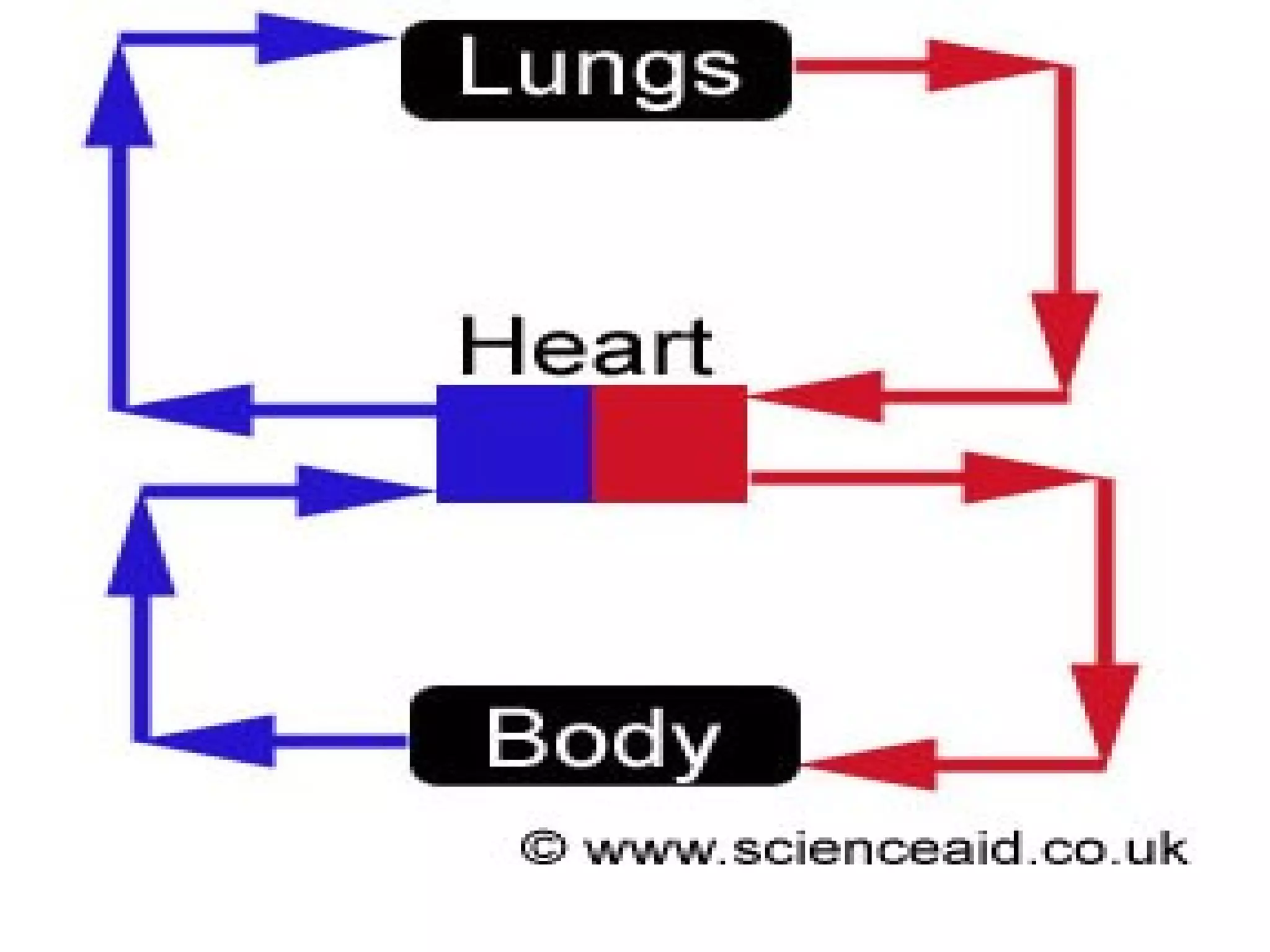
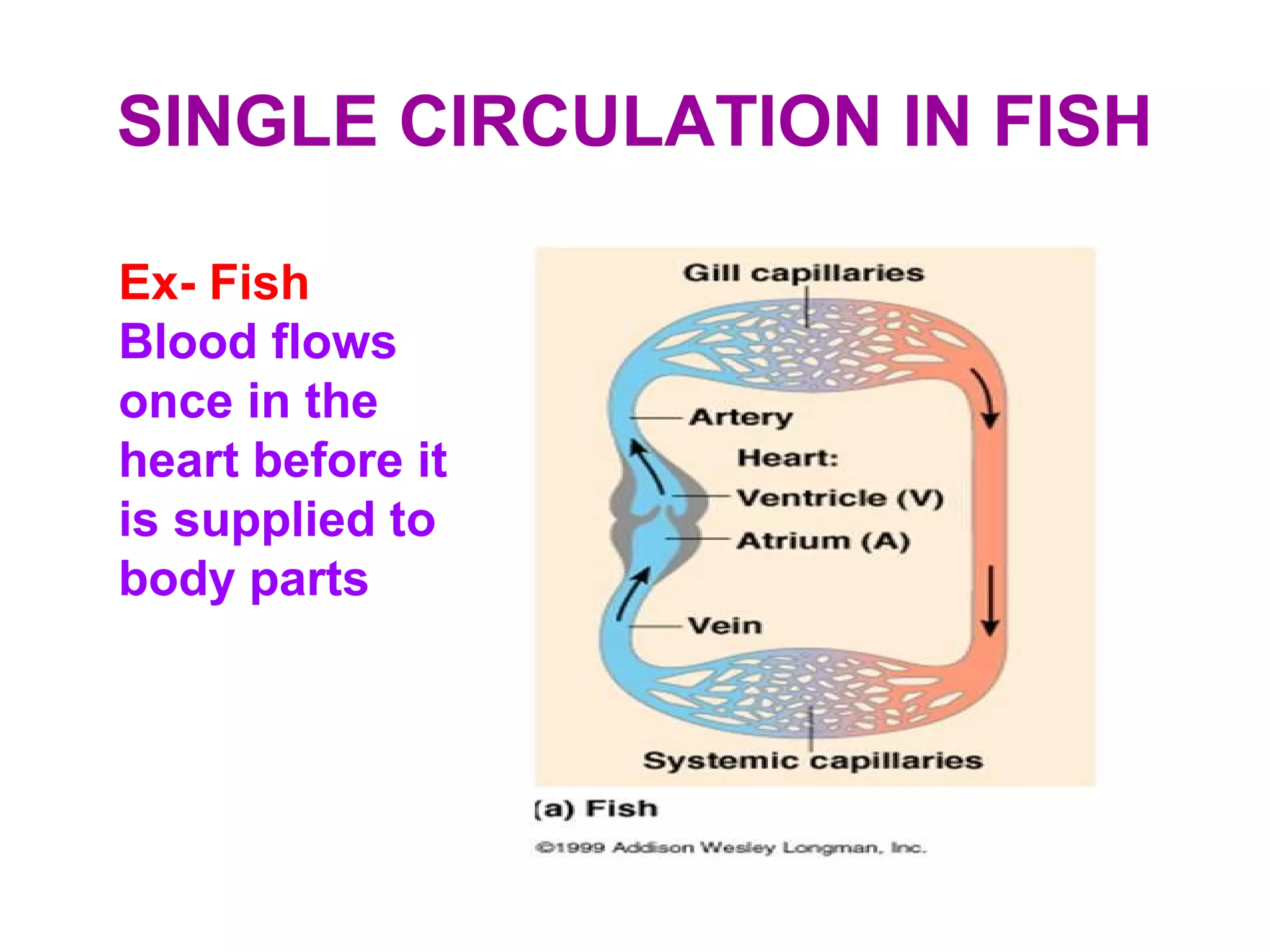
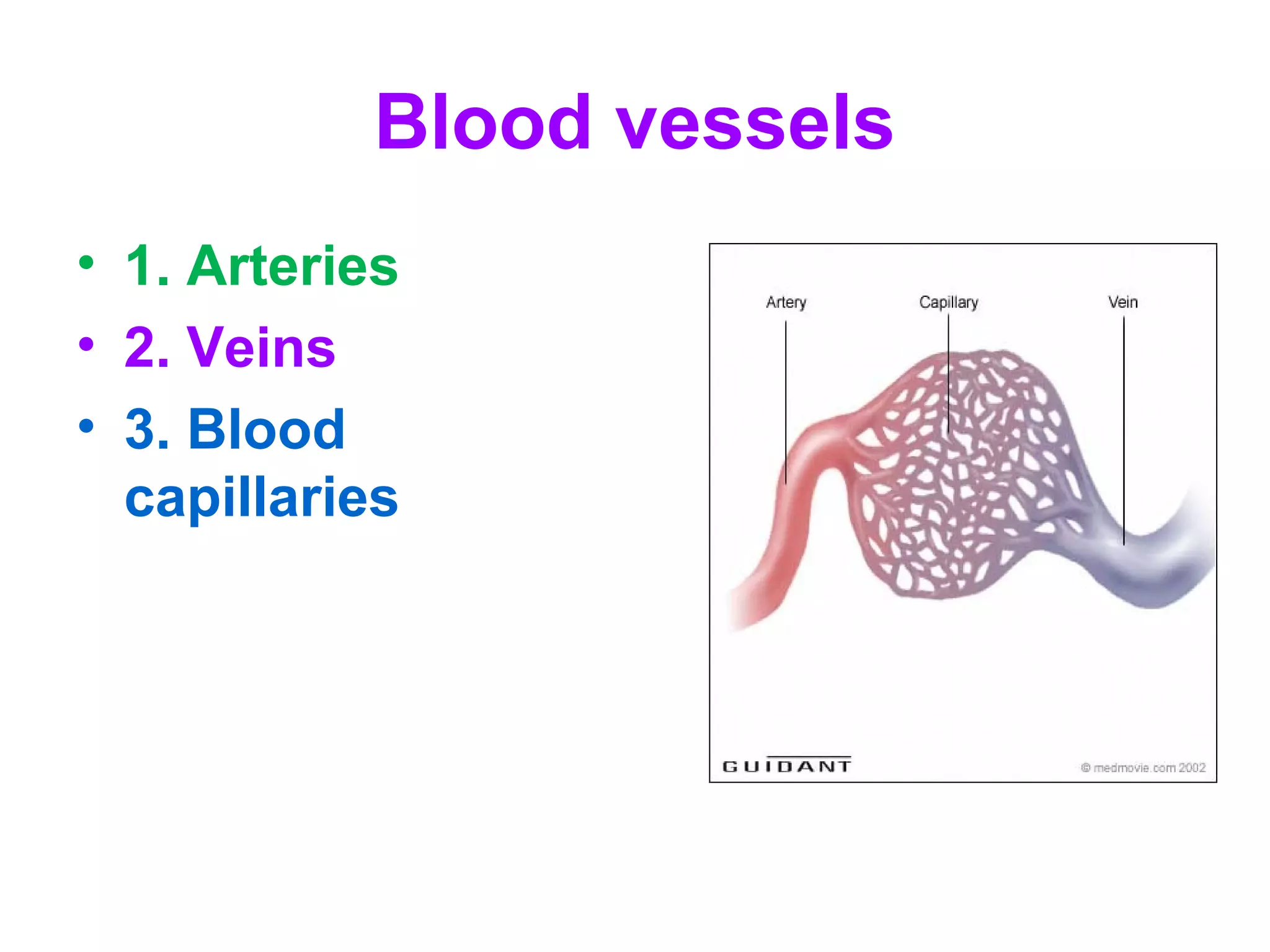
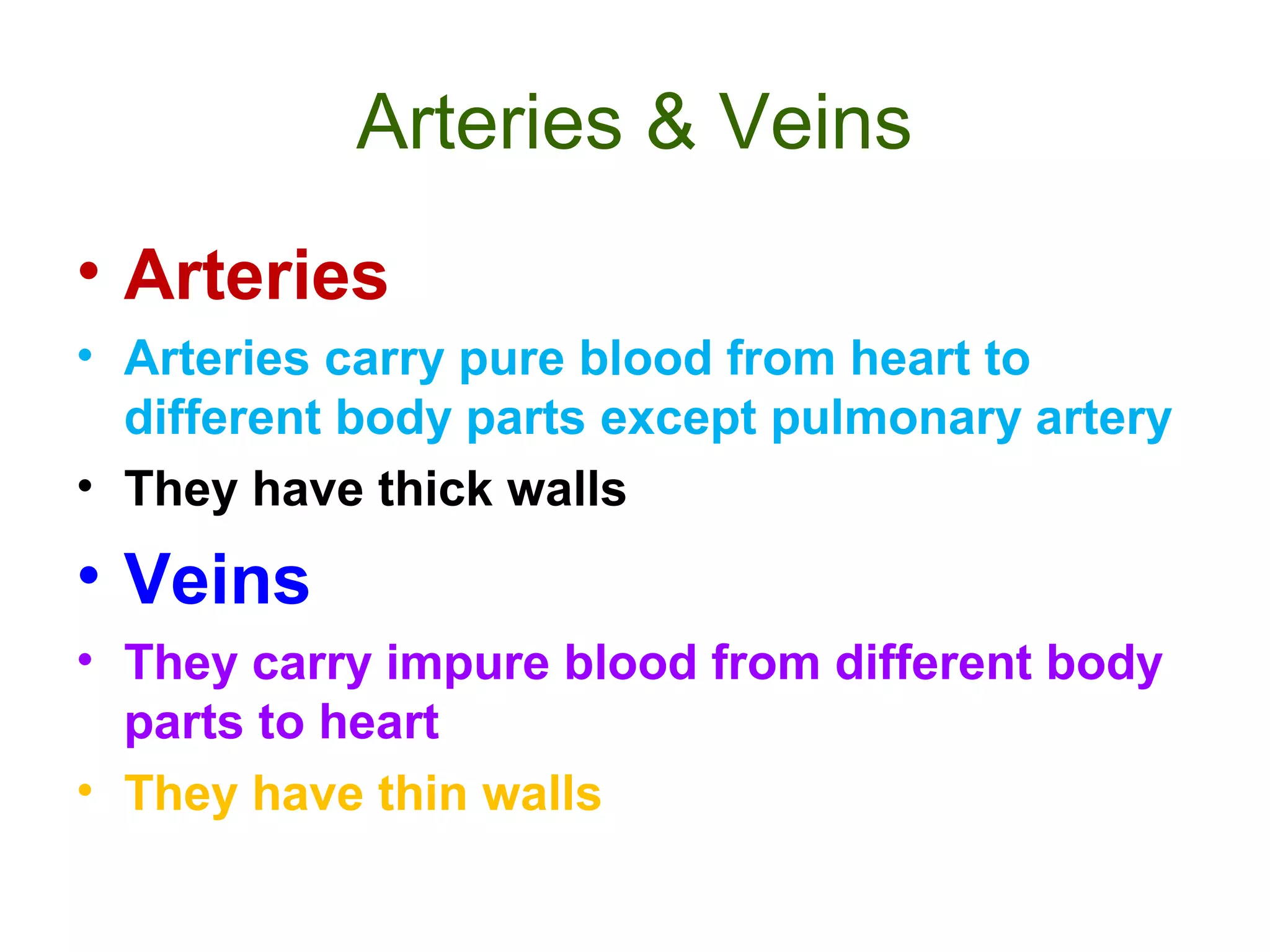
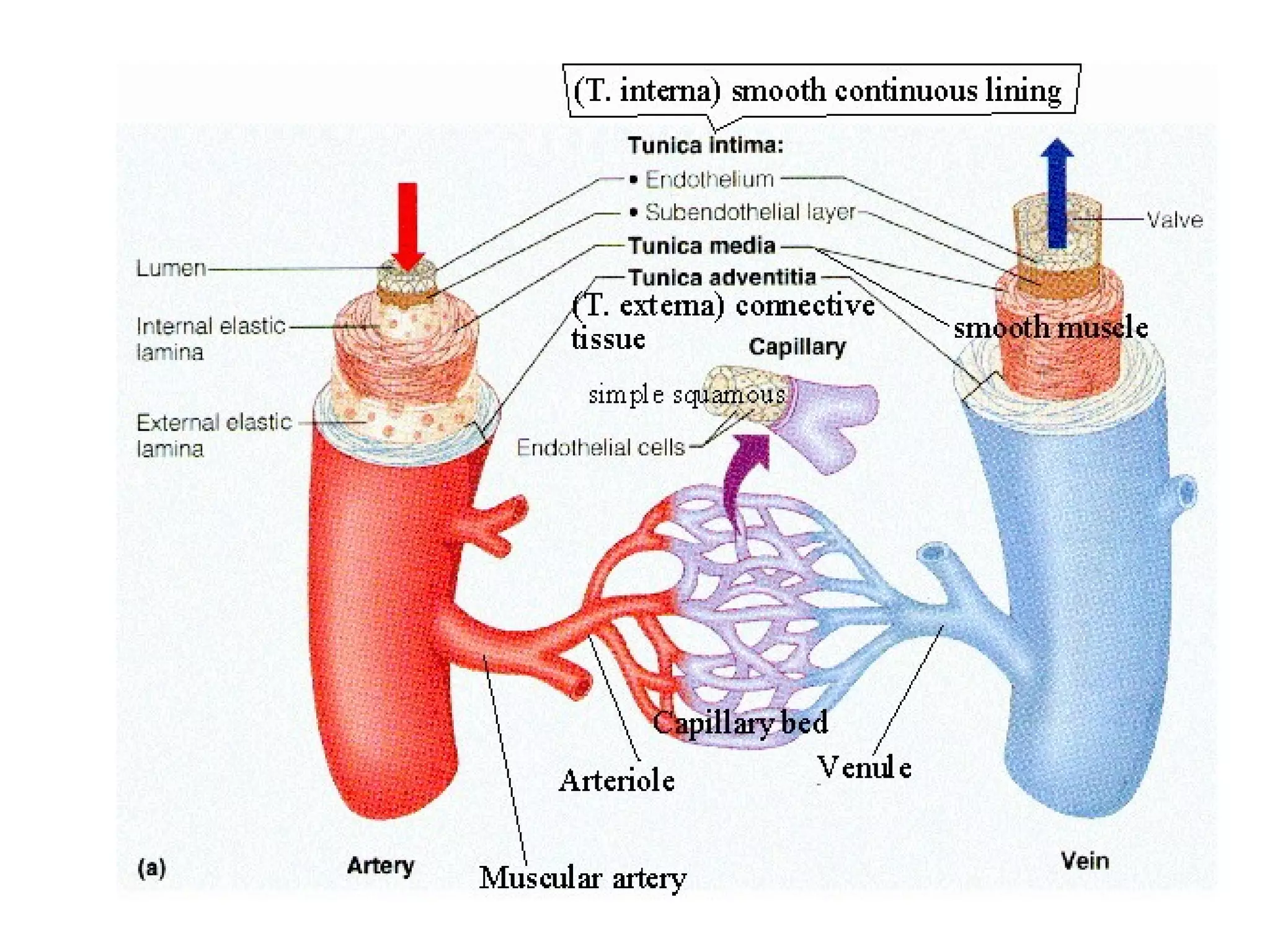
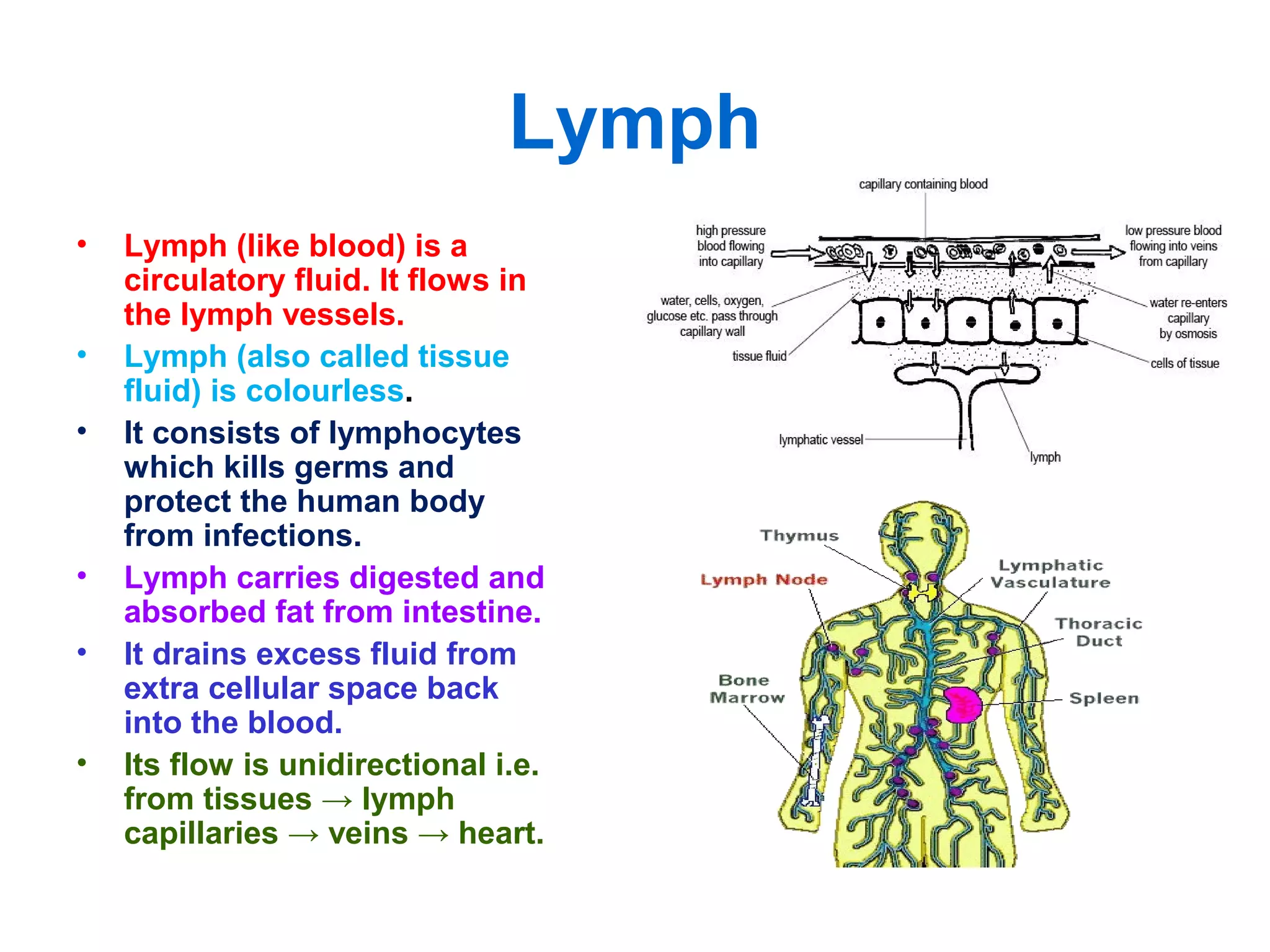
The circulatory system consists of the blood circulatory system and lymphatic system. The blood circulatory system contains blood, heart, and blood vessels. Blood is a connective tissue composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is 90-92% water and contains proteins like albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen. Red blood cells are biconcave and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells help fight infection. The heart has four chambers and uses double circulation to oxygenate blood in the lungs and transport it to the body before repeating the cycle. Lymph flows unidirectionally through lymph vessels and drains excess fluid from tissues.