Embed presentation
Downloaded 21 times


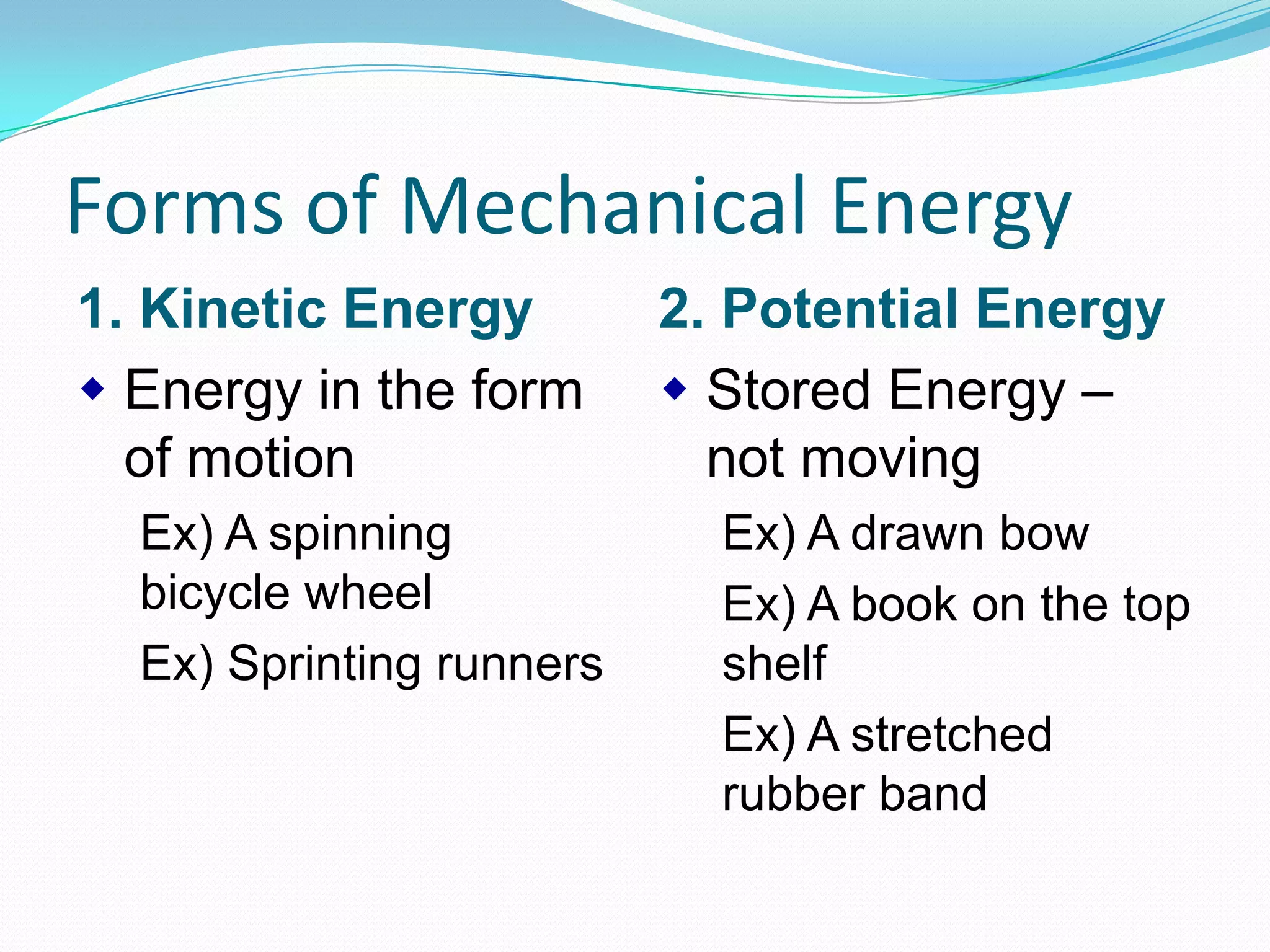
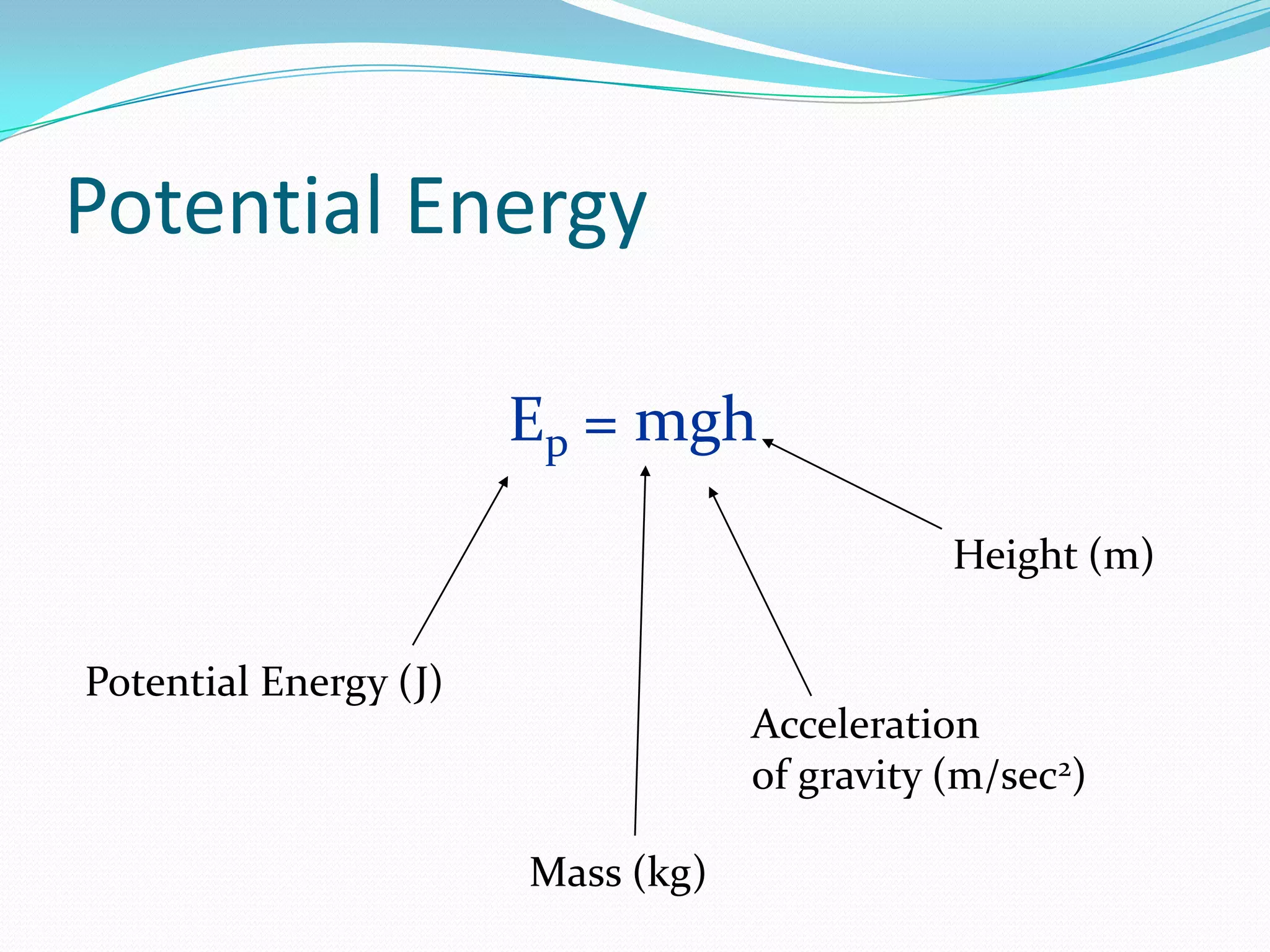

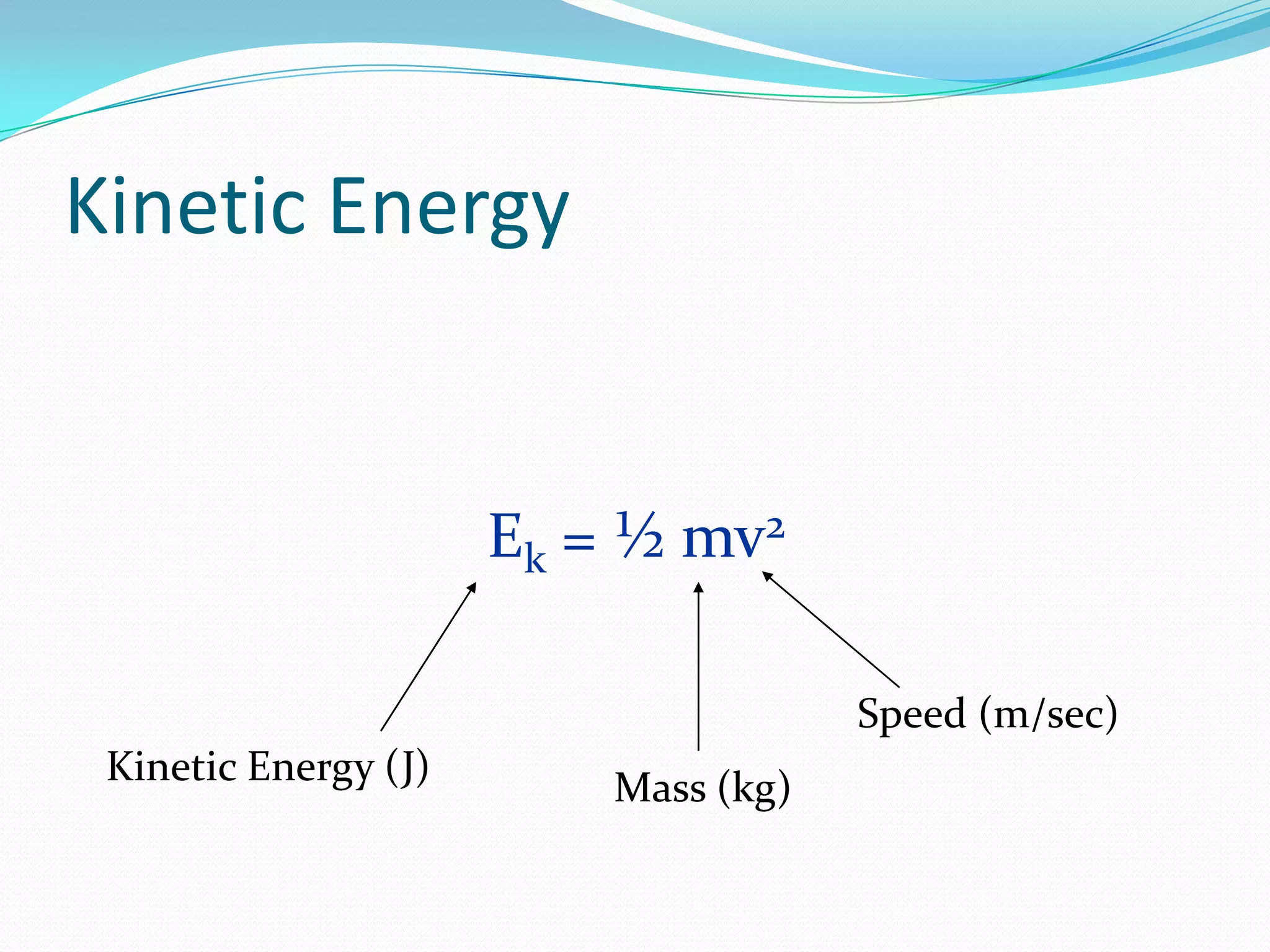
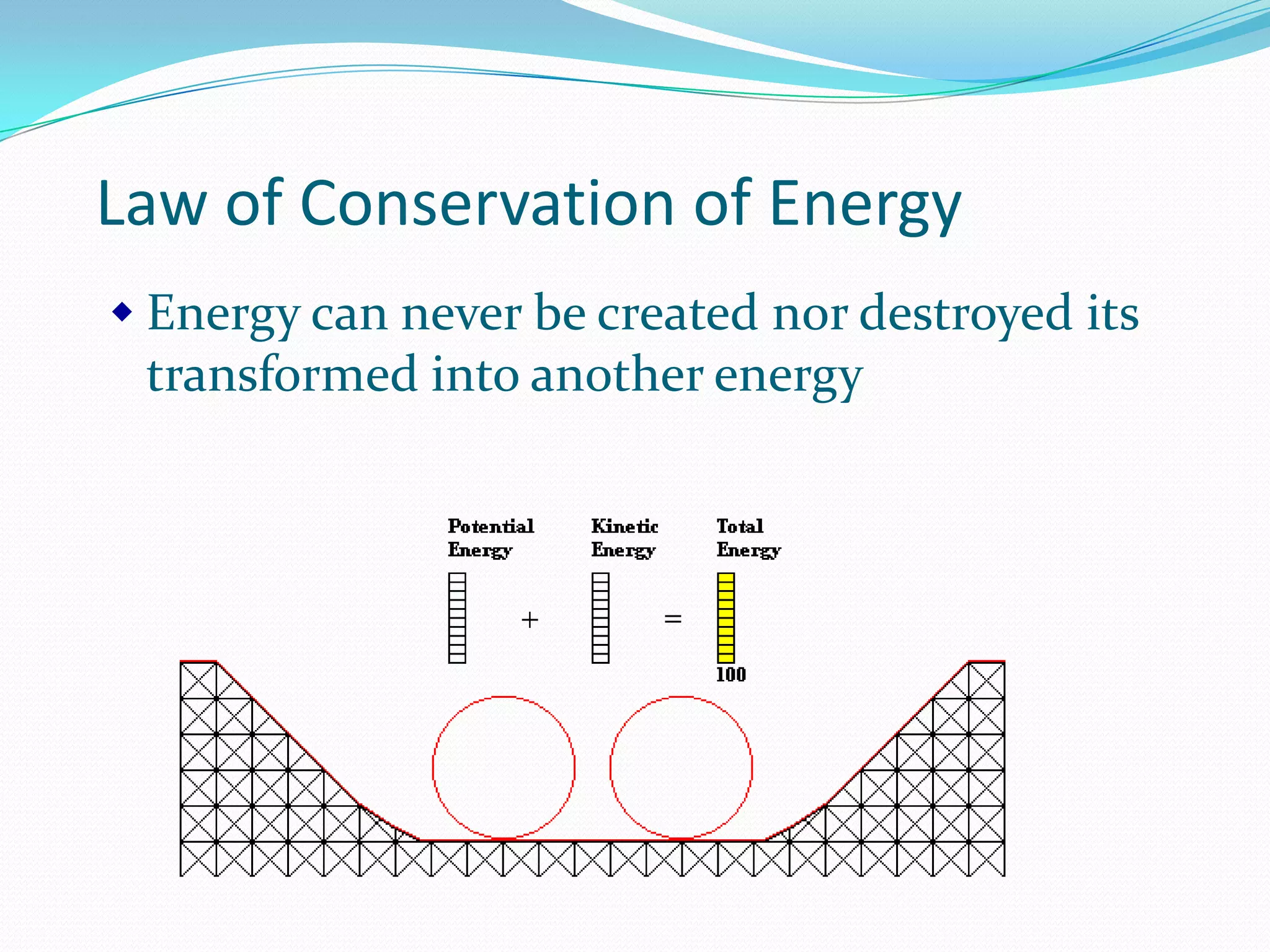

This document discusses different forms of mechanical energy including kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and depends on an object's mass and velocity, while potential energy is stored energy that depends on an object's position or state. The document provides examples and equations for calculating kinetic energy (KE=1/2mv^2) and gravitational potential energy (PE=mgh). It also introduces the law of conservation of energy, which states that the total energy in a system remains constant, as energy is transformed between kinetic and potential forms.









