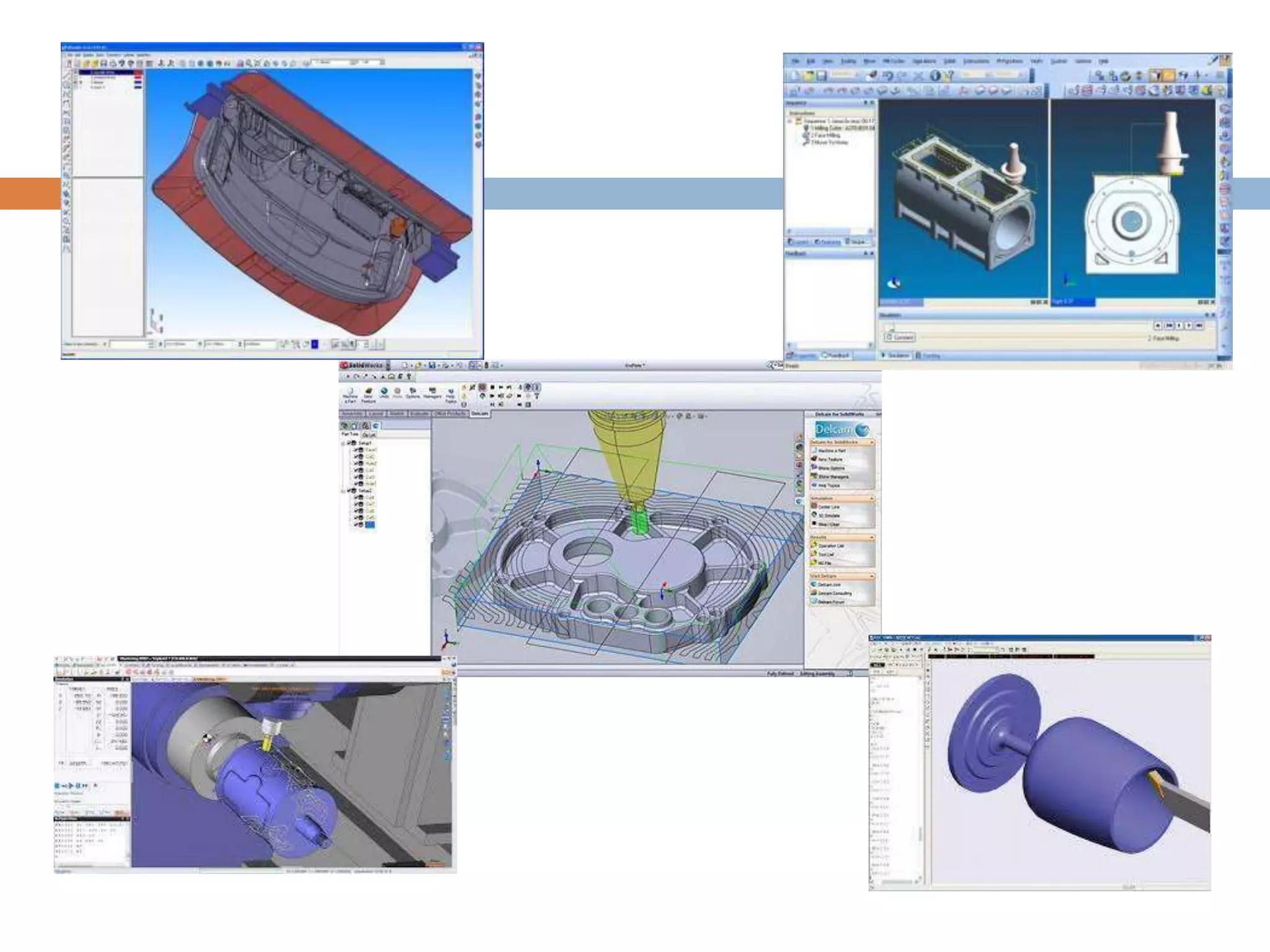
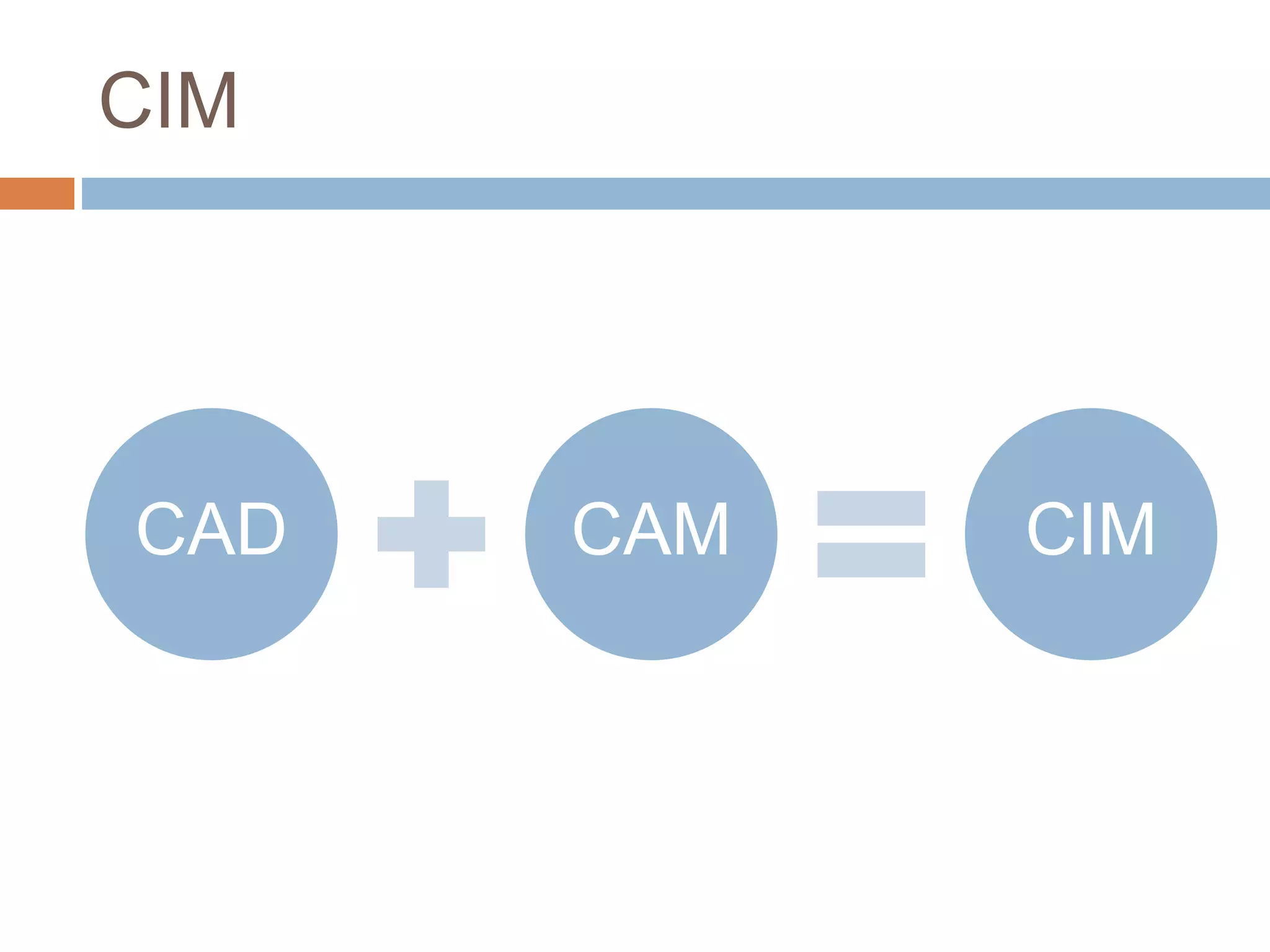
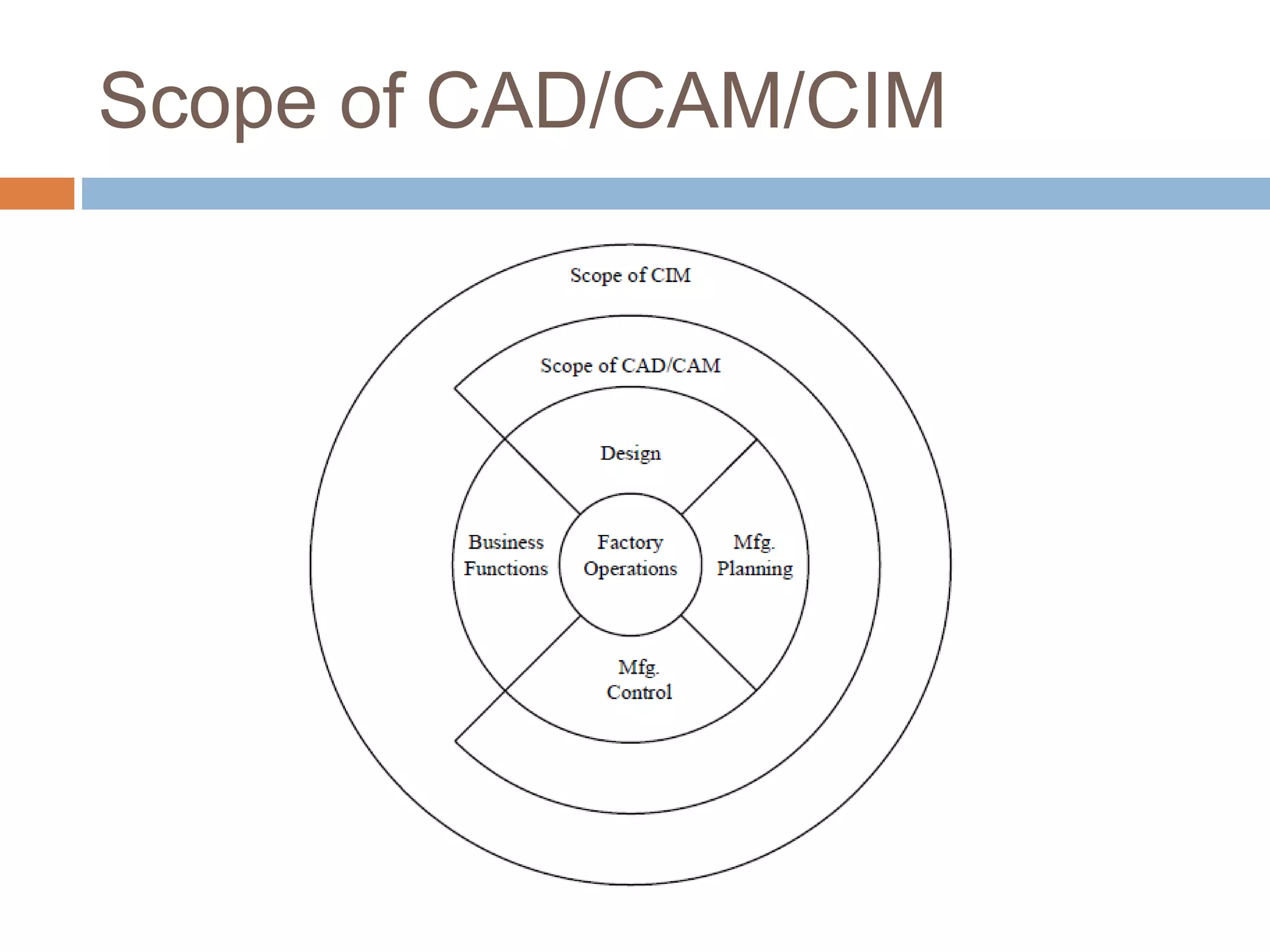
This document provides an introduction to CAD/CAM/CIM. It defines CAD as using computers to assist in the design process. CAM is defined as using computers to plan, manage and control manufacturing operations. CIM attempts complete automation of all manufacturing processes under computer control by integrating CAD, CAM and other business aspects. The document outlines several design disciplines and manufacturing processes. It discusses the need for CAD/CAM/CIM to increase productivity, improve quality and communication, create databases, optimize tool paths, and aid in production scheduling and shop floor control. The scope of CAD/CAM/CIM is also covered.