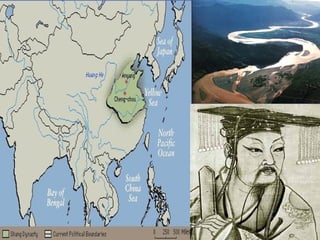
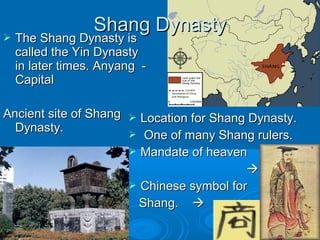
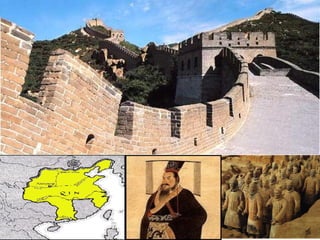
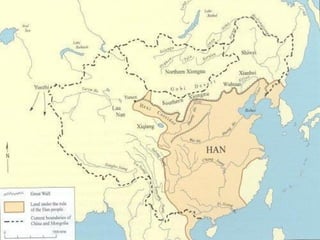
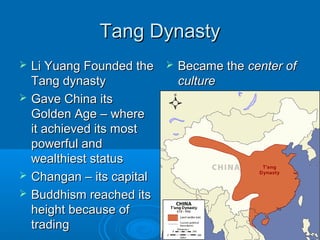
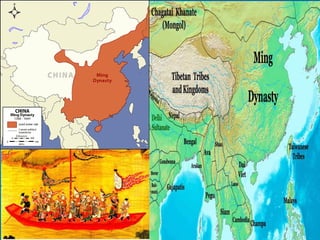
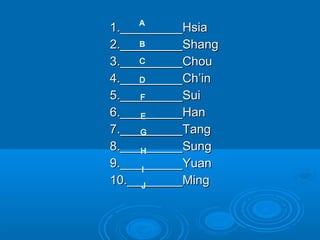
The document discusses the major Chinese dynasties from earliest to most recent. It begins with the Hsia Dynasty established around 2205 BCE by Emperor Yu, followed by the Shang Dynasty noted for its development of a lunar calendar and silk production. The longest ruling Chou or Zhou Dynasty is mentioned for establishing the civil service examination and feudal system. Later dynasties discussed include the Qin which first unified China under Shih Huang Ti, the Han known for establishing Confucianism, the Sui believed to have laid the foundations for China's golden age, and the Tang characterized as China's most powerful period. Later dynasties such as the Song, Yuan, and Ming are also summarized.