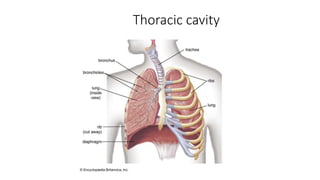
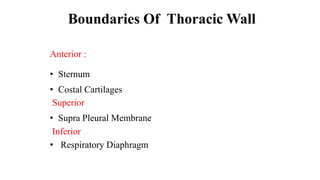
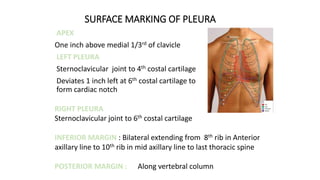
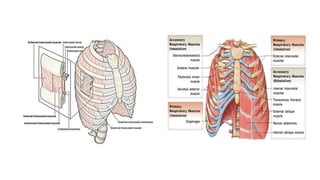
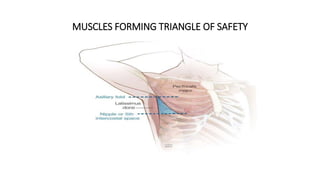
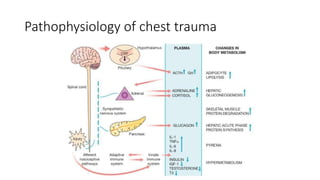
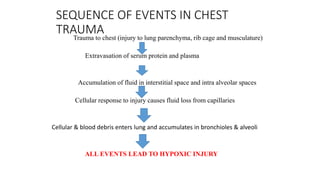
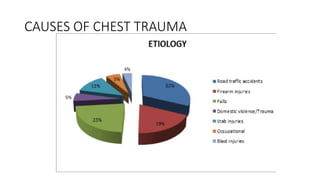
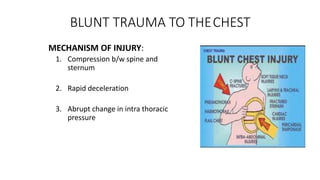
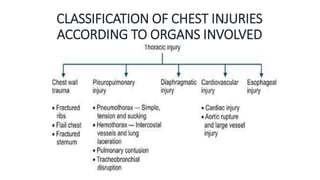
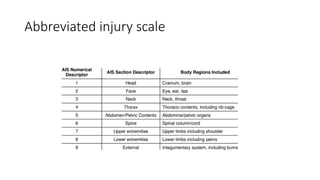
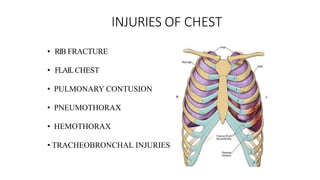
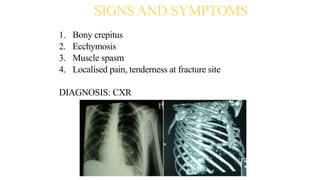
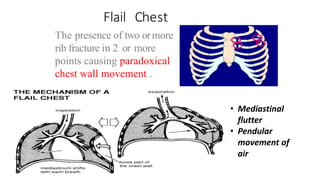
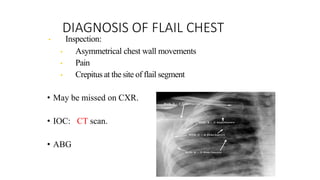
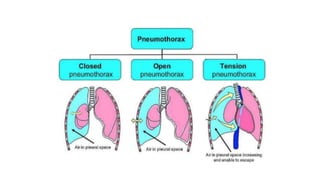
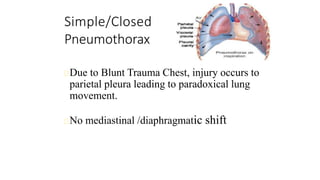
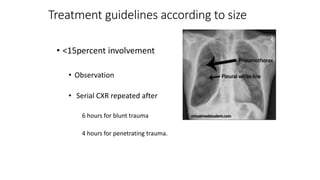
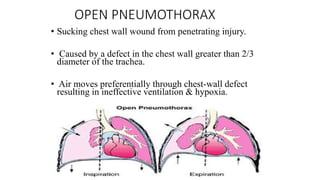
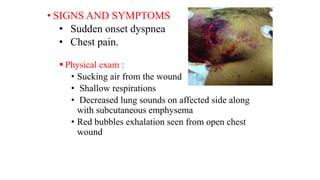
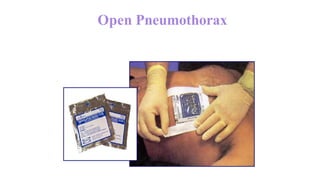
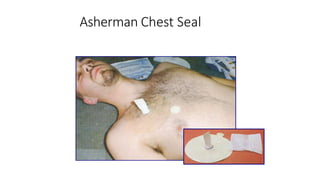
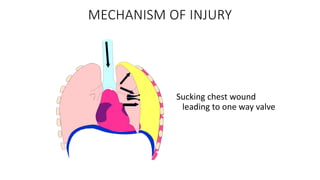
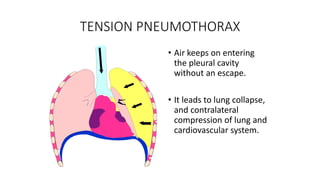
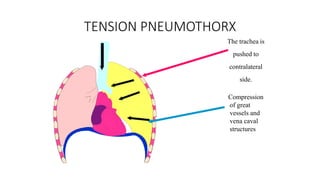
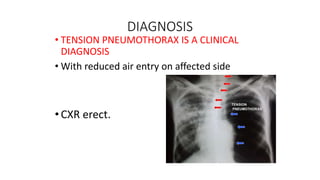
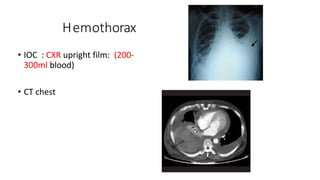
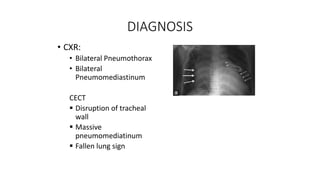
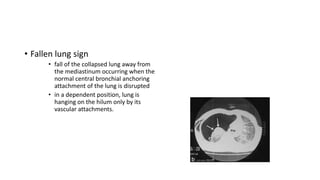
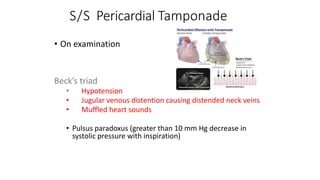
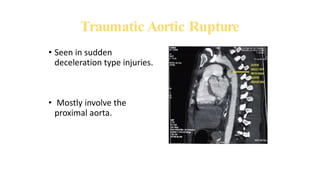
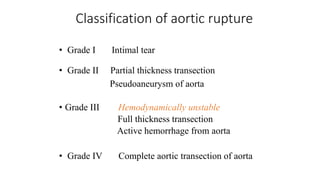
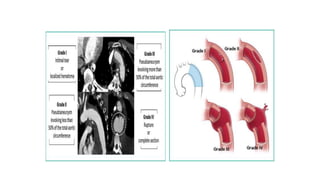
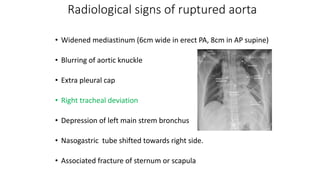
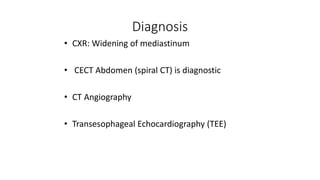
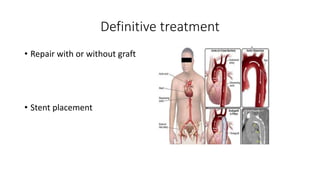
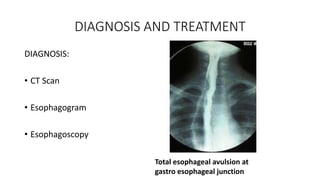
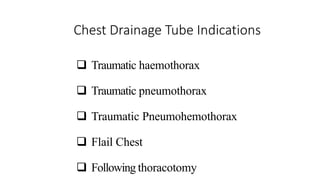
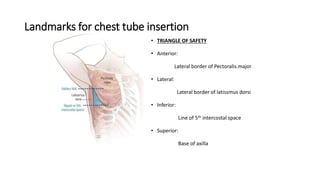
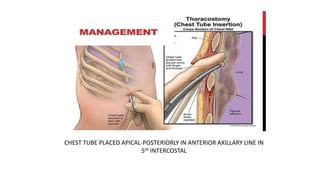
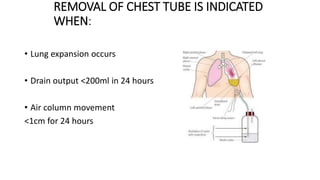
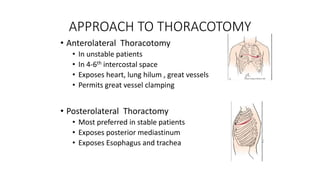
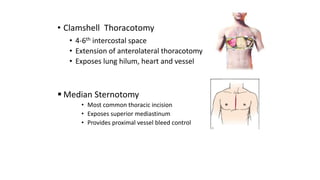
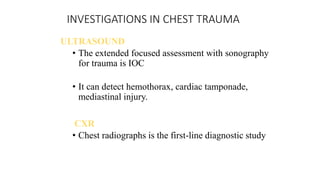
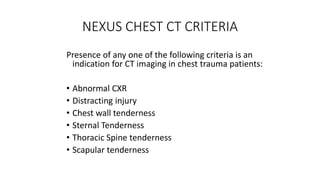
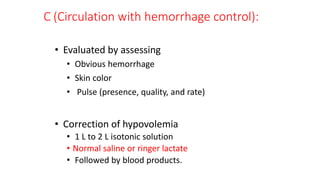
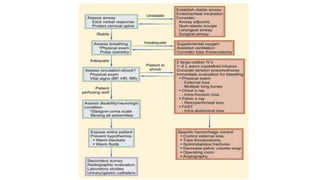
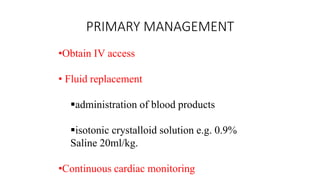
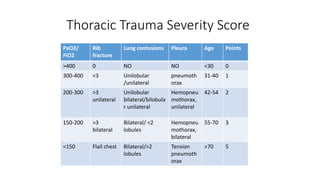
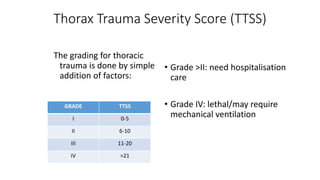
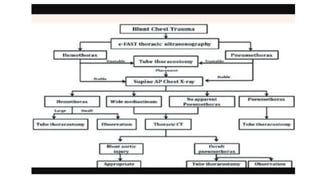
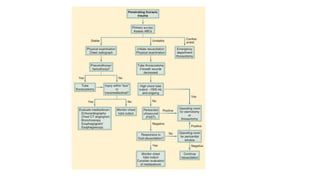
Chest trauma can represent a major burden and lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Chest injuries require prompt evaluation and management to address life-threatening injuries like tension pneumothorax, hemothorax, and cardiac injuries. The chest is divided into the thoracic cavity containing the lungs, heart, and great vessels which are vulnerable to injury from blunt or penetrating trauma. Common injuries include rib fractures, flail chest, pulmonary contusions, and pneumothorax. Immediate airway control and treatment of life-threatening injuries is essential, followed by management of potential injuries and complications to optimize outcomes.