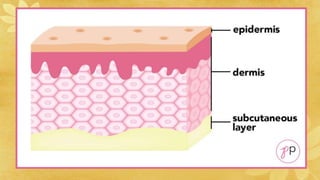
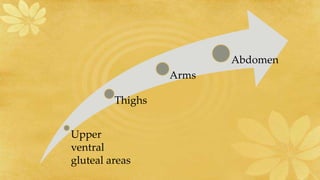
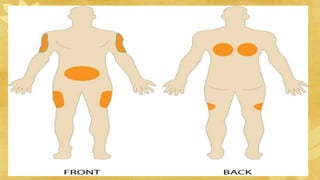
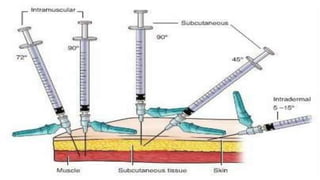
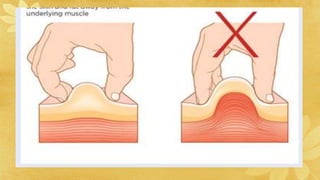
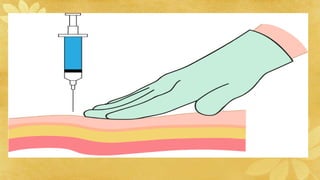
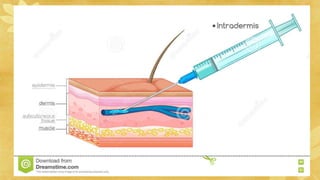
Subcutaneous injections are administered into the adipose tissue layer just below the skin. Drugs absorbed here have a slow, sustained rate of absorption. Various body sites can be used including the upper arm, abdomen, thigh, and back. The amount of subcutaneous tissue and needle length should be considered when choosing the injection site and needle angle. Generally, no more than 1 mL of medication is given subcutaneously and aspiration before injection is not necessary.