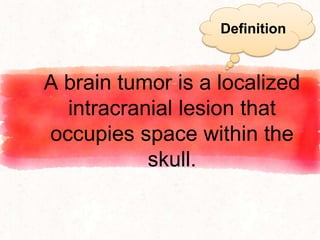
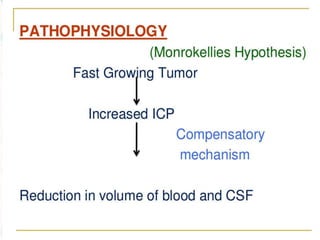
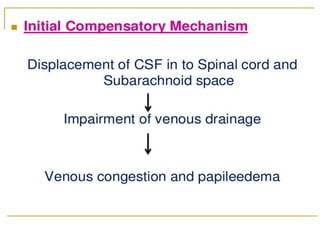
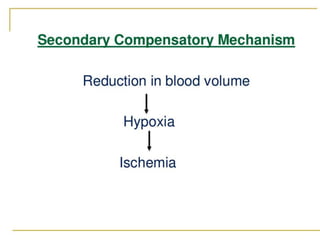
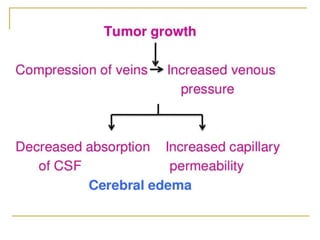
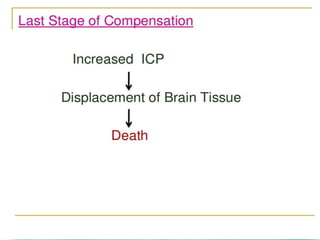
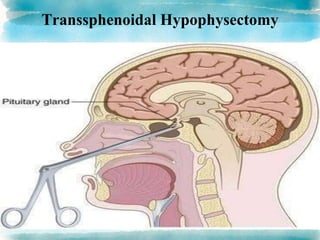
A brain tumor is a localized growth of abnormal cells within the skull that takes up space. Brain tumors are broadly classified as either primary (originating in the brain) or secondary (metastasized from another location). Primary brain tumors include gliomas (arising from brain tissue), meningiomas (arising from membranes surrounding the brain), pituitary adenomas, and acoustic neuromas. Common symptoms include headache, nausea, seizures, and mental status changes. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT and MRI scans as well as biopsy. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy depending on the type and grade of the tumor.