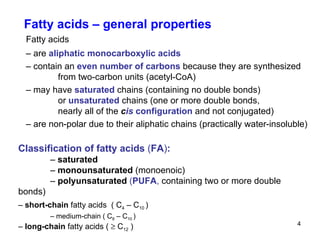
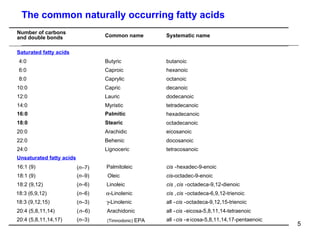
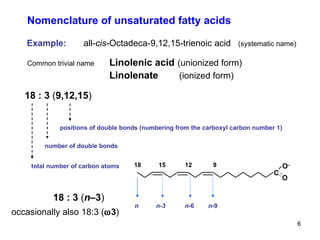
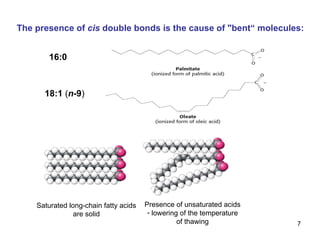
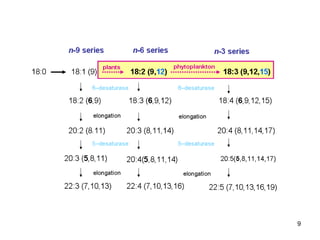
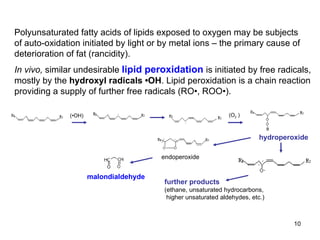
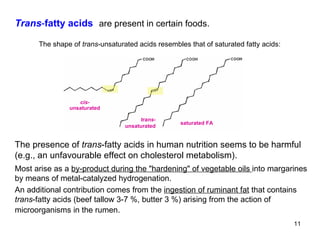
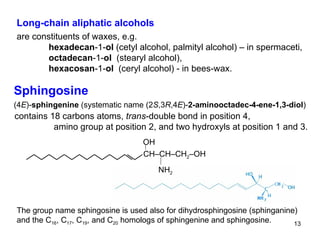
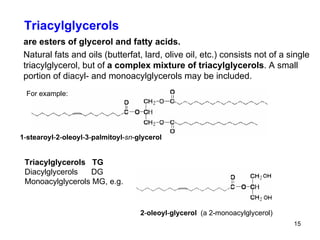
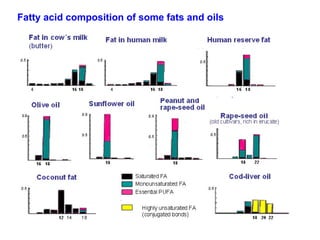
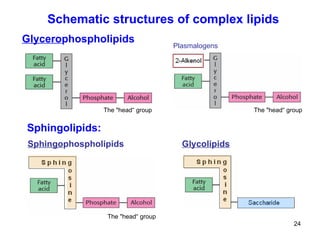
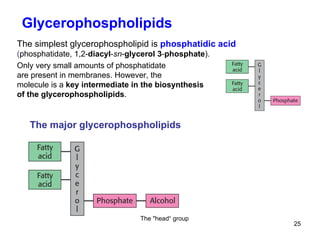
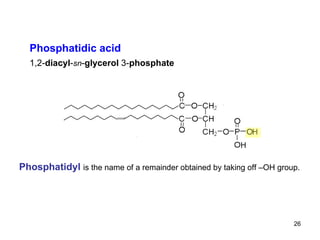
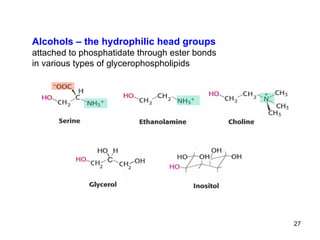
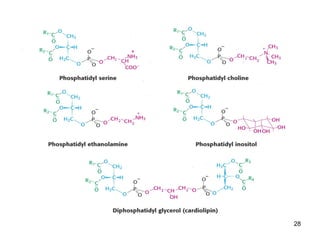
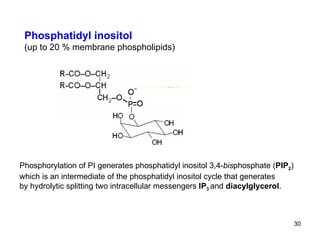
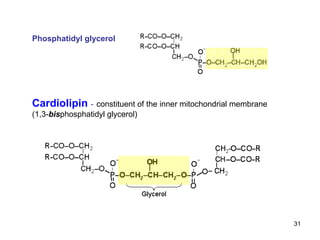
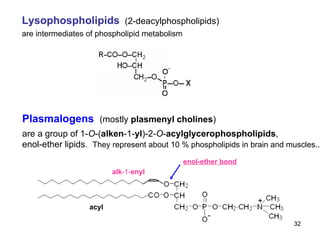
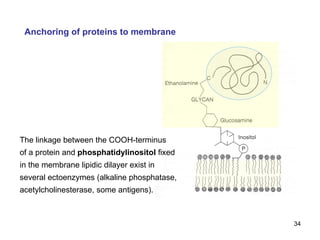
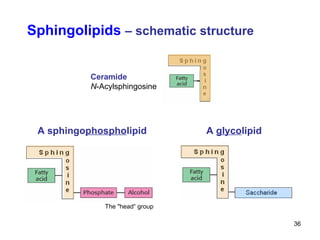
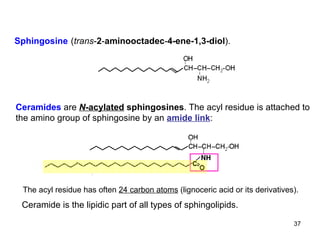
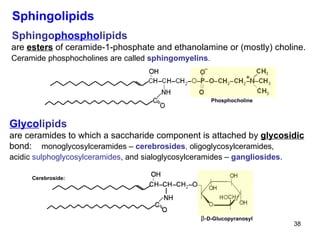
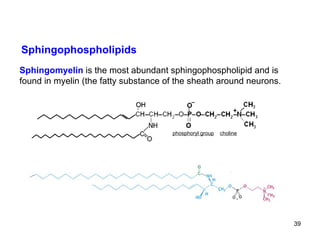
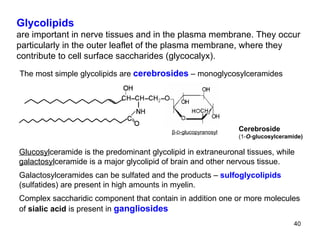
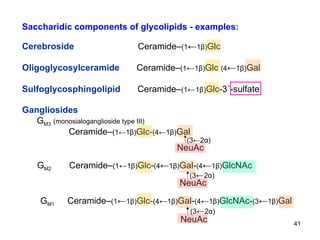
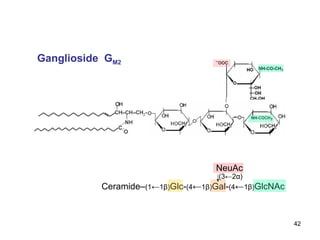
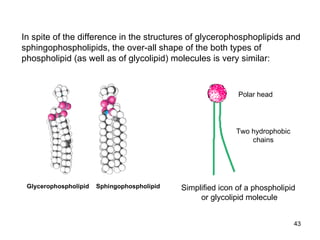
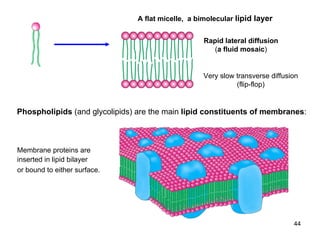
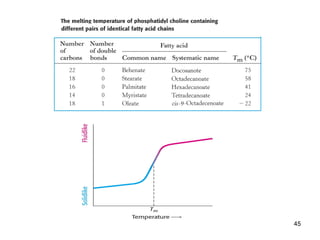
Lipids have two main biological functions: as nutrients and as structural components of cell membranes. Triacylglycerols (fats) are nutrients that provide energy, while phospholipids and glycolipids form the lipid bilayer of biomembranes. Lipids are naturally occurring compounds derived from animals or plants that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include simple lipids like fats and waxes, as well as complex lipids like phospholipids and sphingolipids that perform important structural and signaling roles in cells and membranes.