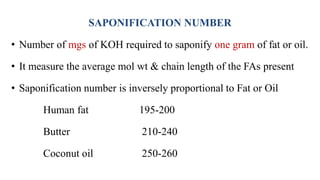
This document provides an overview of lipids, including their classification and properties. It begins by defining lipids as organic substances that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. It then classifies lipids into simple lipids like triglycerides and waxes, and compound lipids like phospholipids and glycolipids. Key points include that triglycerides are the main form of lipid storage, phospholipids are the major components of cell membranes, and various tests can characterize lipids based on properties like iodine number and saponification number.







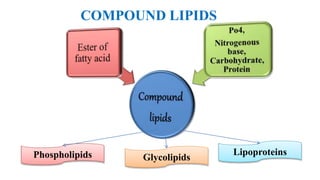


![GLYCOLIPIDS
• Lipids containing carbohydrates are referred as glycolipids
• Contain an alcohol [sphingosine (sphingol)] and nitrogenous
base, without phosphorous group.
Eg: Cerebrosides,Globosides & Gangliosides](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cl-02lipidclasificationsimplelipids-210705103617/85/CL-02-Lipid-classification-Simple-lipids-11-320.jpg)