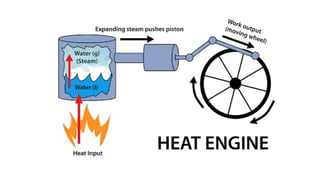
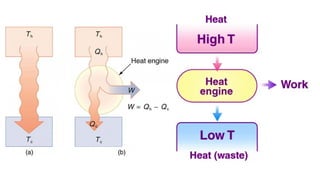
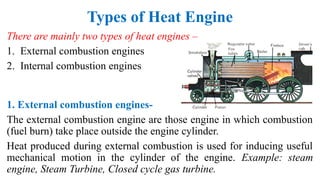
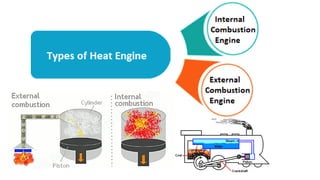
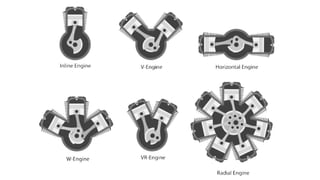
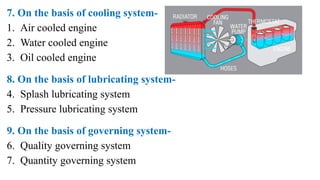
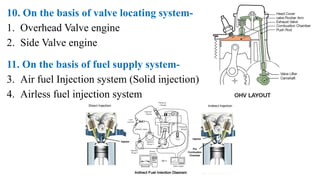
The internal combustion engine are those engine in which combustion (fuel burn) take place inside the engine cylinder. Chemical energy of the fuel is converted to thermal energy, and thermal energy is converted to mechanical energy, which moves the piston up and down inside the cylinder. Example: Car engine, bike engine.