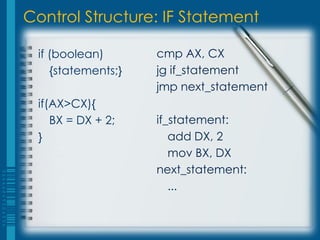
The document discusses control transfer instructions in assembly language programming. It describes unconditional jumps that transfer control without regard for conditions, and conditional jumps that transfer control based on a truth value set in flags registers by a comparison instruction. Some examples of conditional jump instructions are JE for equality, JNE for inequality, JL/JNGE for less than, JLE/JNG for less than or equal, and others. The document shows how conditional jumps can be used to implement if statements by comparing values and branching to a label if the condition is true.



![Group Activity
2. sum = x + y;
mov bl, [x]
add bl, [y]
mov [sum], bl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2a-120918111516-phpapp01/85/Chapter2a-4-320.jpg)
![Group Activity
3. prod = x * y;
mov al, [x]
mul byte[y]
mov [prod], ax](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2a-120918111516-phpapp01/85/Chapter2a-5-320.jpg)



![Control Transfer Instructions
mov al, 5 next:
add [num1],al
mov eax, 4
jmp next
mov ebx, 1
mov ecx, num2
mov eax, 4 mov edx, 1
mov ebx, 1 int 80h
mov ecx, num1
mov edx, 1
int 80h
(1) (2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2a-120918111516-phpapp01/85/Chapter2a-9-320.jpg)