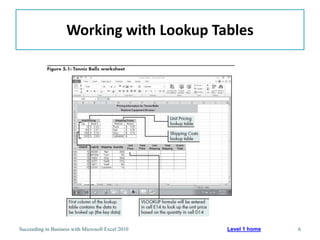
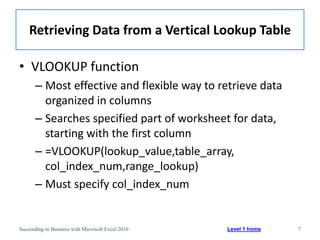
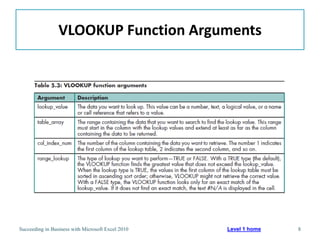
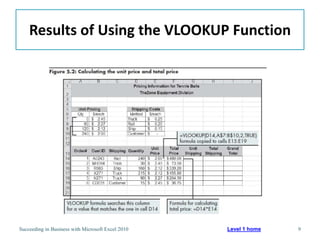
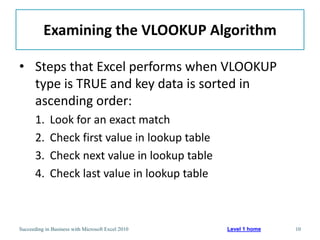
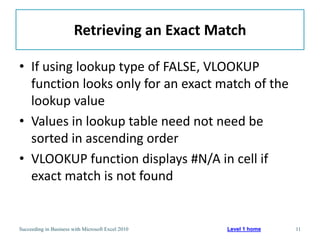
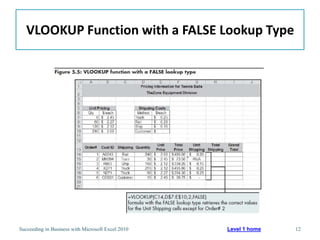
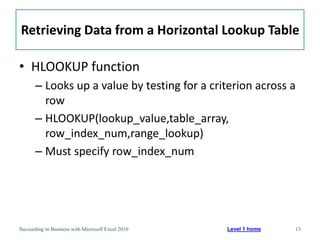
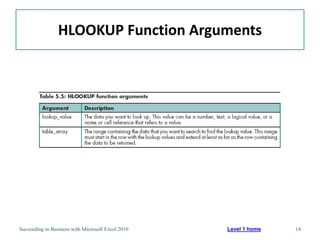
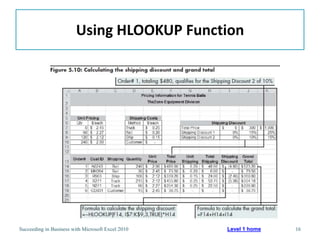
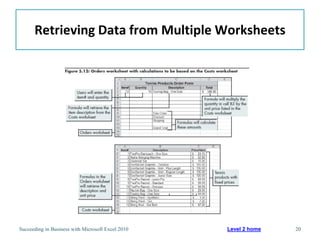
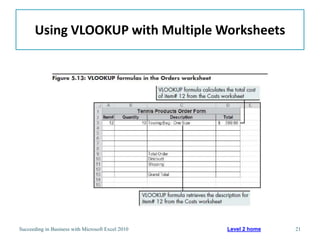
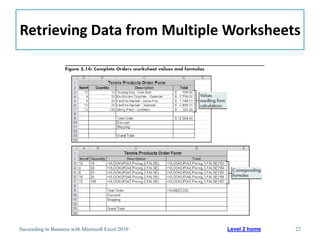
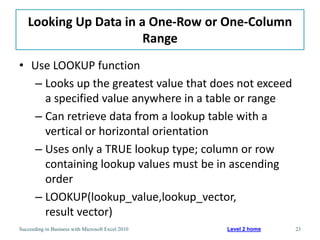
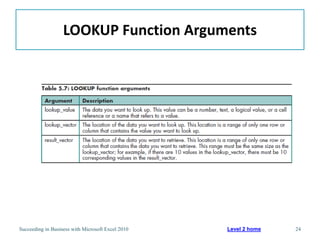
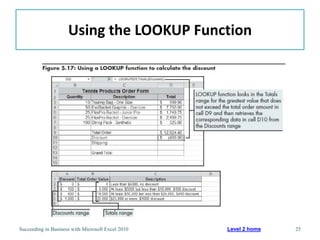
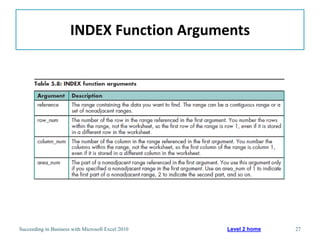
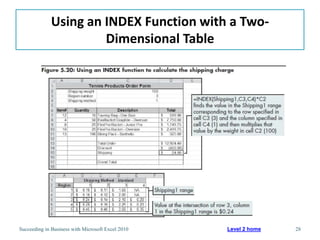
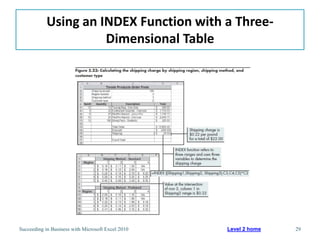
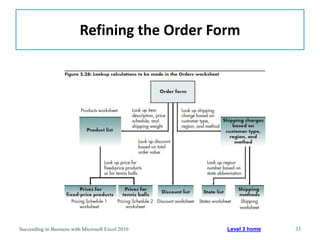
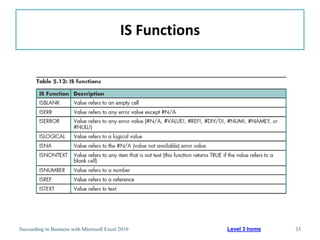
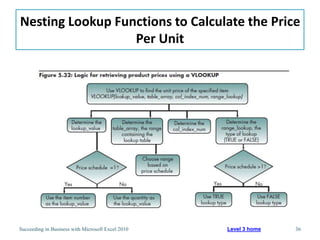
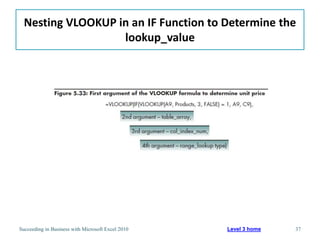
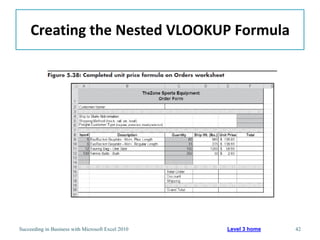
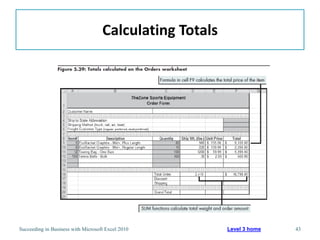
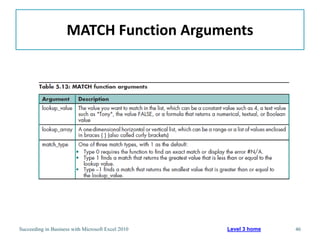
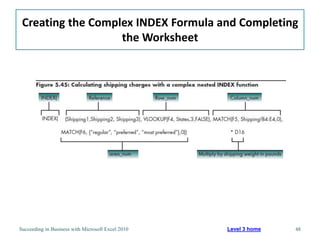
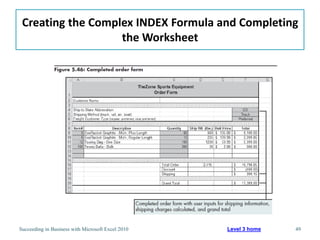
This chapter discusses lookup and reference functions in Microsoft Excel for retrieving data from tables. It covers basic functions like VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP. It also covers more complex functions and techniques like nested formulas, INDEX, MATCH and CHOOSE for retrieving data from multiple worksheets and multidimensional tables. The chapter provides examples and step-by-step instructions for using these functions to perform calculations on an order form.