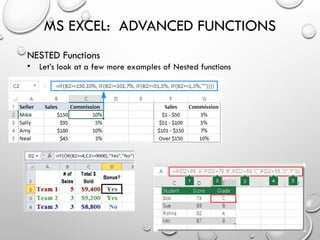
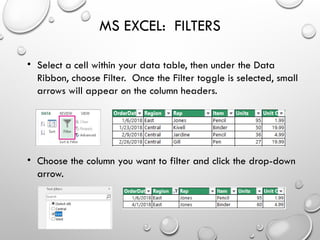
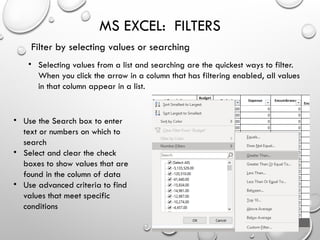
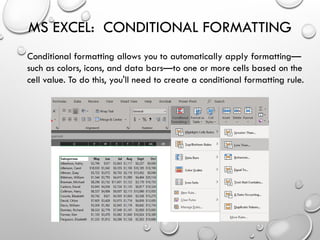
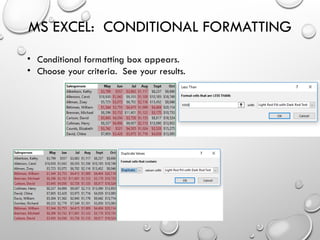
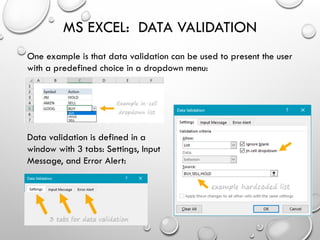
The document provides an overview of advanced Microsoft Excel features including filters, conditional formatting, data validation, and various functions like VLOOKUP and CONCATENATE. Each feature is described in detail, outlining how to use them effectively to manage and manipulate data. It also covers the use of nested functions and the SUBTOTAL function for summarizing data, emphasizing practical application tips.






![MS EXCEL: ADVANCED FUNCTIONS
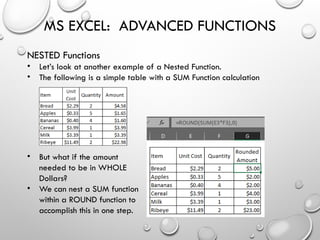
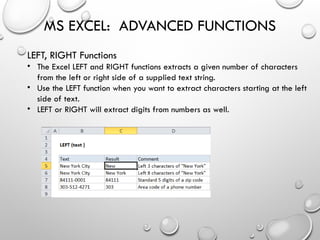
SUBTOTAL Function
• The Excel SUBTOTAL function provides a subtotal of values in a list of data.
The SUBTOTAL function can return a SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MAX, and
others and the function can either include or exclude values in hidden rows.
• SUBTOTAL behavior is controlled by the
function_num argument, which is
provided as a numeric value. There are
11 functions available, each with two
options.
1. function_num - A number that specifies which function to use in calculating subtotals within a list
2. ref1 - A named range or reference to subtotal
3. ref2 - [optional] A named range or reference to subtotal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microsoftexcel-250122044933-e484a7b0/85/This-is-a-presentation-on-Microsoft-Excel-13-320.jpg)