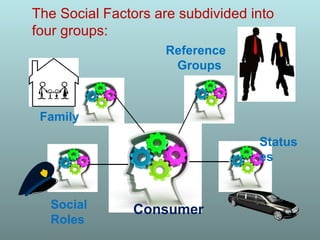
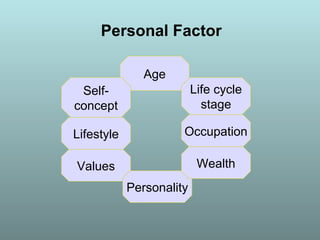
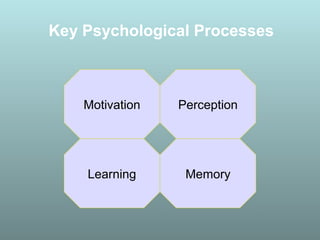
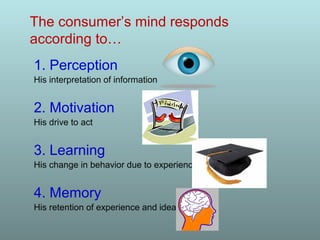
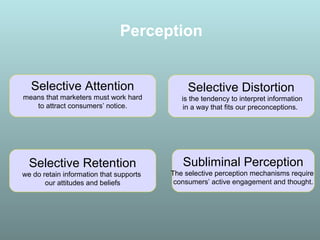
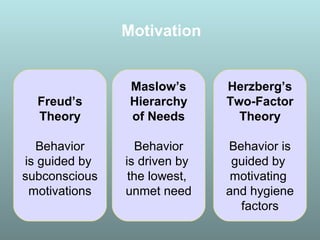
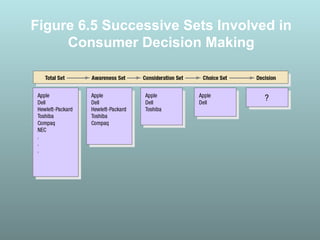
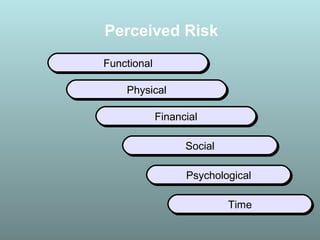
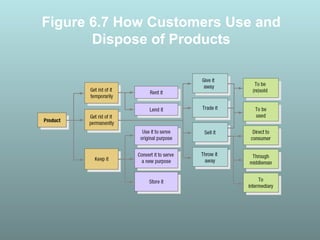
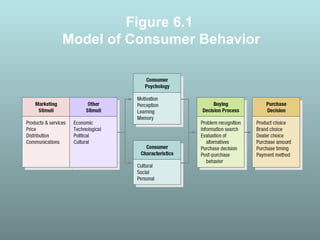
This document discusses factors that influence consumer buying behavior, including cultural, social, and personal factors. It analyzes how culture, subcultures, family, social roles, and reference groups shape consumer decisions. On a personal level, it examines how age, values, life cycle stage, occupation, personality, self-concept, wealth, and lifestyle all affect what consumers buy. Key psychological processes like perception, motivation, learning, and memory are also summarized in how they guide consumer responses to marketing. Models of consumer decision making and the perceived risks involved are presented.