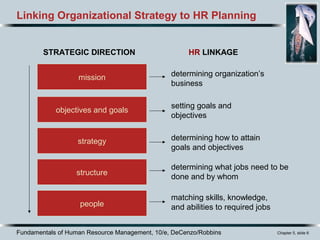
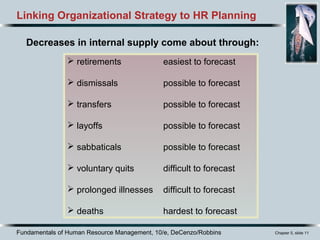
The document discusses the importance of effective job analysis for human resource planning and management. It explains that HR planning must be linked to organizational strategy to identify the necessary skills, knowledge, and abilities for roles. A key part of this process is job analysis, which systematically explores job activities, requirements, and conditions. Insights from job analysis inform job descriptions and help ensure an organization has the right people in the right roles to achieve its goals.