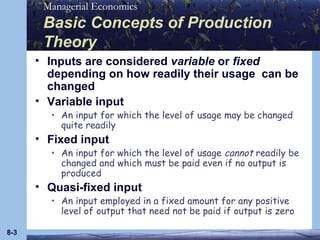
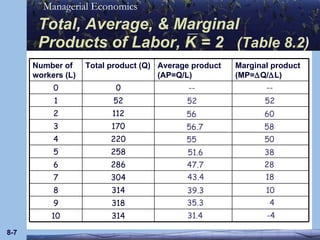
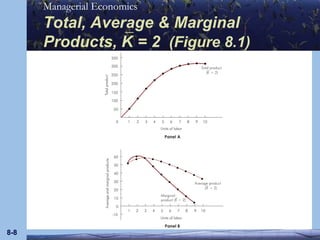
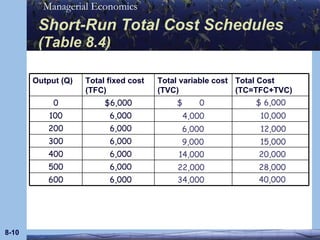
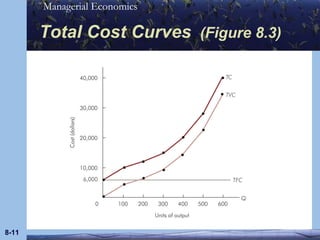
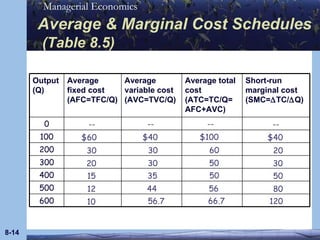
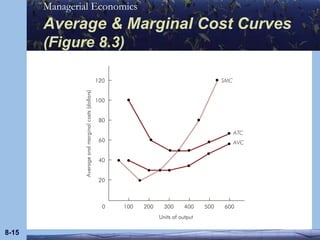
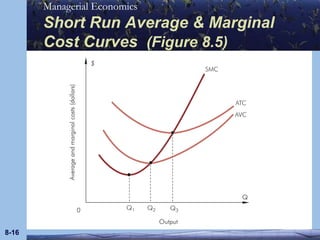
This document discusses key concepts in production theory and short-run costs. It defines short-run as having at least one fixed input, with output varied using variable inputs only. Average and marginal products are introduced, along with total, average, and marginal costs. Graphs and tables are provided to illustrate the relationships between these concepts and how average and marginal costs change with different levels of output in the short-run.