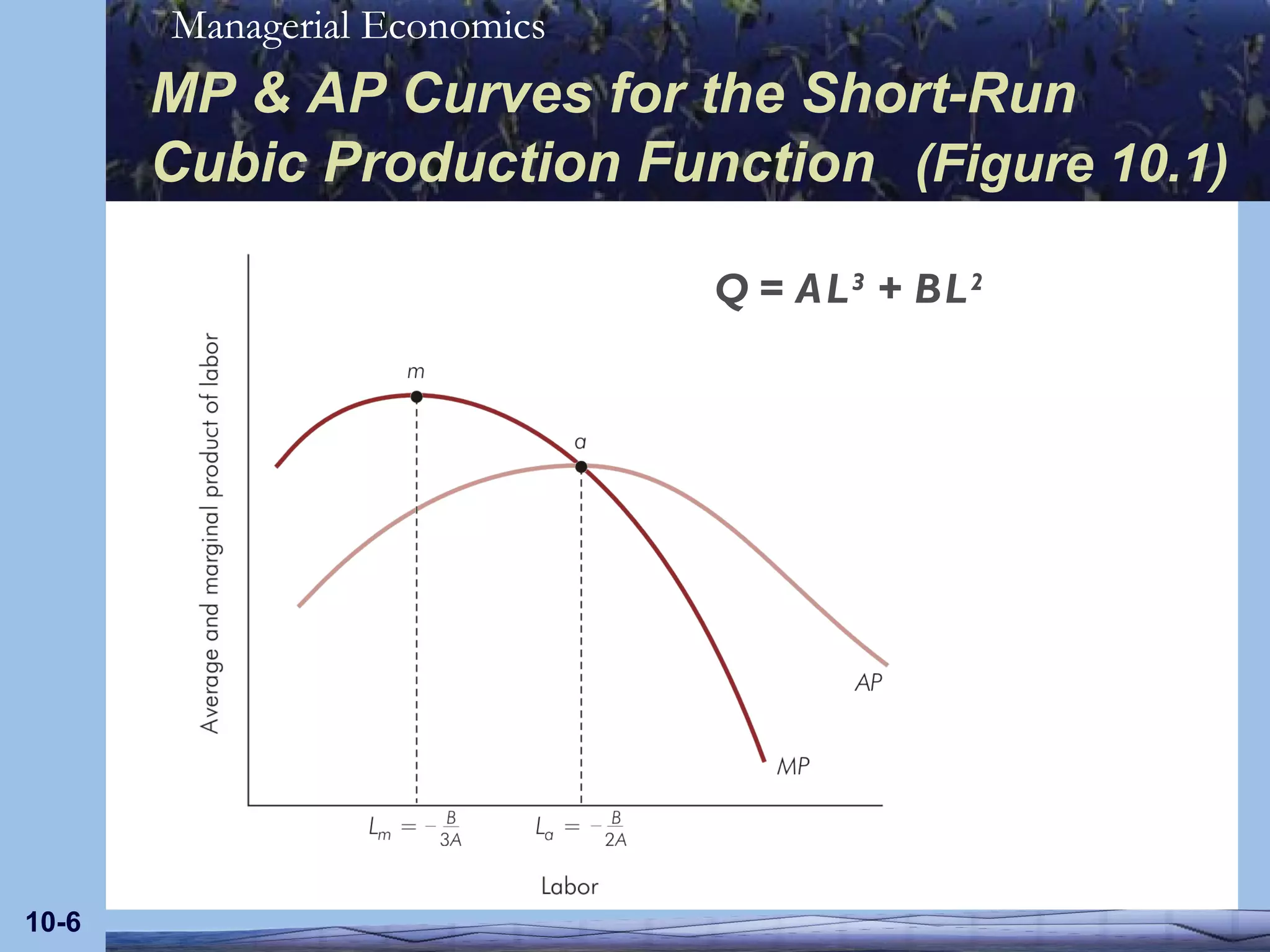
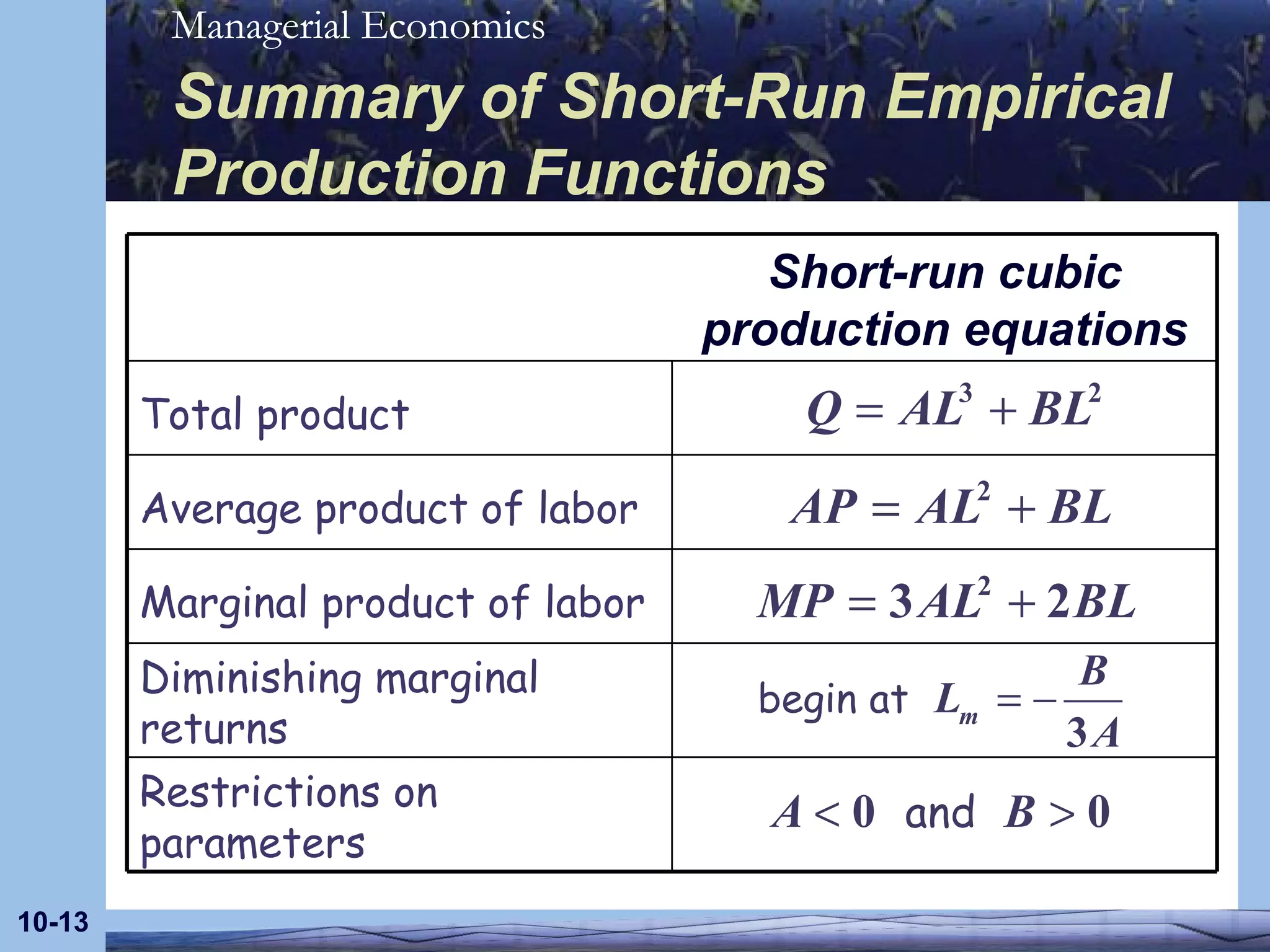
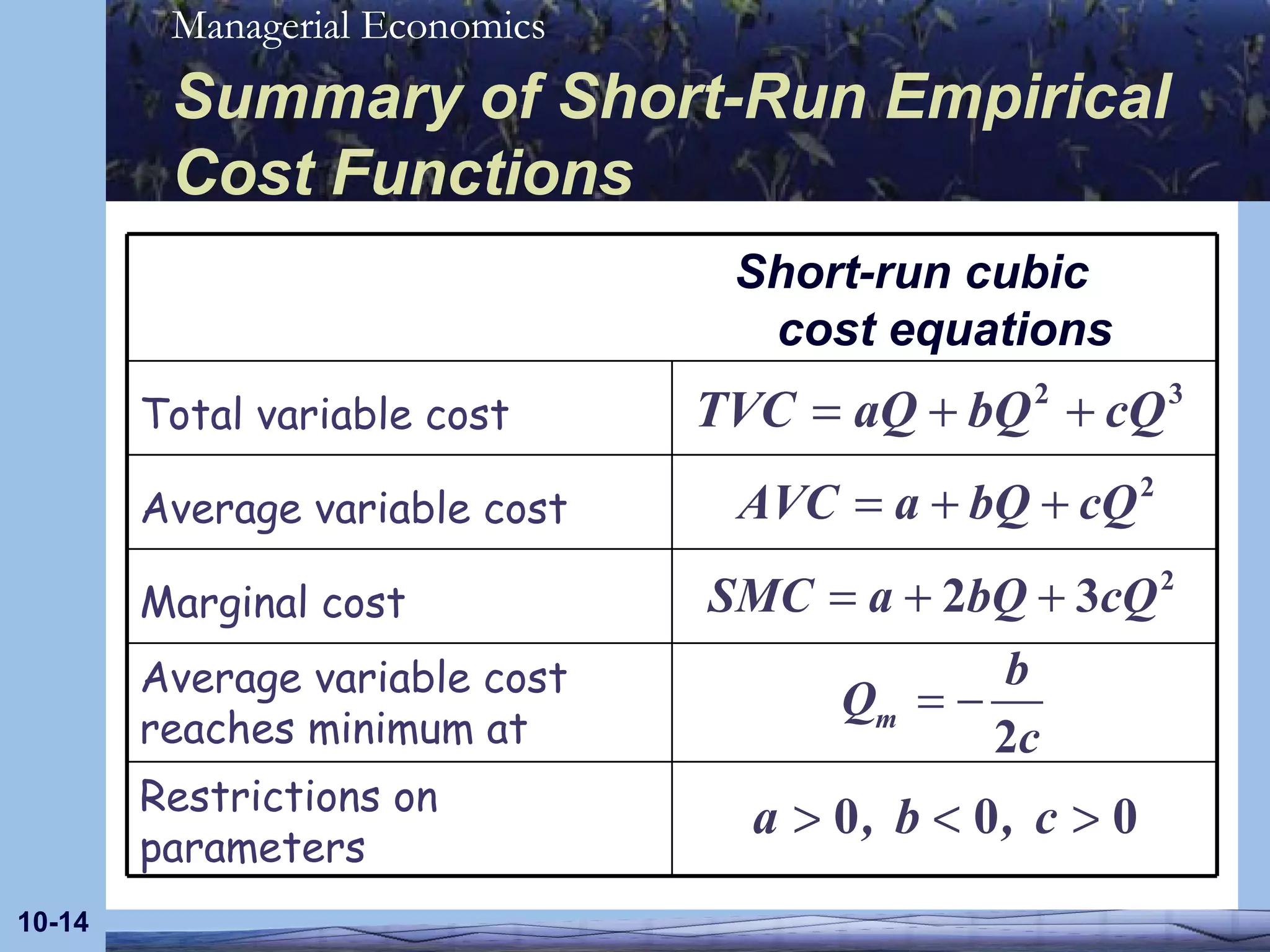
The document discusses empirical models for short-run production and cost functions using cubic specifications. It describes how a cubic long-run production function can be used to derive a short-run cubic production function by holding capital constant. It also outlines the properties of average and marginal products and costs for such short-run cubic specifications, including how they are estimated and restrictions on the parameters.