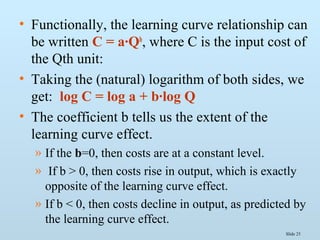
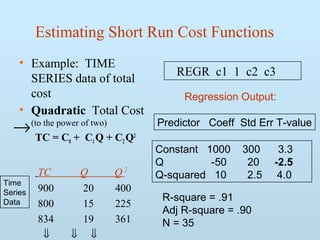
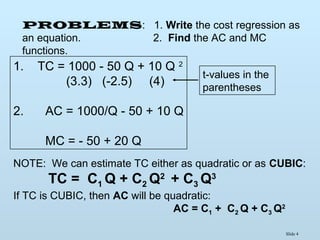
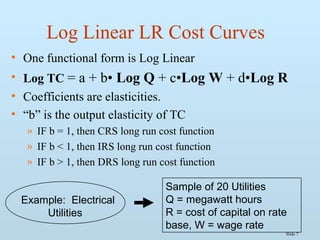
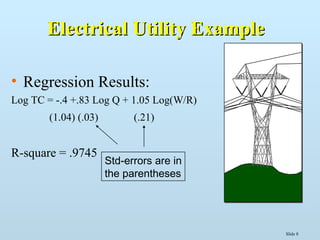
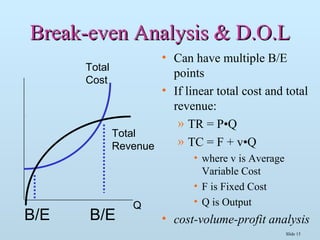
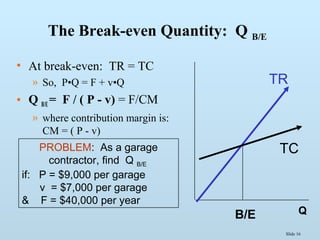
The document discusses various methods for estimating cost functions, including both short run and long run techniques, such as regression analysis and engineering cost approaches. It provides examples of cost estimates for firms like Boeing and utilities, and includes discussions on break-even analysis and the degree of operating leverage. Additionally, it touches on the learning curve effect in production processes.









![Slide 17
• Amount of sales
revenues that breaks
even
• P•QB/E = P•[F/(P-v)]
= F / [ 1 - v/P ]
Break-even Sales Volume
Variable Cost Ratio
Ex: At Q = 20,
B/E Sales Volume is
$9,000•20 =
$180,000 Sales Volume
Answer: Q = 40,000/(2,000)= 40/2 = 20
garages at the break-even point.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/me09-140429095149-phpapp02/85/Chapter-9-Application-of-Cost-Theory-17-320.jpg)
![Slide 18
Target Profit Output
Quantity needed to attain a target
profit
If π is the target profit,
Q target π = [ F + π] / (P-v)
Suppose want to attain $50,000 profit, then,
Q target π = ($40,000 + $50,000)/$2,000
= $90,000/$2,000 = 45 garages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/me09-140429095149-phpapp02/85/Chapter-9-Application-of-Cost-Theory-18-320.jpg)
![Slide 19
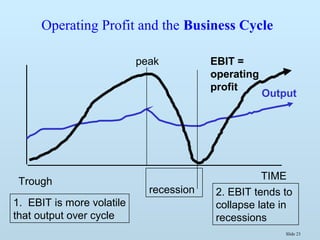
Degree of Operating Leverage
or Operating Profit Elasticity
• DOL = Eπ
» sensitivity of operating profit (EBIT) to
changes in output
• Operating π = TR-TC = (P-v)•Q - F
• Hence, DOL = ∂ π/∂ Q•(Q/π) =
(P-v)•(Q/π) = (P-v)•Q / [(P-v)•Q - F]
A measure of the importance of Fixed Cost
or Business Risk to fluctuations in output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/me09-140429095149-phpapp02/85/Chapter-9-Application-of-Cost-Theory-19-320.jpg)

![Slide 21
DOL as
Operating Profit Elasticity
DOL = [ (P - v)Q ] / { [ (P - v)Q ] - F }
• We can use empirical estimation methods to find
operating leverage
• Elasticities can be estimated with double log
functional forms
• Use a time series of data on operating profit and
output
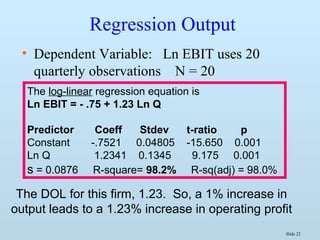
» Ln EBIT = a + b• Ln Q, where b is the DOL
» then a 1% increase in output increases EBIT by b%
» b tends to be greater than or equal to 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/me09-140429095149-phpapp02/85/Chapter-9-Application-of-Cost-Theory-21-320.jpg)