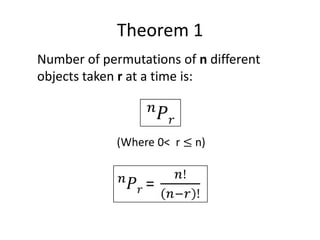
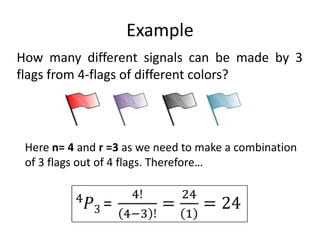
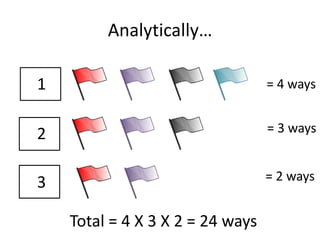
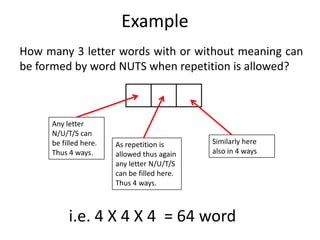
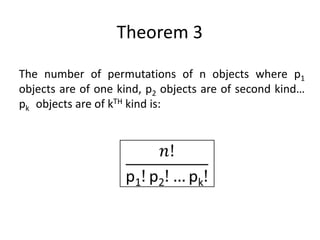
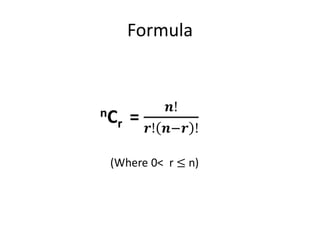
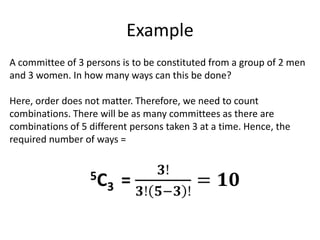
The document covers permutations and combinations, detailing the fundamental principles of counting, definitions, theorems, and examples for both concepts. It explains how to calculate arrangements when order matters (permutations) and when it does not (combinations). Additionally, it provides specific examples illustrating various scenarios for better understanding of the application of these mathematical principles.