1. The document discusses various topics in physics including mechanics, motion, vectors, and kinematics formulas.
2. Mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the study of motion of material objects. Motion can be rectilinear, circular, rotational, translational, and one, two, or three dimensional.
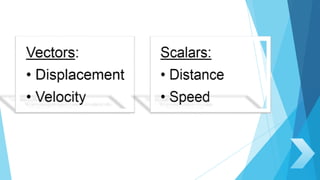
3. Important concepts in motion include speed, velocity, distance, displacement, scalars, and vectors. Kinematics formulas summarize relationships for one dimensional motion with constant acceleration.