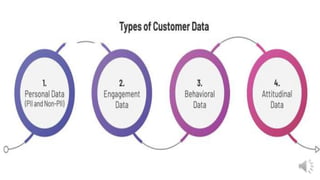
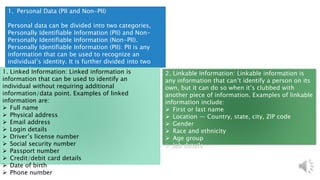
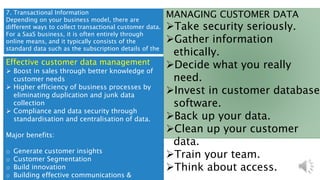
Customer data includes personal information, engagement data, behavioral data, and attitudinal data that businesses collect from customers through their interactions and transactions. This data can be collected through various channels like websites, mobile apps, social media, emails, surveys, customer service software, and transaction records. It is important for businesses to properly manage customer data by keeping it secure, collecting it ethically, using it to generate insights and build better customer experiences and communications.