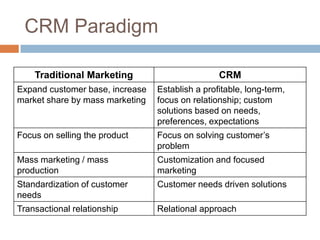
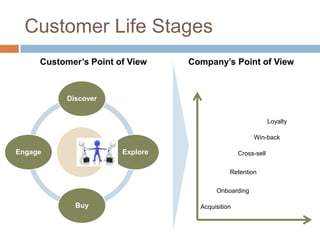
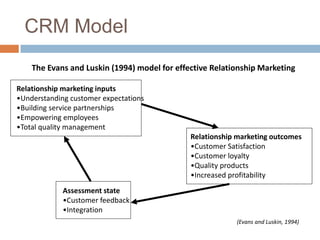
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is an approach that companies take to manage interactions with current and potential customers. It involves understanding customer needs and preferences at each stage of the customer lifecycle in order to develop long-term and profitable relationships. CRM provides tools for market research, product development, customer segmentation and more to help companies gain a competitive advantage. Effective CRM relies on understanding customer expectations, building partnerships, empowering employees and obtaining customer feedback.