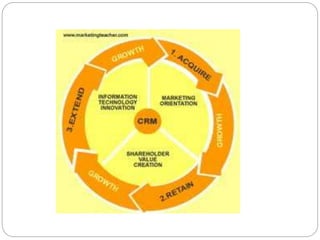
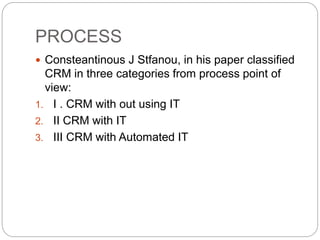
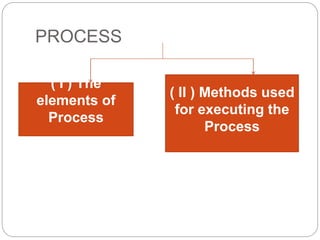
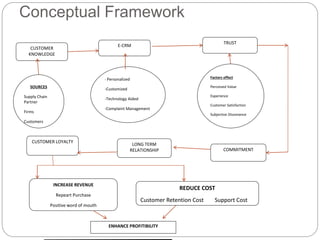
The document discusses the evolution and significance of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in a competitive market driven by technology and globalization. It emphasizes the transition from a transactional model to a relationship model focused on long-term customer satisfaction and retention, highlighting how effective CRM can enhance customer lifetime value and overall profitability. The conclusion underscores that CRM not only improves customer service and satisfaction but also serves as a crucial strategy for maintaining competitive advantage.