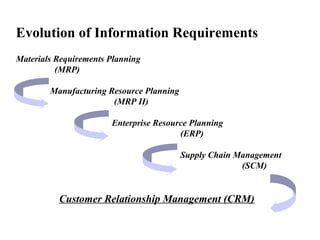
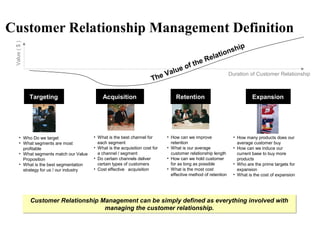
The document provides an overview of customer relationship management (CRM). It discusses the history and evolution of CRM from database marketing in the 1980s to relationship marketing in the 1990s to CRM in the early 2000s. It defines CRM as everything involved with managing the customer relationship. The goals of CRM are also outlined, such as providing better customer service and cross-selling products more effectively. Different types of relationship marketing are described, from basic transactions to partnership models. The document also discusses implementing a CRM program and the importance of an integrated approach.











![Marketing Selling Servicing
Customer Management Process Threads
Broadcast
Mail
Field Personnel
Agents/Distributors
Call Center
Retail
Internet
Back Office Process/Systems
CustomerInteractionChannels
Are we making the right level
and type of marketing, sales,
and service investments in
each of our customer
segments?
Customer RelationshipCustomer Relationship
StrategiesStrategies
Are we taking a holistic
approach to our customers
across processes and
channels?
Customer RelationshipCustomer Relationship
StructureStructure
Have we implemented best
practices and technology in
process/channel?
Customer RelationshipCustomer Relationship
PerformancePerformance
ScopeScope DepthDepth
Importance of CRM[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mbaiiewisu-ivcrm-150317045240-conversion-gate01/85/Mba-ii-ewis-u-iv-crm-14-320.jpg)
![Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
The Customer
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Take Action to
Enrich the Customer
Relationship Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Build and Manage
Customer Value
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Capture
Customer Data
and Measure
Results
Store Data, Mine
and Make
Information
Accessible
The CRMThe CRM
DynamicDynamic
Customer Relationship Management is a ongoing, dynamic learning process for an organizationCustomer Relationship Management is a ongoing, dynamic learning process for an organization
Customer Relationship Management Process[2]
The building blocks of CRM allow an organization to manage this cycle and use the
knowledge on customers to enhance the Life Time value of the customer portfolio.
No organization has perfect information on its customers. Knowledge of customers is
continuously enhanced through the CRM dynamic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mbaiiewisu-ivcrm-150317045240-conversion-gate01/85/Mba-ii-ewis-u-iv-crm-15-320.jpg)
![Implementing CRM must be approached from an
Integrated Perspective[3]
All areas must be implemented, to some degree, to effectively manage the customer
relationship. When pieces are implemented in isolation, the benefits are less than
overwhelming.
All areas must be implemented, to some degree, to effectively manage the customer
relationship. When pieces are implemented in isolation, the benefits are less than
overwhelming.
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
The Customer
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Take Action to
Enrich the Customer
Relationship Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Build and Manage
Customer Value
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Capture Customer
Data and Measure
Results
Capture
Customer Data
and Measure
Results
Store Data, Mine
and Make
information
Accessible
CRMCRM
without anwithout an
IntegratedIntegrated
ApproachApproach
A data warehouse full of data without
the tools to extract knowledge is
nothing more than expensive
inventory.
Sophisticated mining tools only
produce results only as good as the
data they mine.
Developing insights on how to improve the value of the
customer relationship without having the infrastructure to
take action has no impact on the bottom line. In addition,
there is no opportunity to test the ‘theoretical’ analysis.
Implementing new technologies without
the knowledge on how to enrich the
relationship is likely to yield a return below
the cost of the capital expenditure.
Taking action to improve the
relationship without measuring the
results provides no evidence of
success or failure and limits the
opportunity for learning.
Capturing gigabytes of customer data
in disparate operational systems that
are next to impossible to access may
render the data useless.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mbaiiewisu-ivcrm-150317045240-conversion-gate01/85/Mba-ii-ewis-u-iv-crm-16-320.jpg)

![Business Processes
Profiles &
Preferences
Business PartnerBusiness Partner
Business to CustomerBusiness to Customer
Business to BusinessBusiness to Business
The ValueThe Value
PropositionProposition
ofof
ElectronicElectronic
BusinessBusiness
SolutionsSolutions
Integrating
more directly
with the
business
processes of
customers and
partners
Tailoring
products and
services to
customers
needs and
values
Business
Processes
Extending key business
applications to clients and
business partners
Business PartnerBusiness Partner
e-Business is all about integrating the internal and external processes between business partners and
customers.
e-Business is all about integrating the internal and external processes between business partners and
customers.
e-Business – Definition[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mbaiiewisu-ivcrm-150317045240-conversion-gate01/85/Mba-ii-ewis-u-iv-crm-19-320.jpg)


