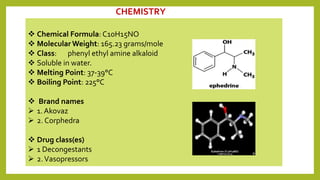
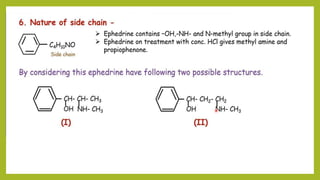
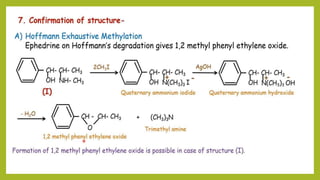
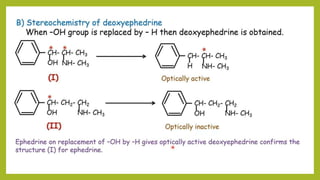
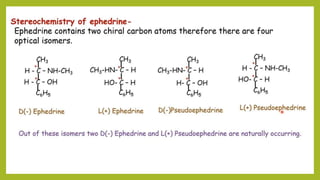
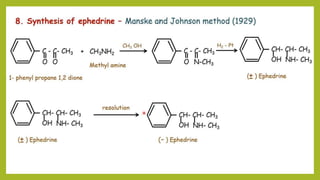
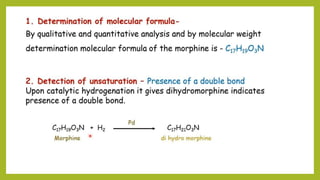
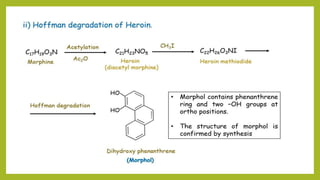
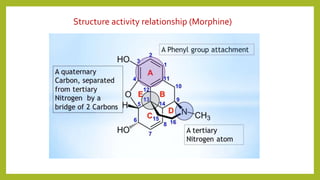
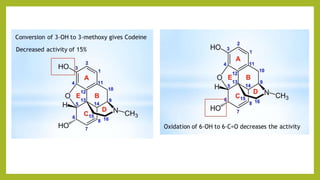
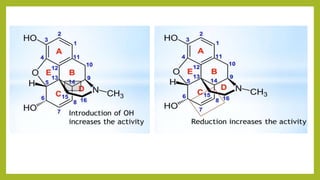
This document discusses the structural elucidation and stereochemistry of ephedrine and morphine. It provides background on the history and traditional uses of ephedrine. The chemistry, extraction process, and mechanism of action of ephedrine are described. The structural elucidation of ephedrine is explained through determination of molecular formula, identification of functional groups, and degradation studies. Similarly, the structural elucidation of morphine is summarized through identification of molecular formula, detection of unsaturation, identification of functional groups, and degradation studies to reveal the phenanthrene ring structure.