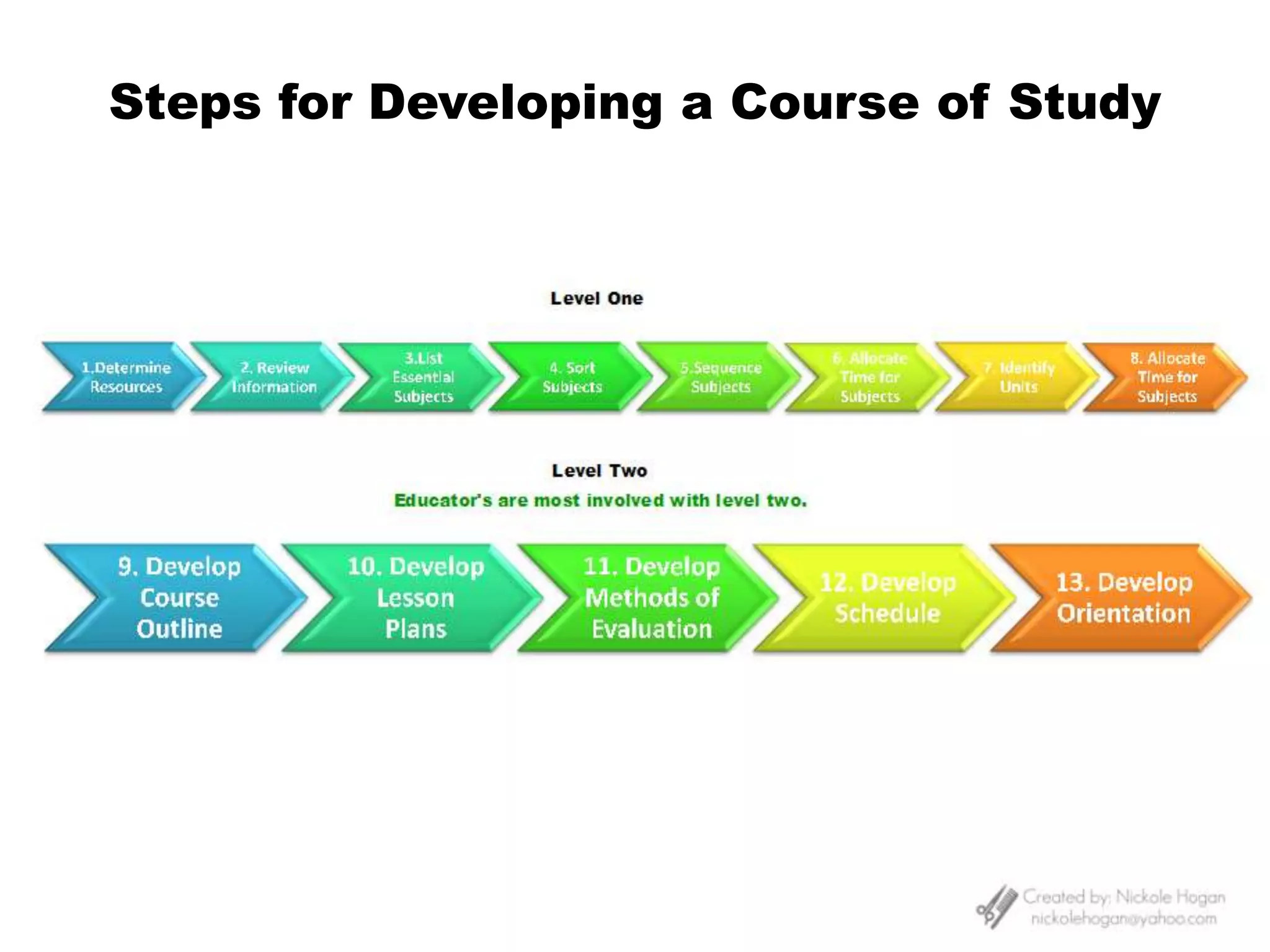
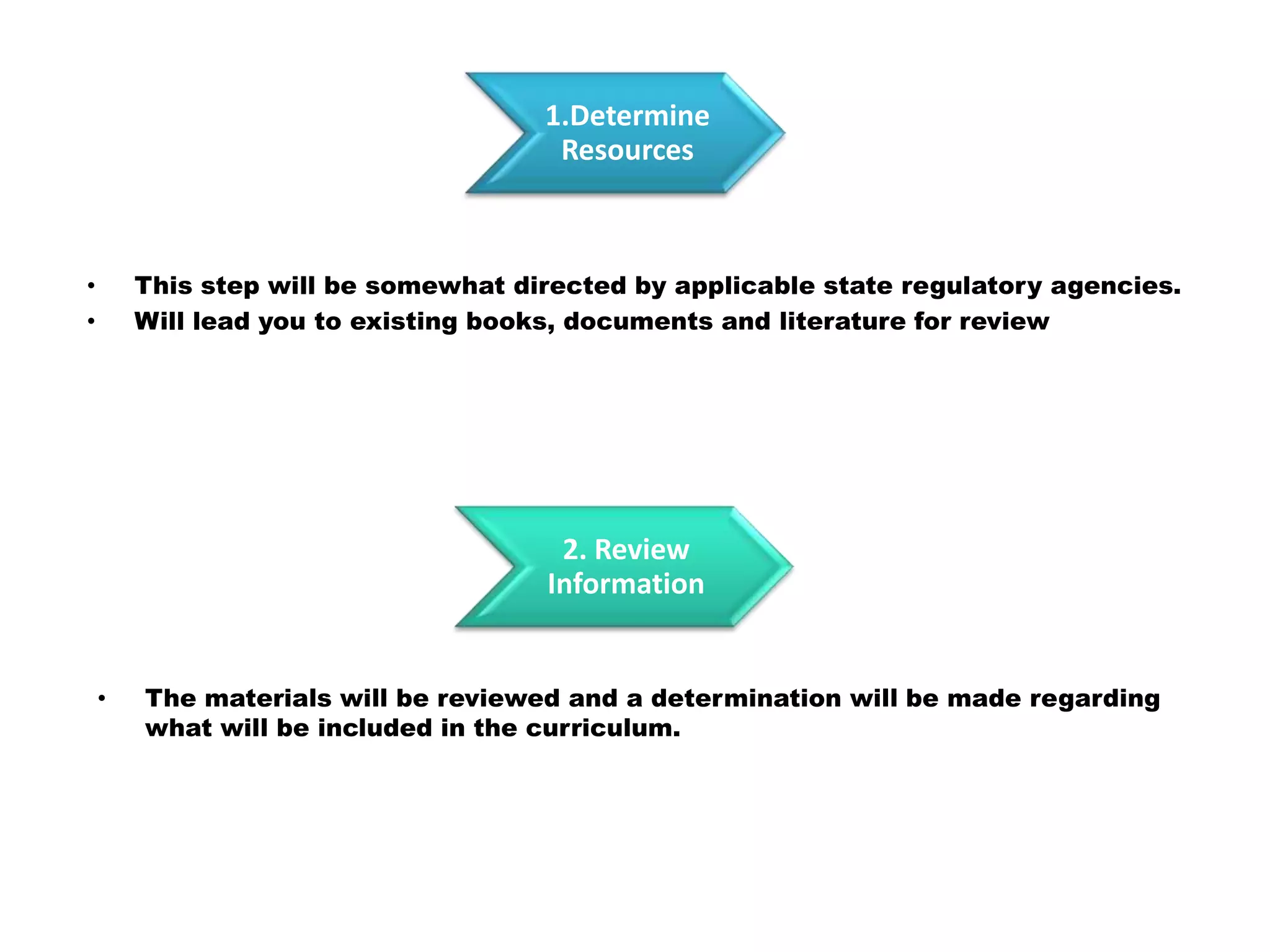
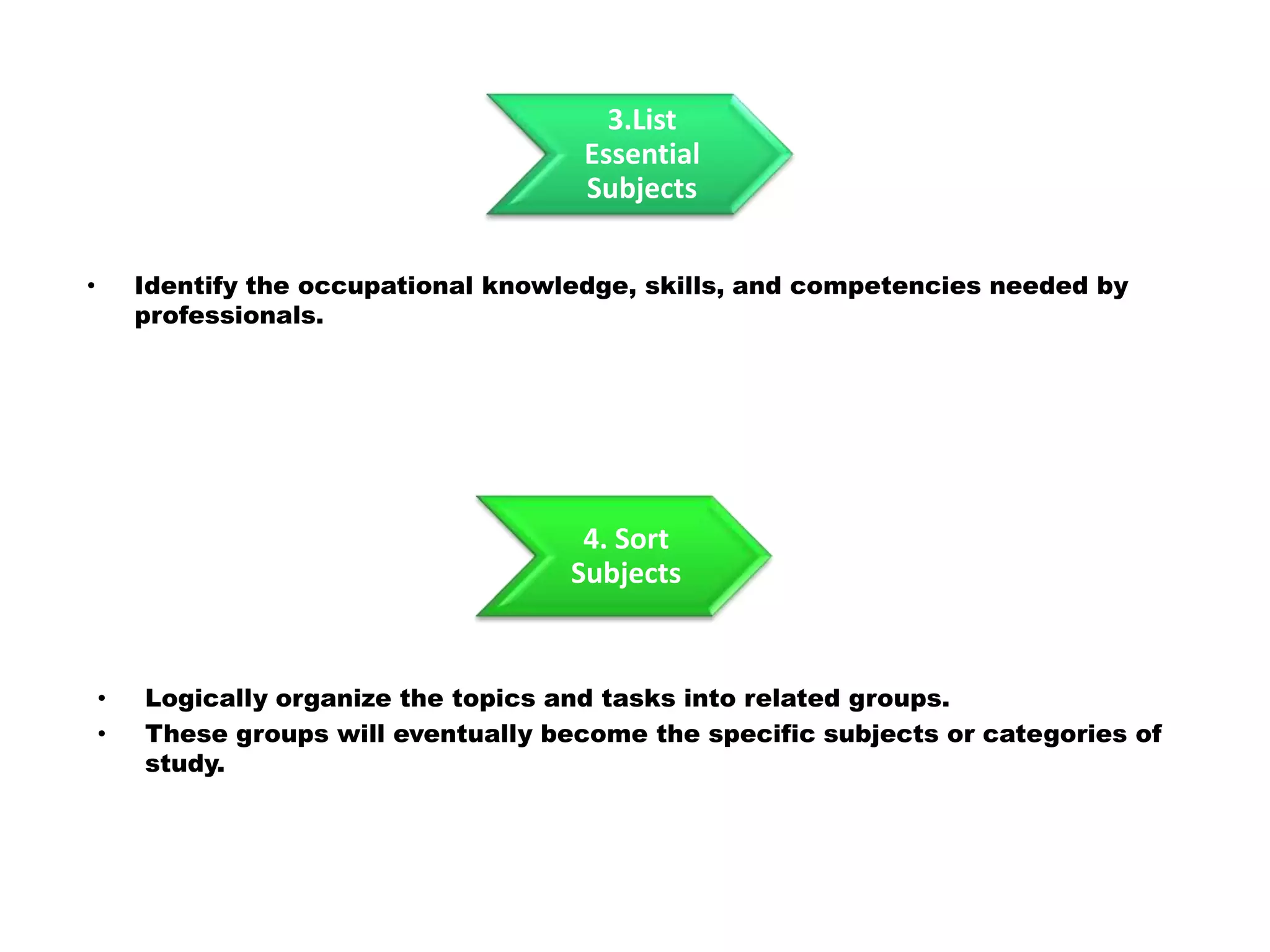
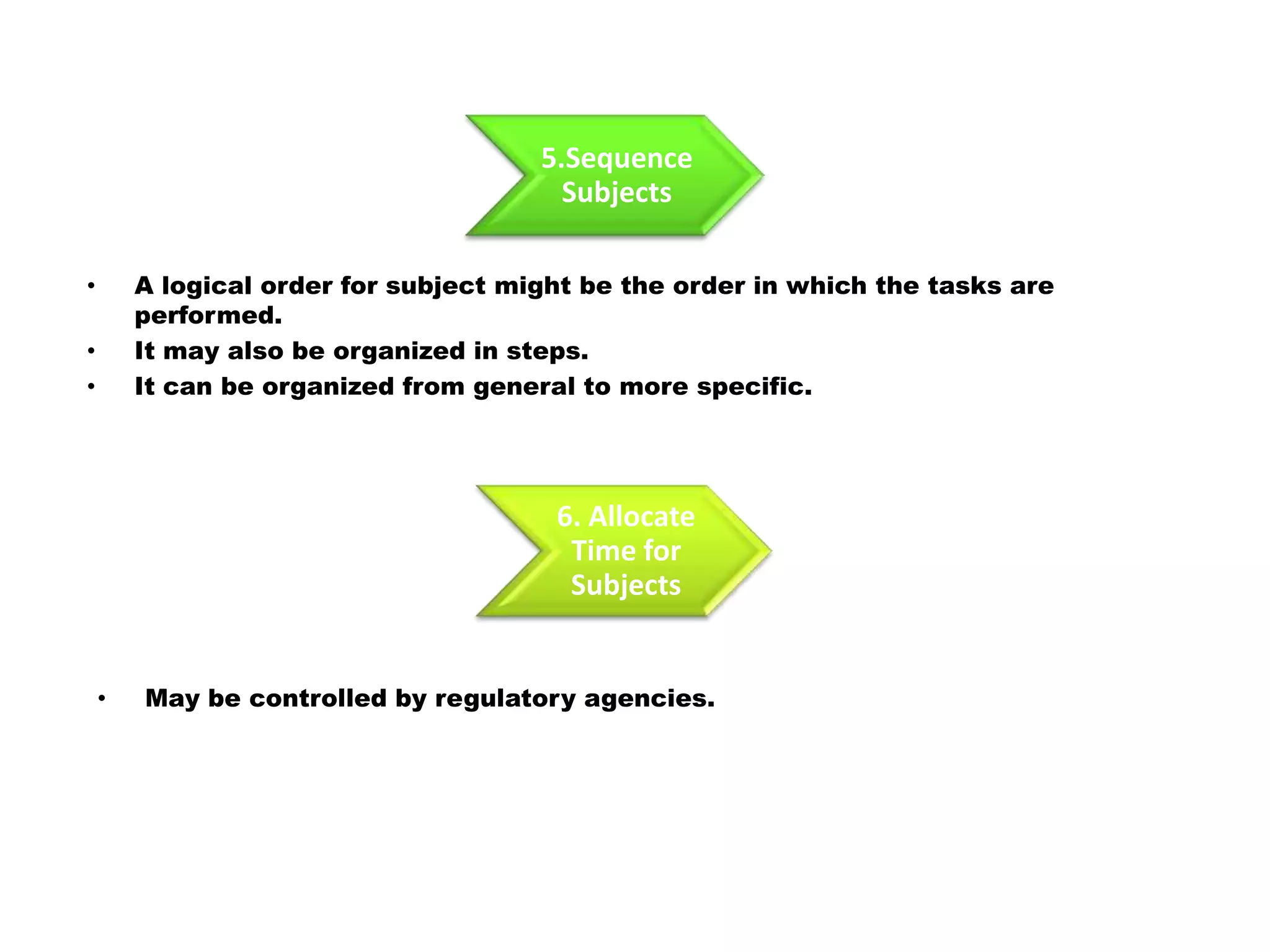
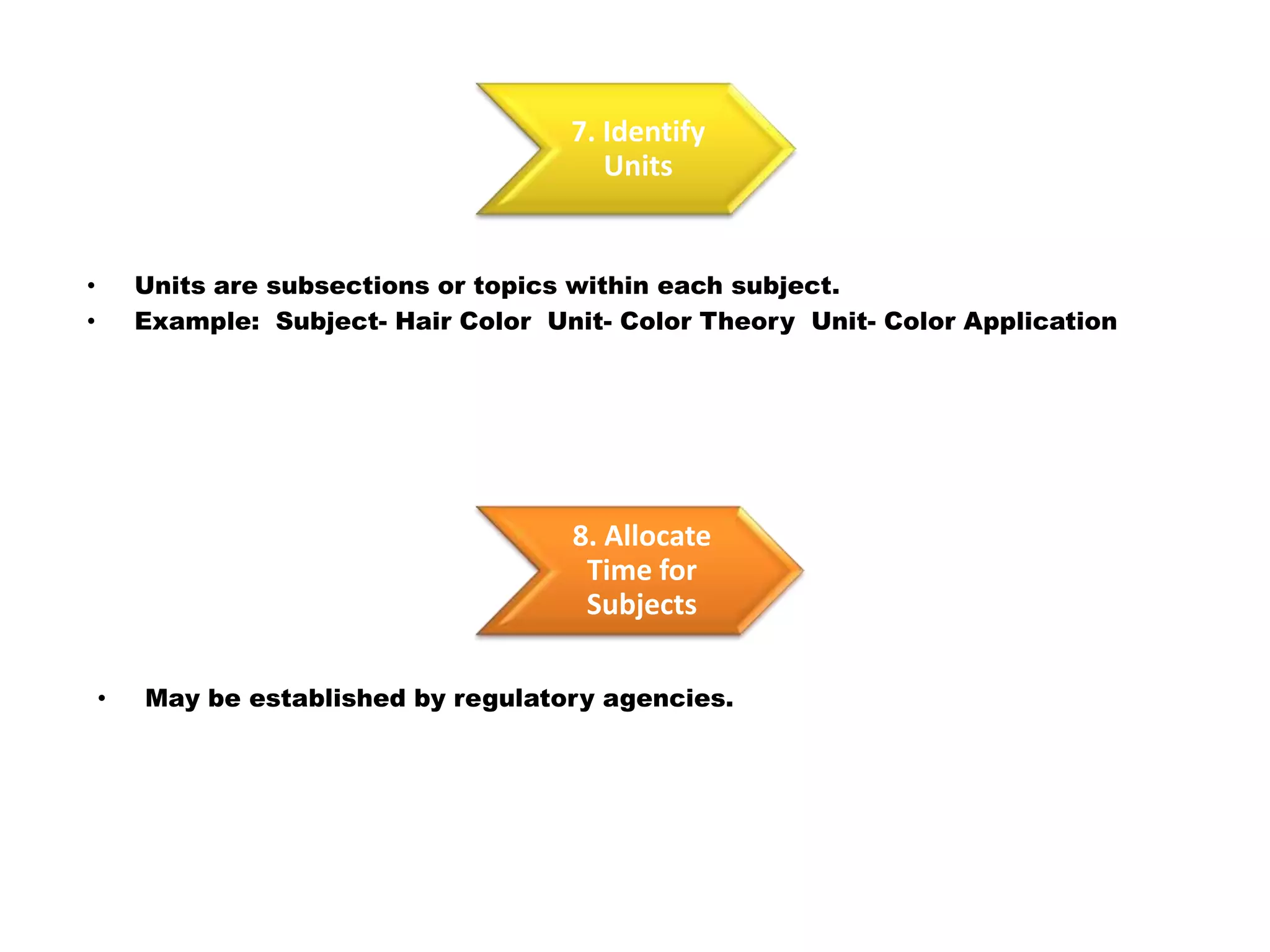
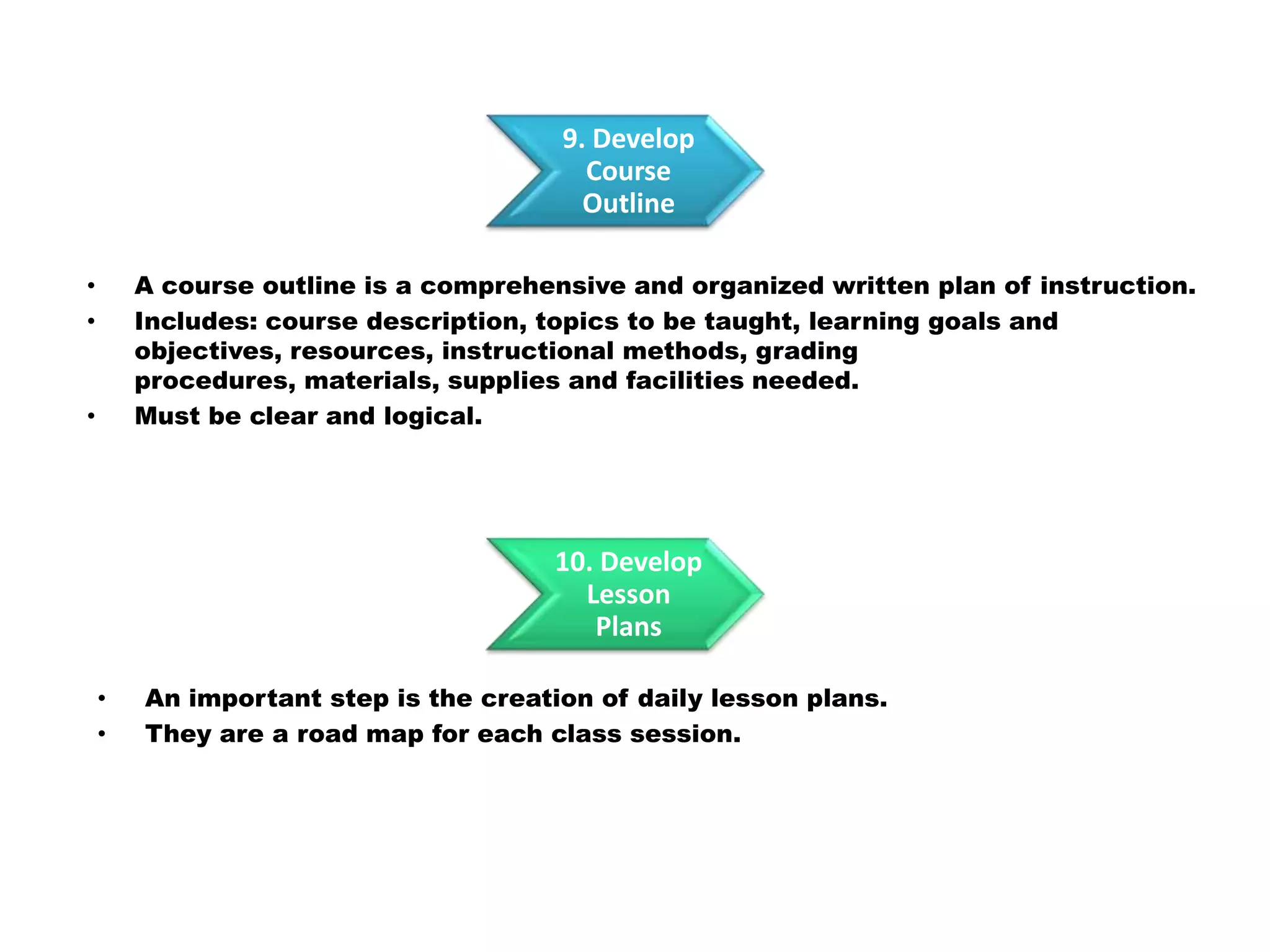
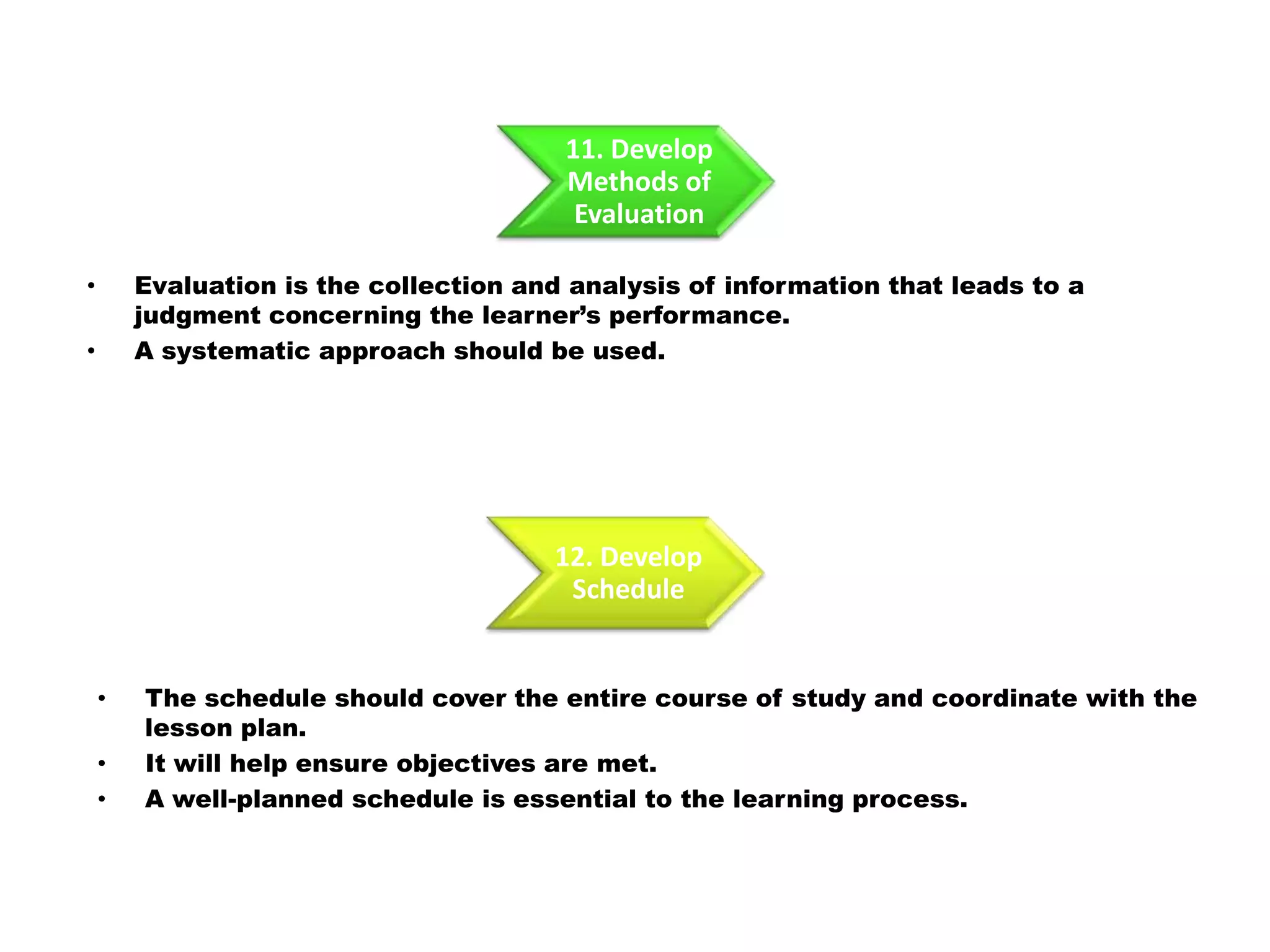
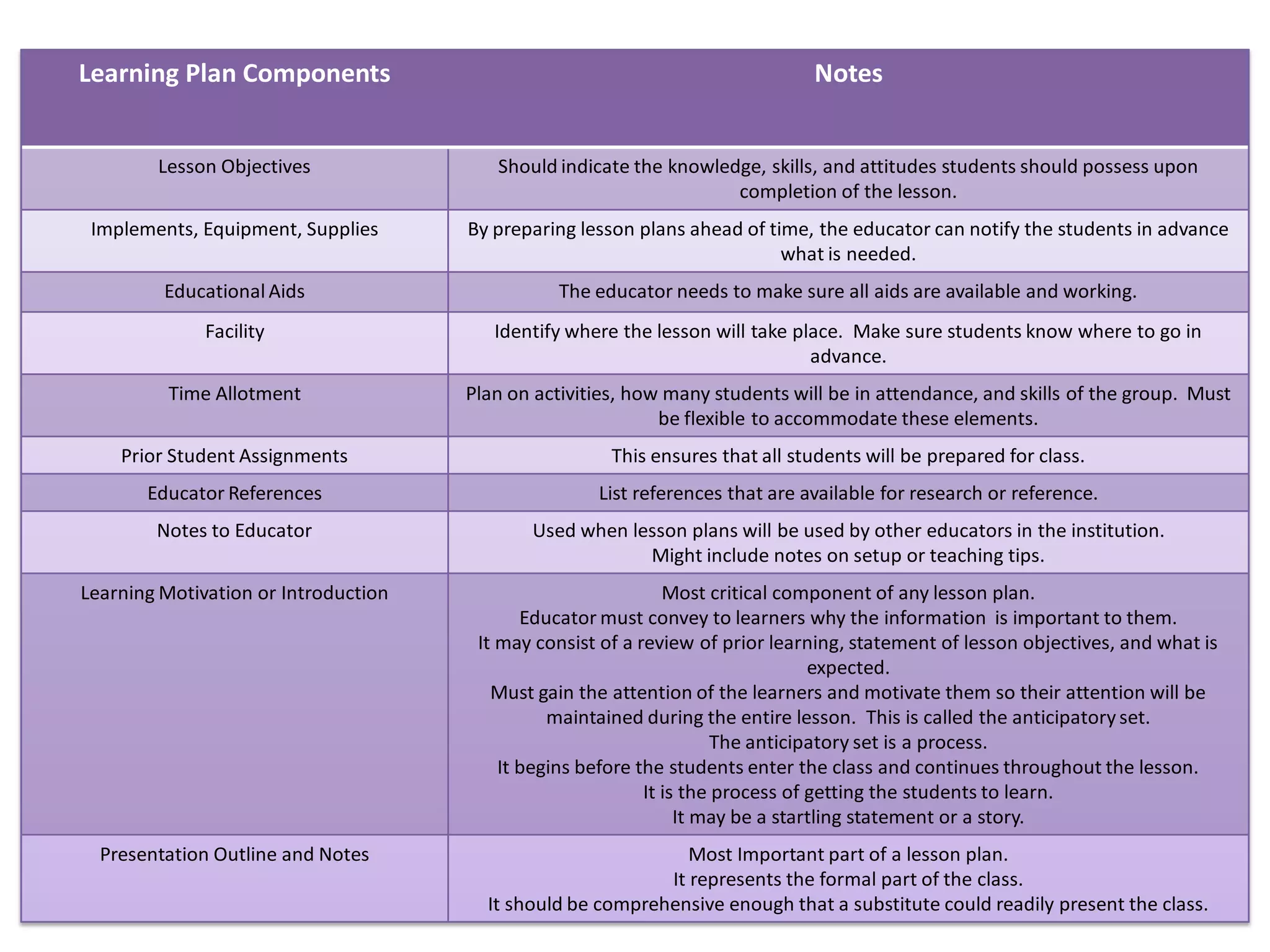
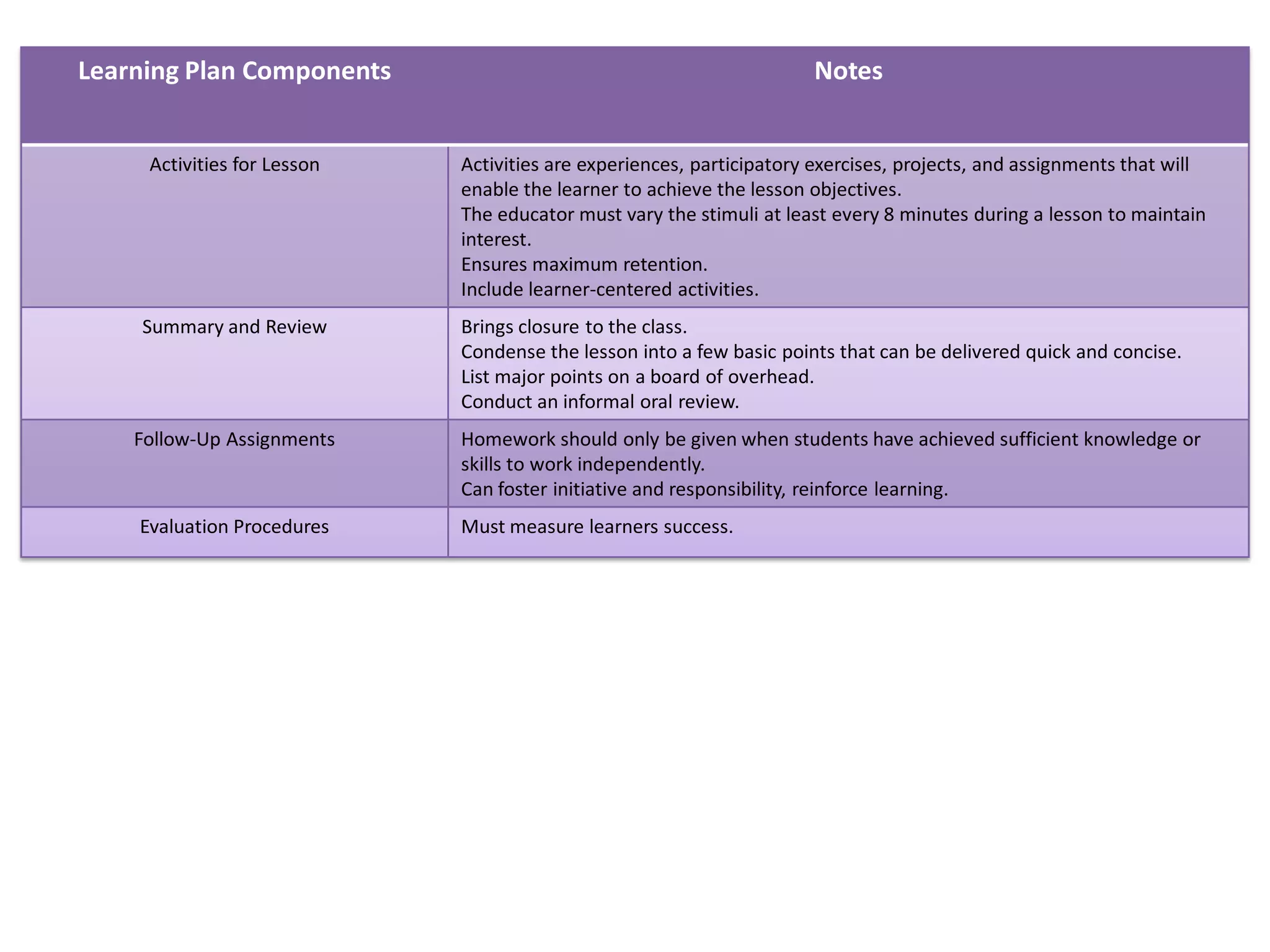
Here is a draft lesson plan on hair coloring techniques:
Course Title: Cosmetology
Subject: Hair Coloring
Topic: Basic Hair Coloring Techniques
Objectives:
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
1. Identify the different types of hair color and their effects
2. Demonstrate proper hair sectioning and application techniques
3. Explain the importance of a patch test and consultation
Teaching Aids:
- PowerPoint presentation on hair color theory
- Video on proper hair sectioning
- Mannequin heads
- Color swatches
- Gloves, towels, bowls
- Developer and various hair color