The document provides guidance for educators on organizing their classroom and teaching plans. It emphasizes the importance of preparation, understanding students, and creating a positive learning environment. Key points include:
1) Educators should focus on organization, preparation, and creating a dynamic learning environment to facilitate student learning. This involves knowing the subject matter, identifying necessary materials, and setting the tone on the first day.
2) Understanding individual students through profiles and discussions helps tailor instruction and promote motivation. Student files must be kept private according to regulations.
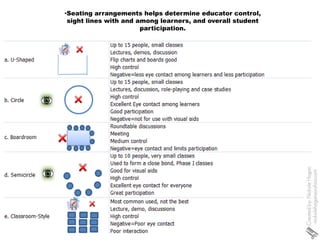
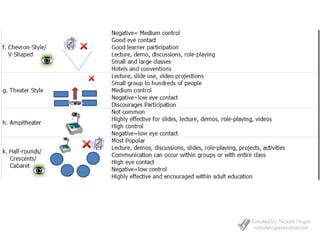
3) The physical classroom environment, seating, lighting, supplies and accessibility impact the learning experience. Color, bulletin boards and limiting distractions can make the room more engaging.