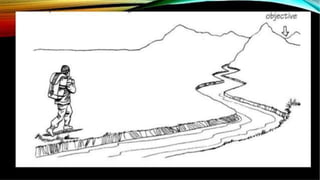
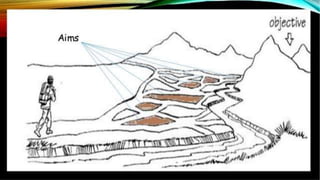
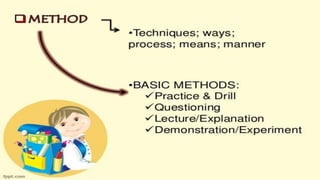
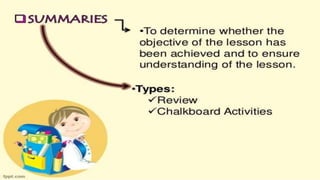
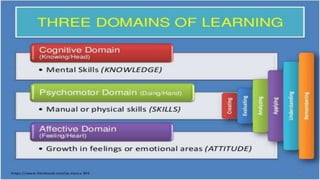
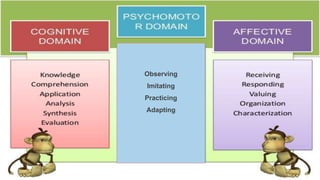
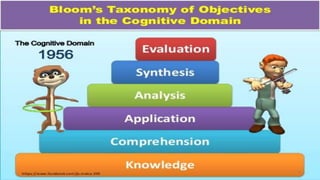
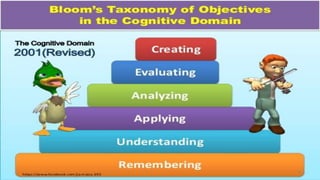
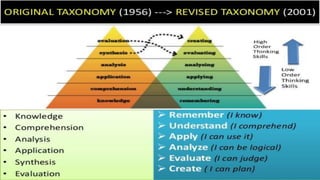
This document discusses the importance of planning for instruction. It defines planning as what the teacher prepares for presenting a lesson in class. Effective teaching depends on effective lesson planning, which is more difficult than delivering instruction. There are several steps and components to planning a lesson, including setting goals, designing a unit plan, and designing a lesson plan. A unit plan contains multiple related lessons while a lesson plan maps out the teacher's intentions for a single lesson. Both include elements like objectives, procedures, and assessment. Proper planning is essential for effective teaching and student learning.