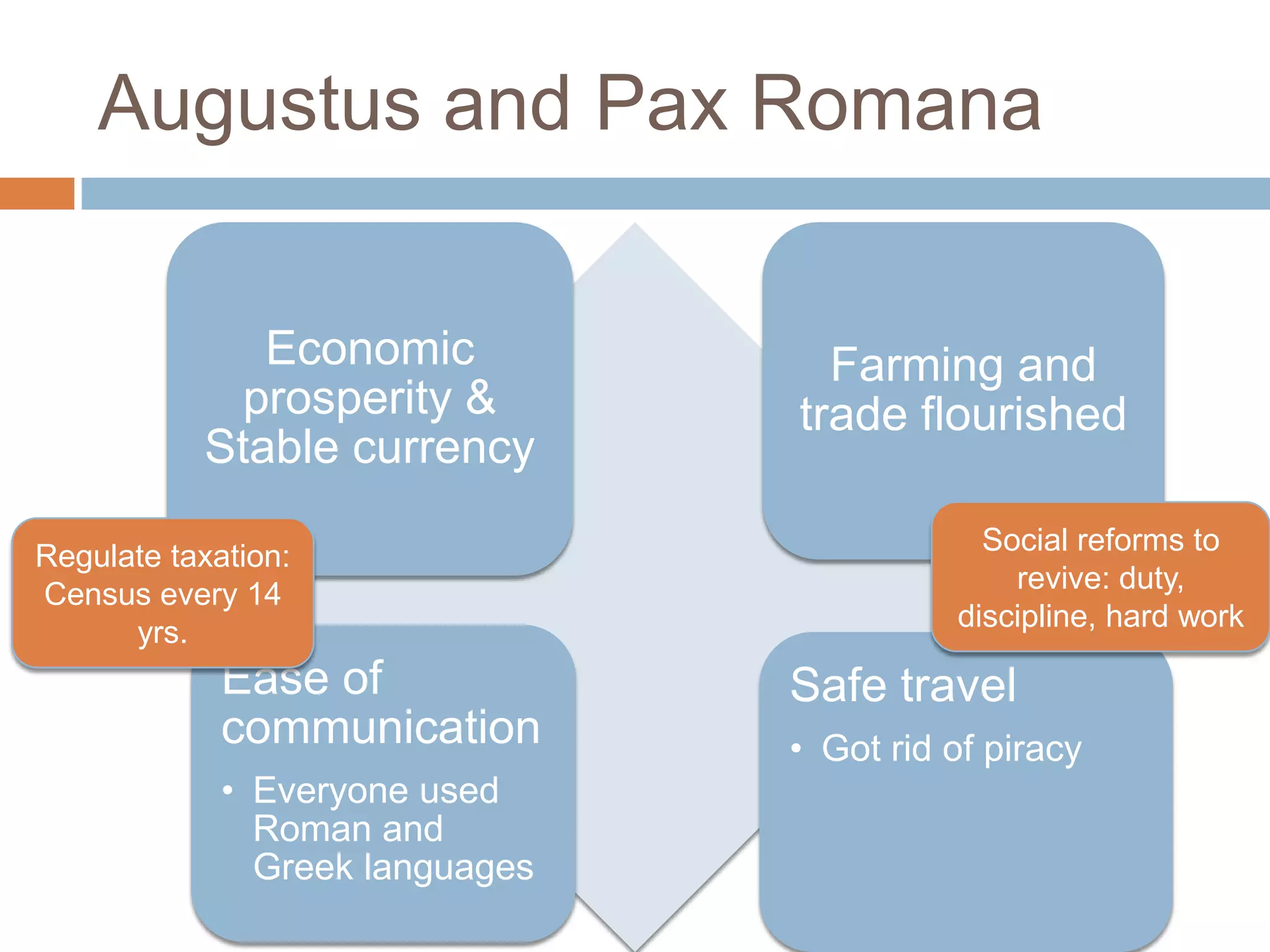
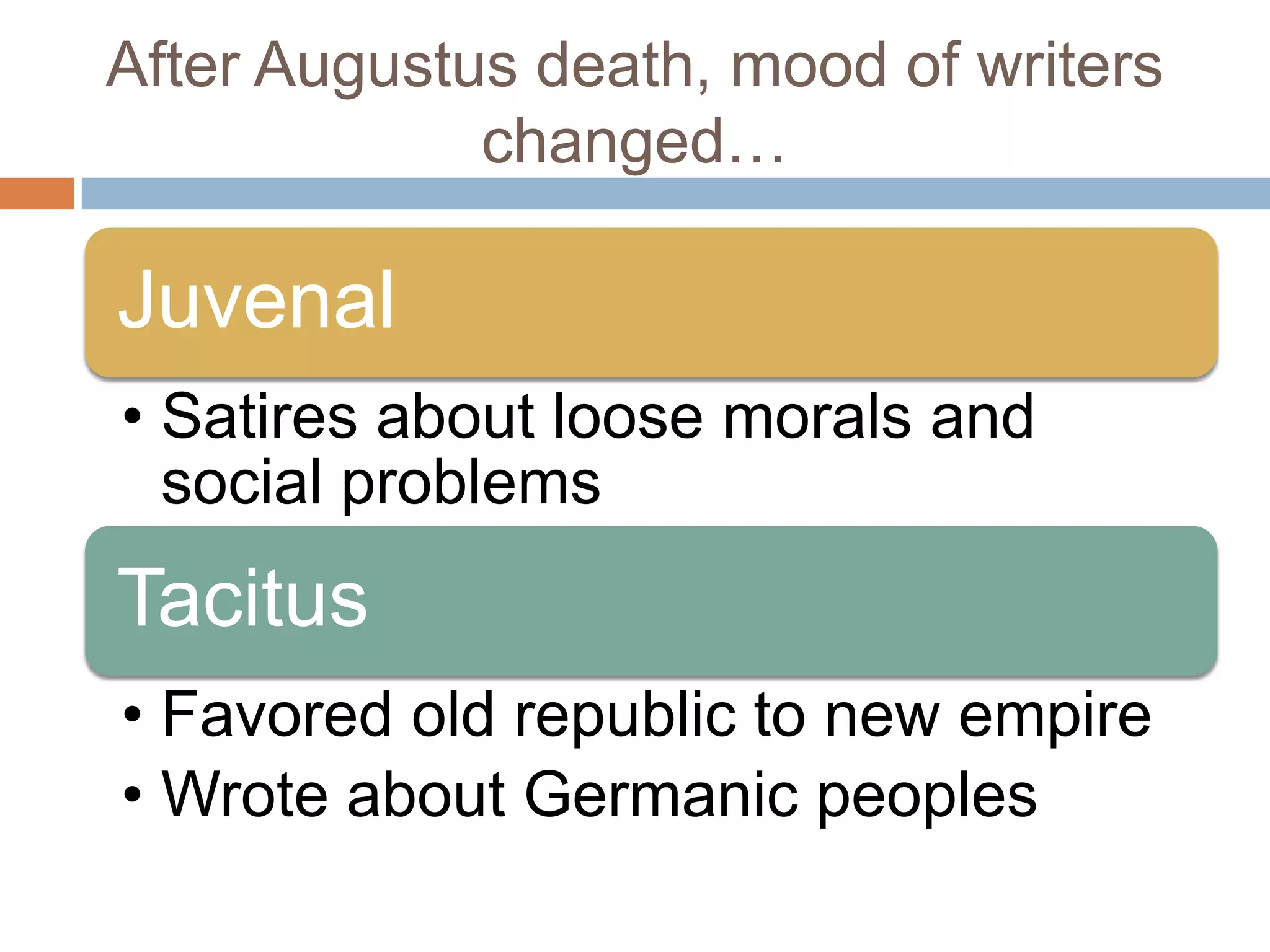
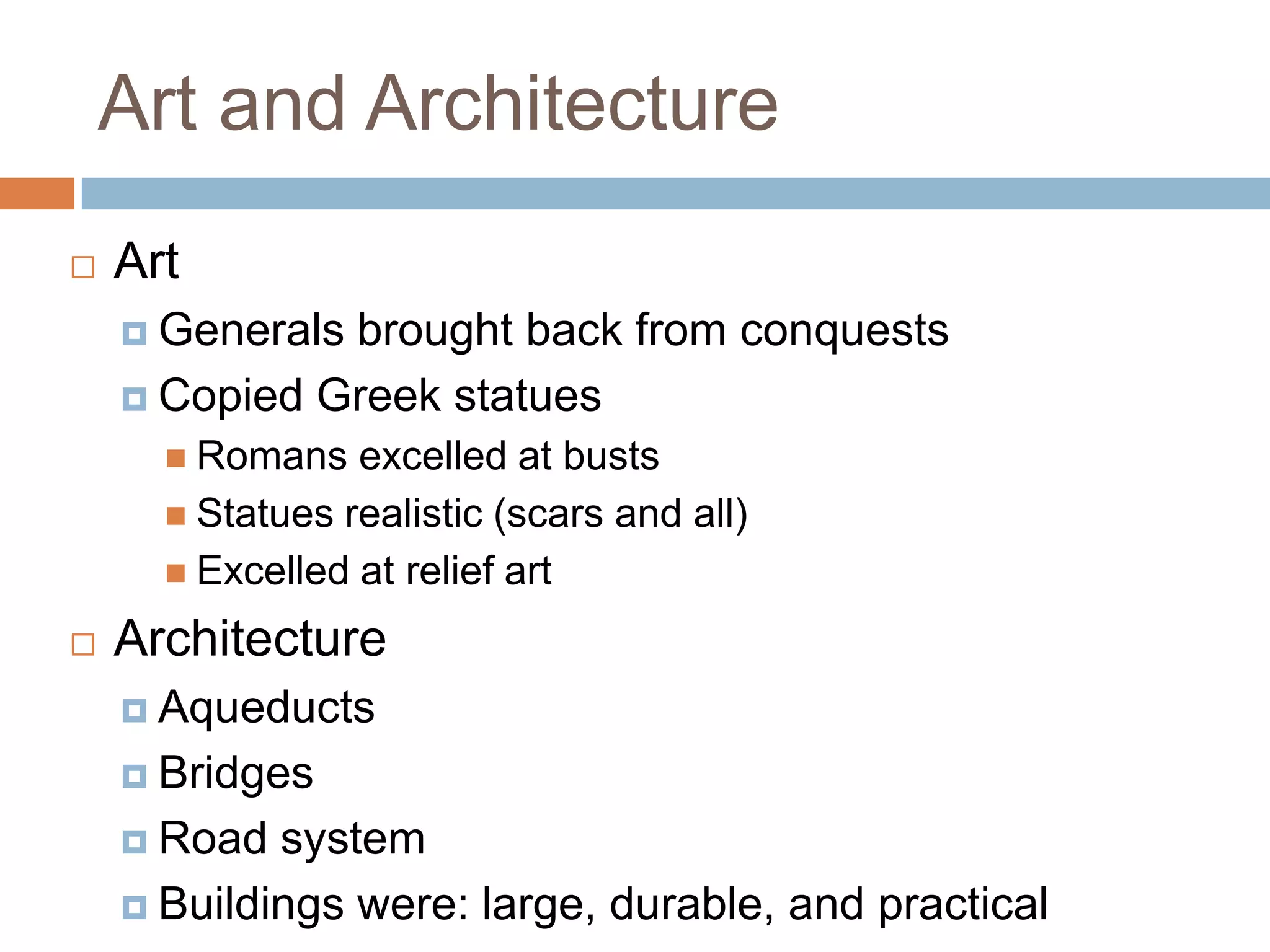
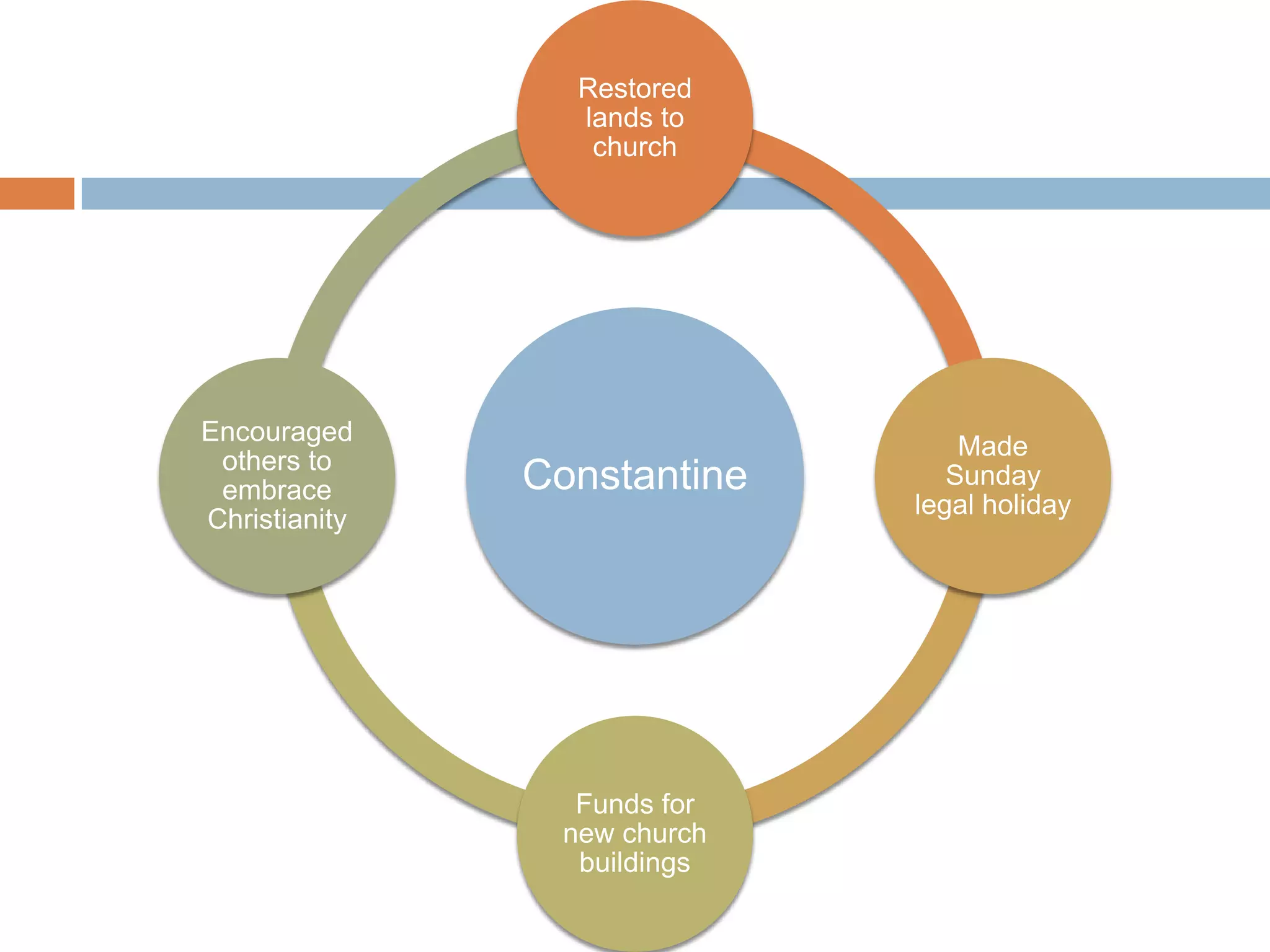
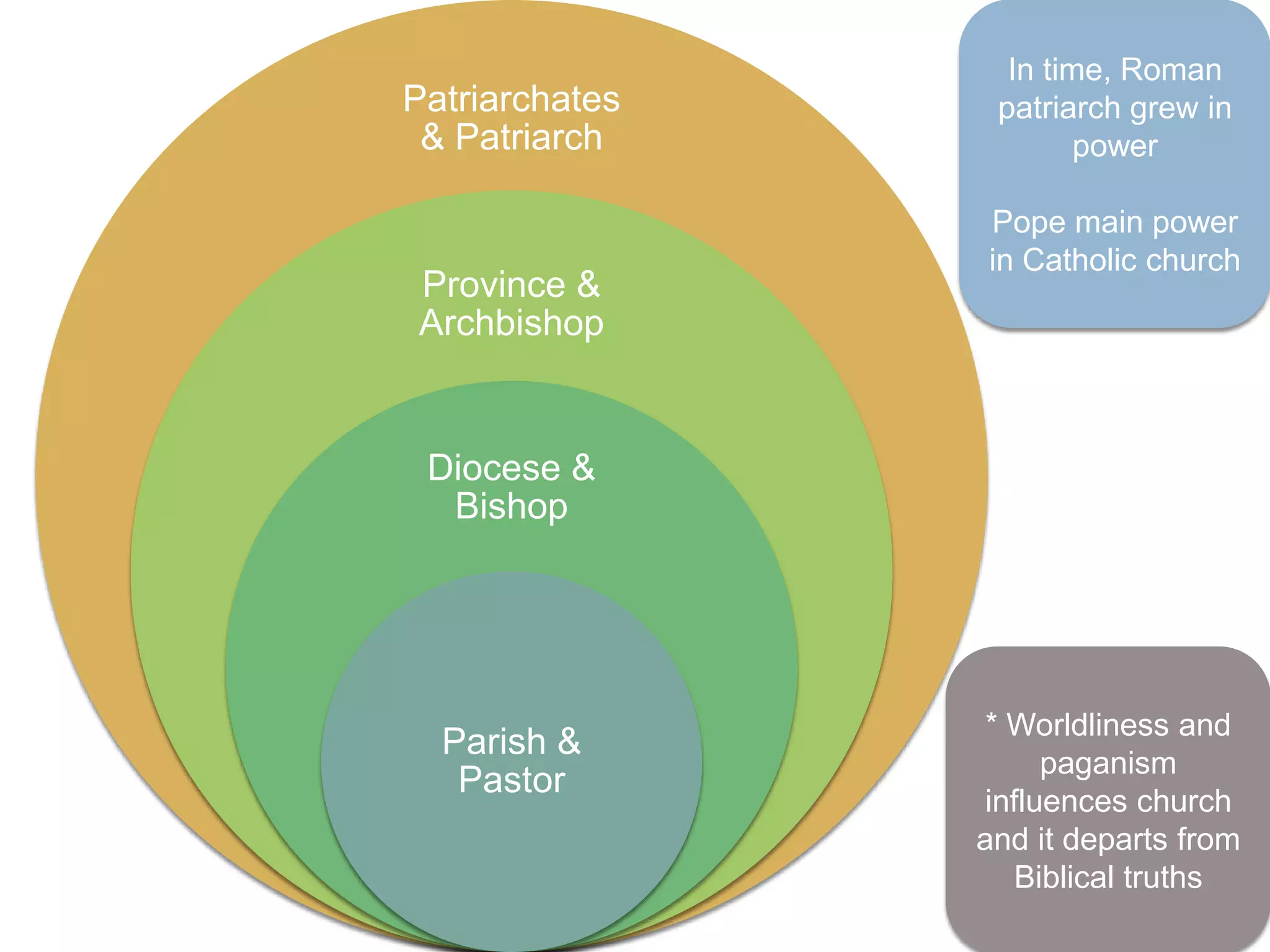
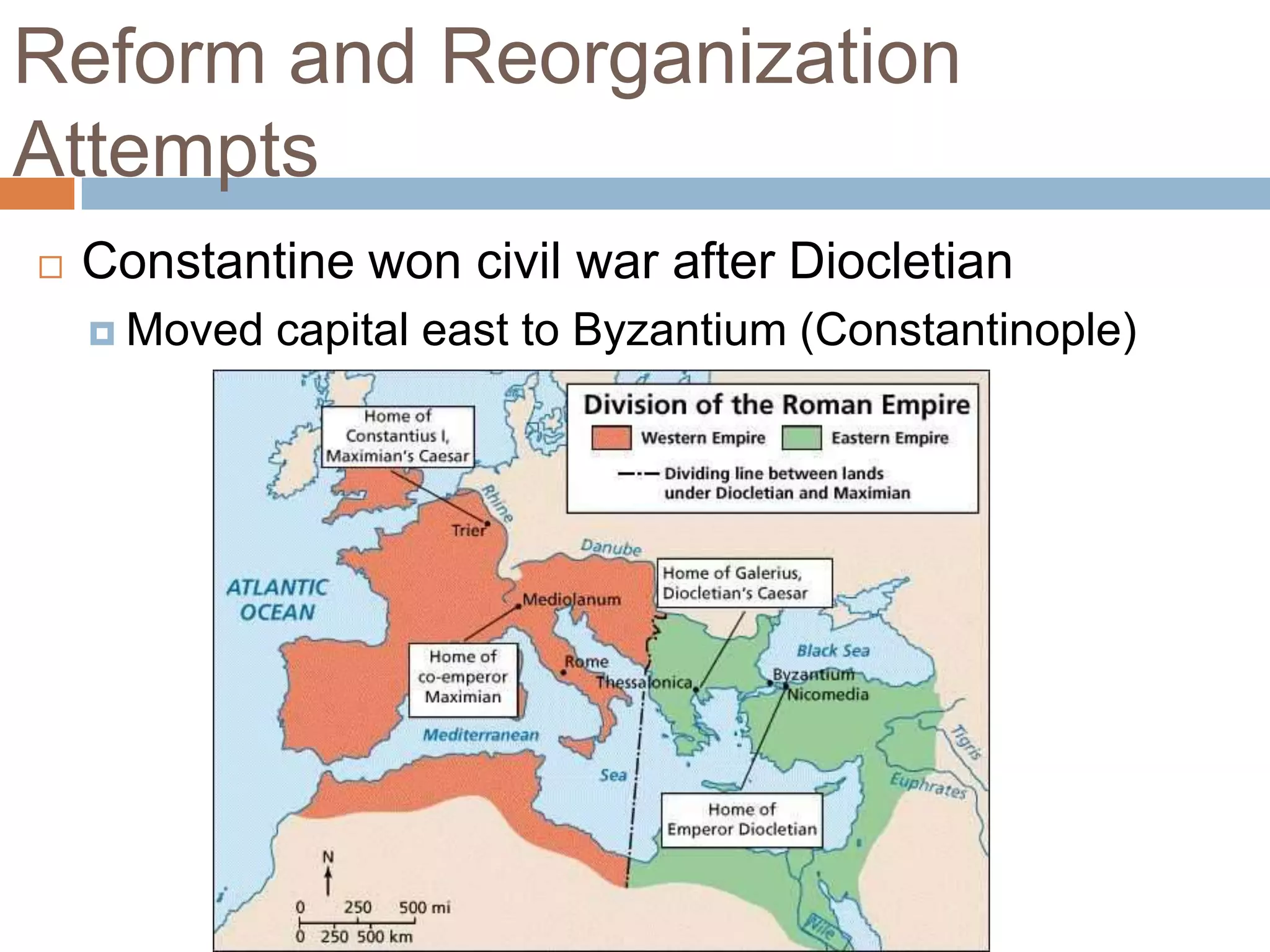
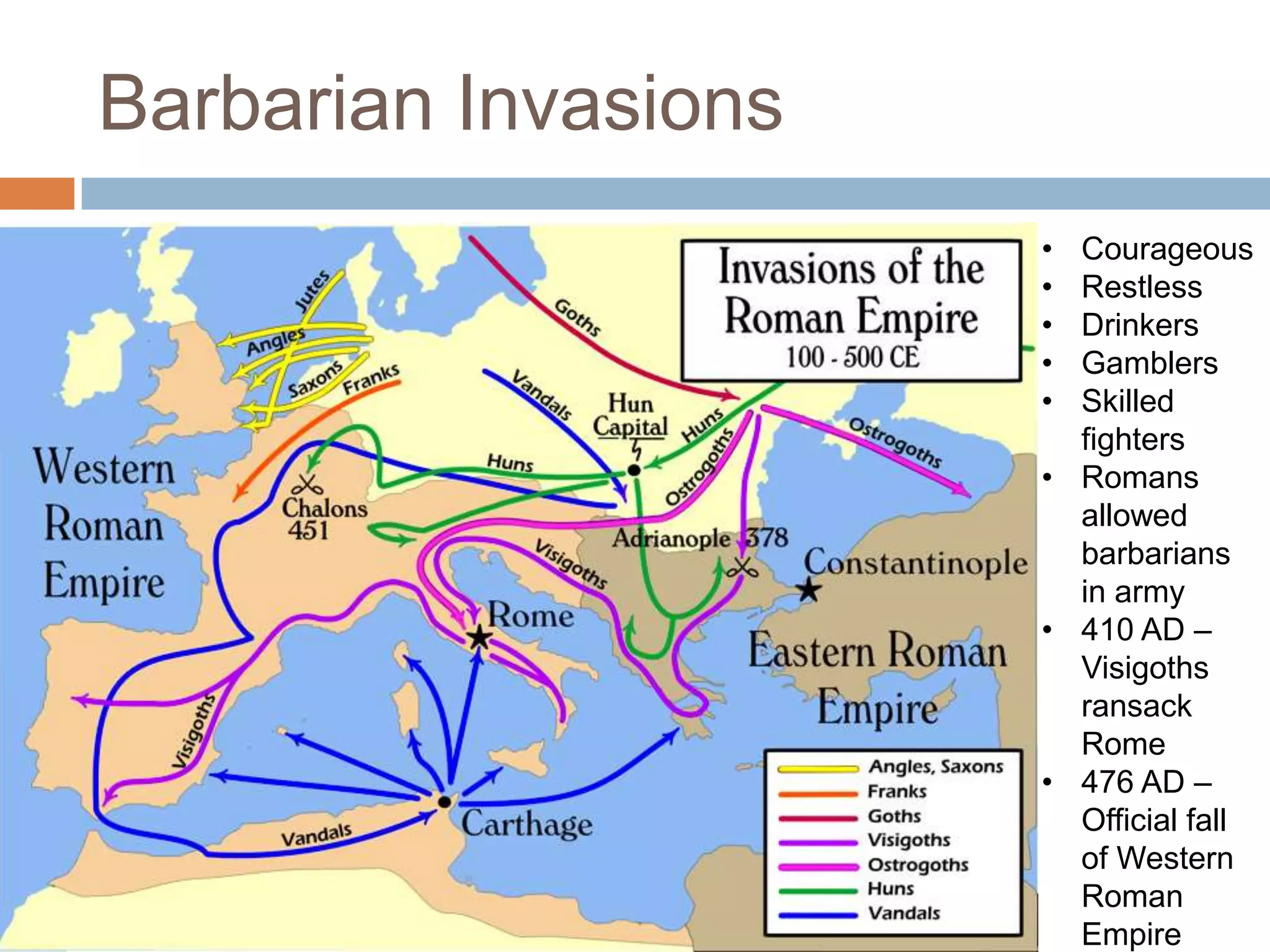
The Roman Empire reached its peak during the Pax Romana period when Jesus was born. The first emperor, Augustus, brought stability and prosperity by regulating taxation and encouraging farming and trade. However, moral decline and the costs of maintaining a large empire contributed to the collapse of Rome. Barbarian invasions and the sacking of Rome in 410 AD marked the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD.