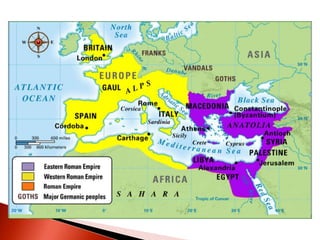
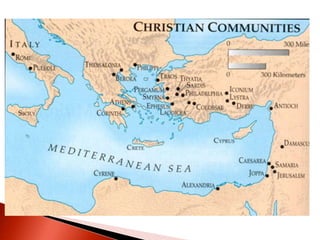
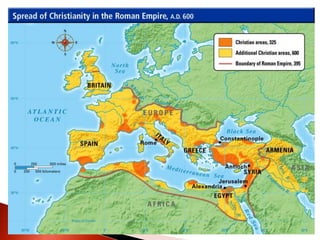
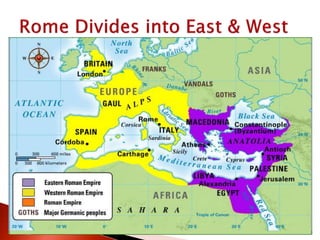
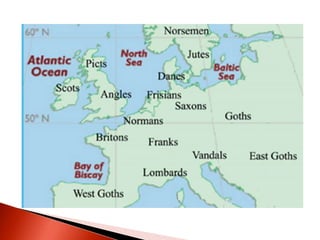
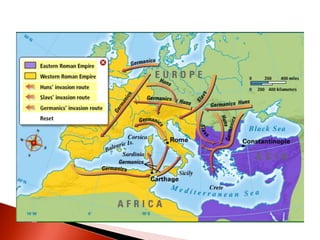
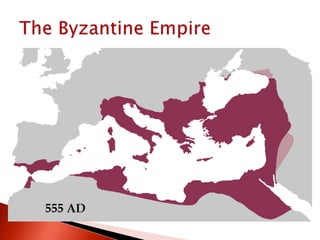
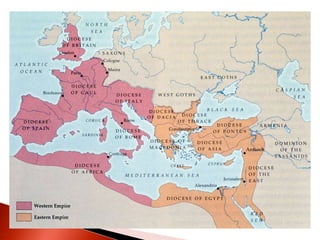
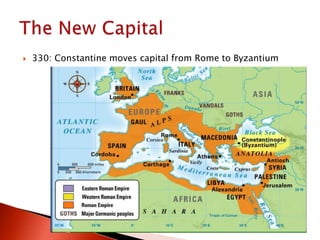
Rome initially persecuted Christians but later adopted Christianity as the official religion. Constantine legalized Christianity and the Edict of Milan made it one of the empire's legal religions. By 380, Christianity became the official religion of Rome. However, the Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476 due to military pressures and economic difficulties. The Eastern Roman Empire, based in Constantinople, lasted until 1453 and adopted Orthodox Christianity.