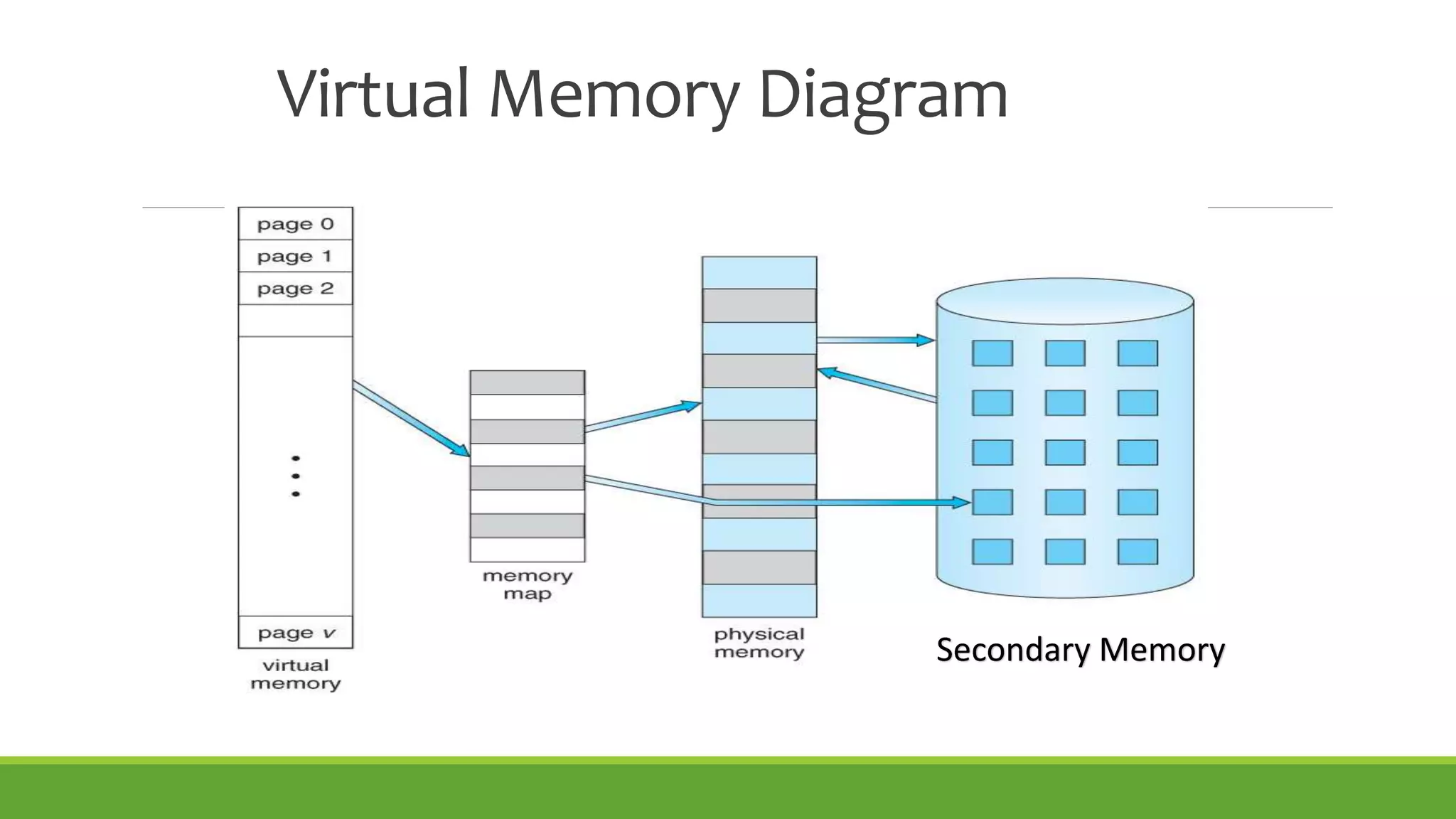
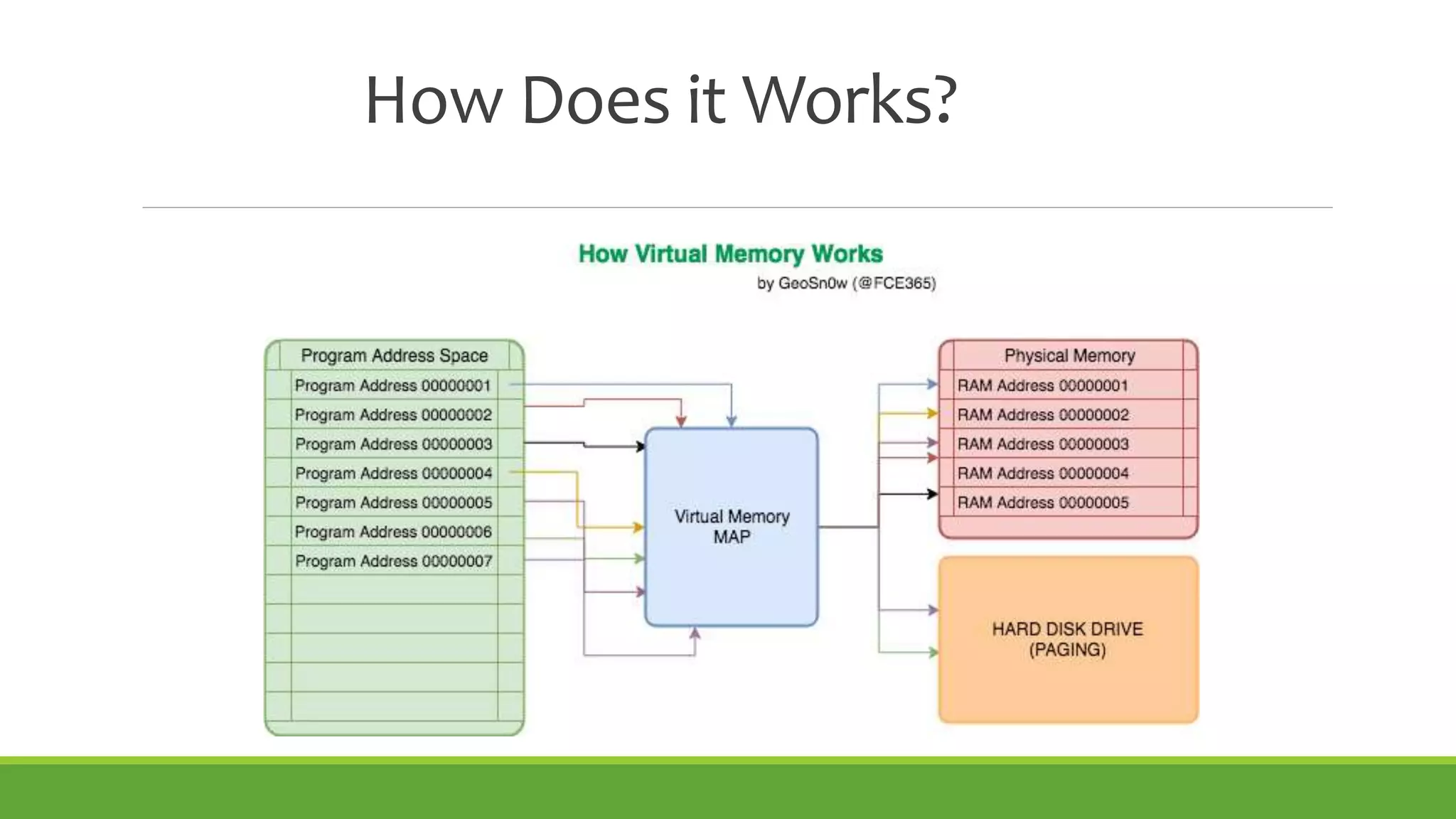
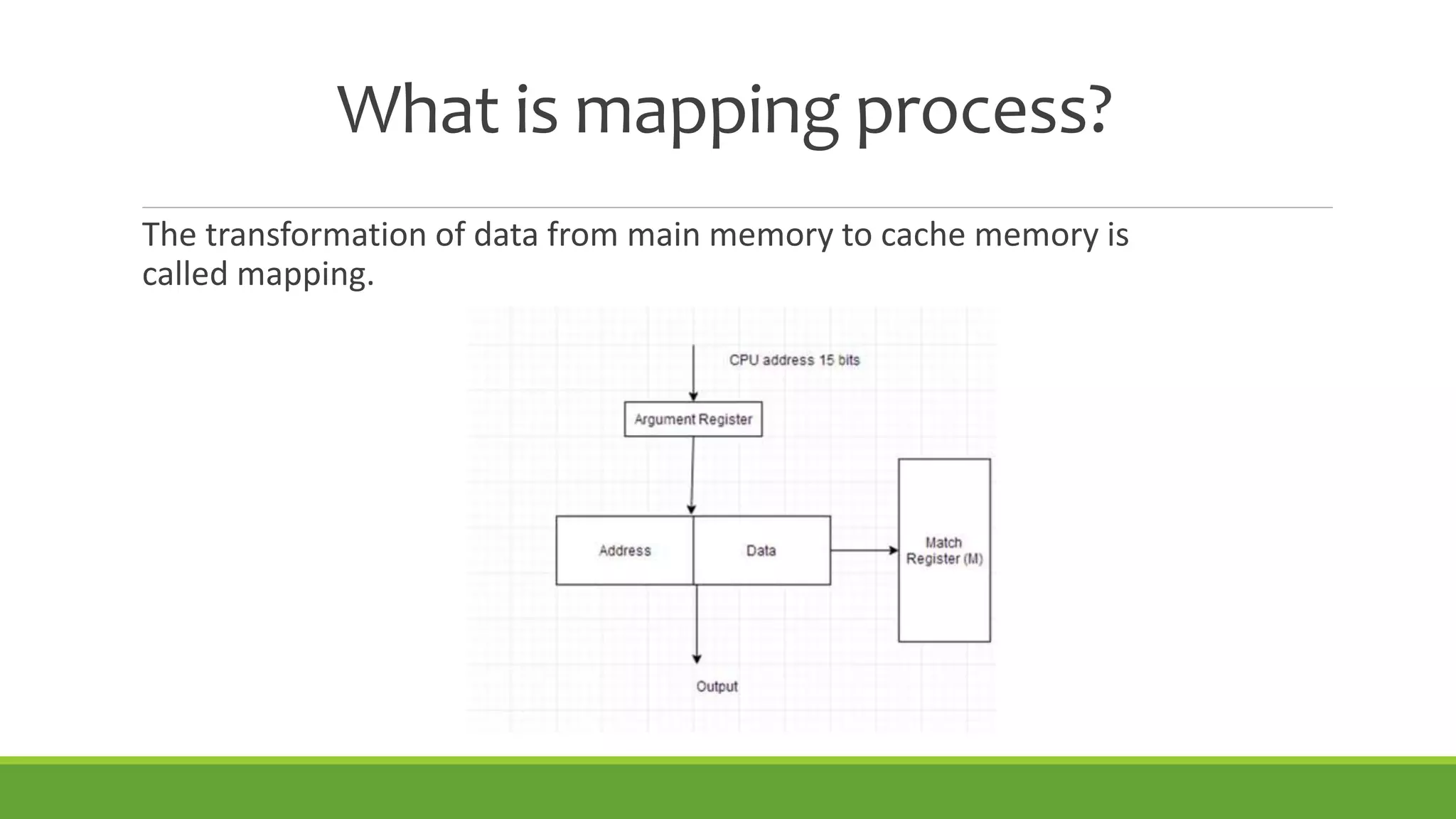
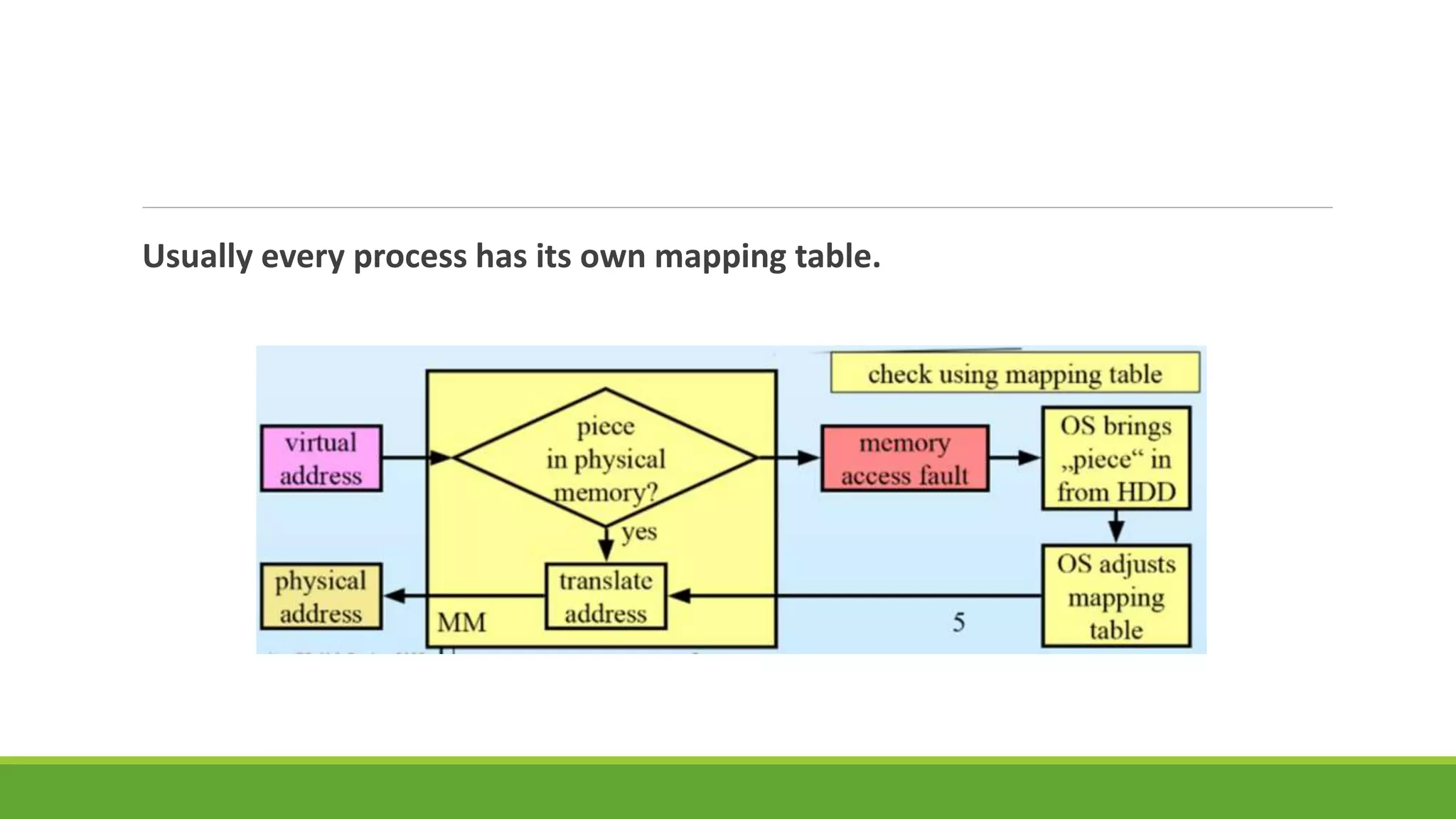
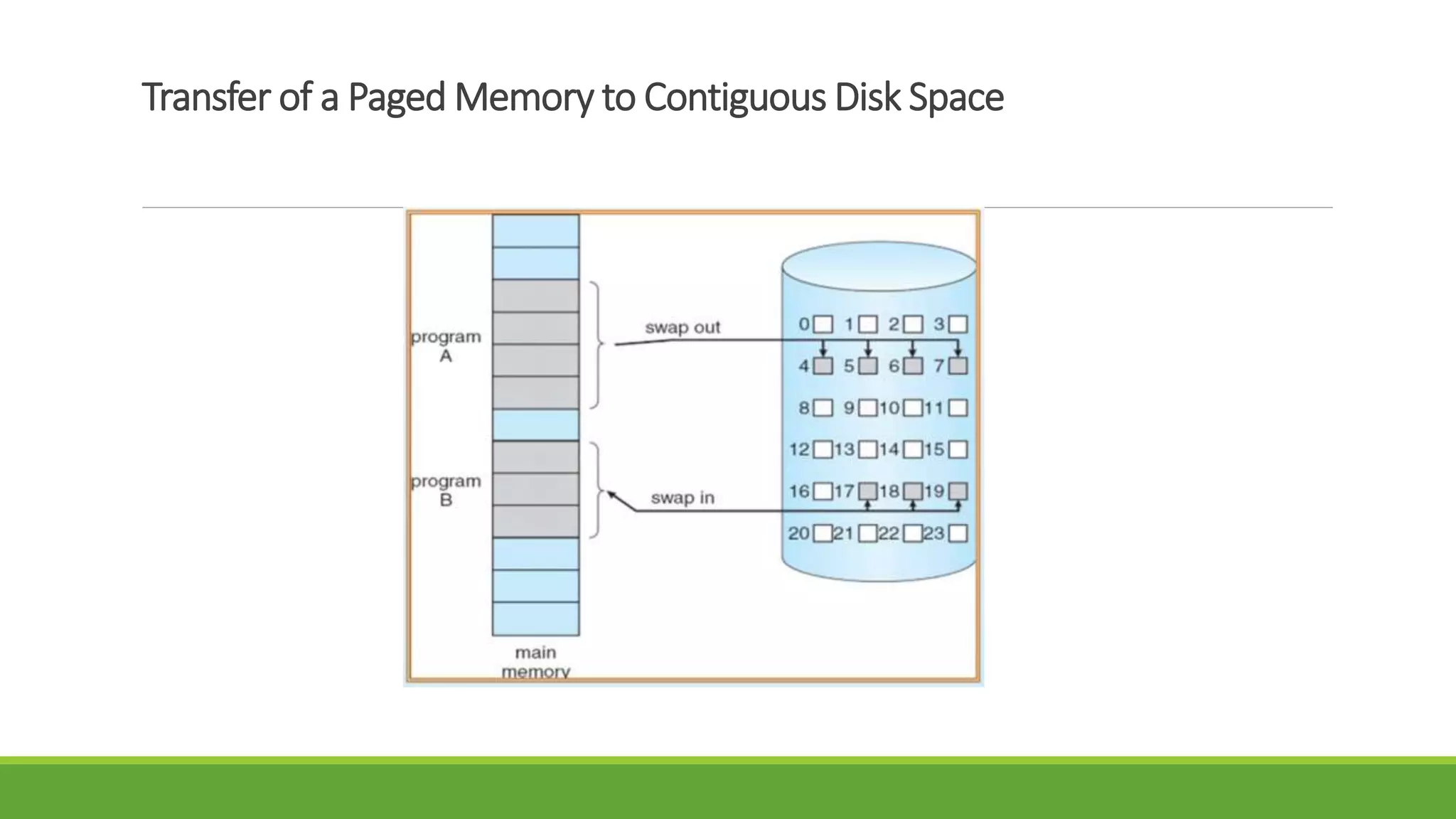
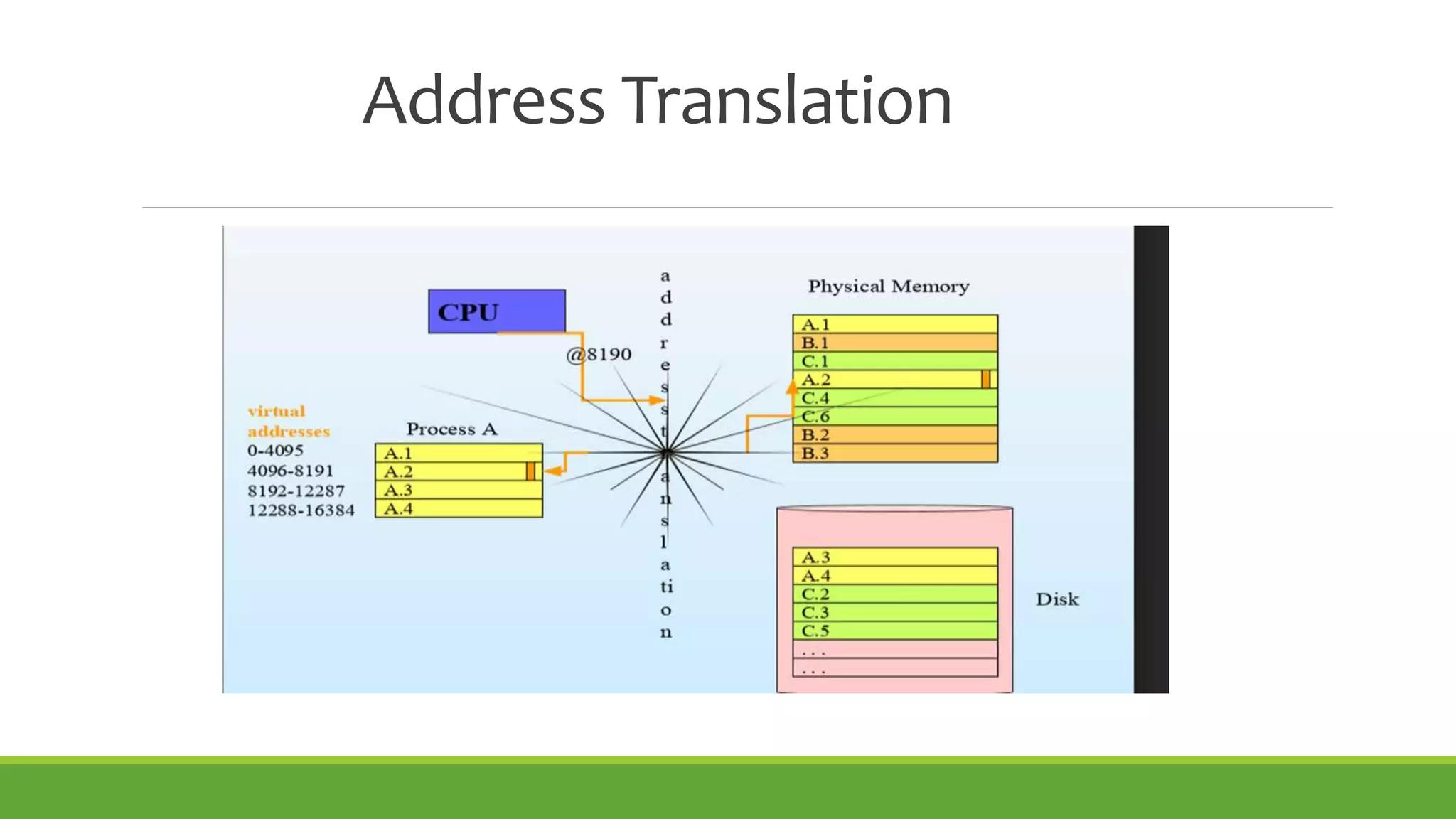
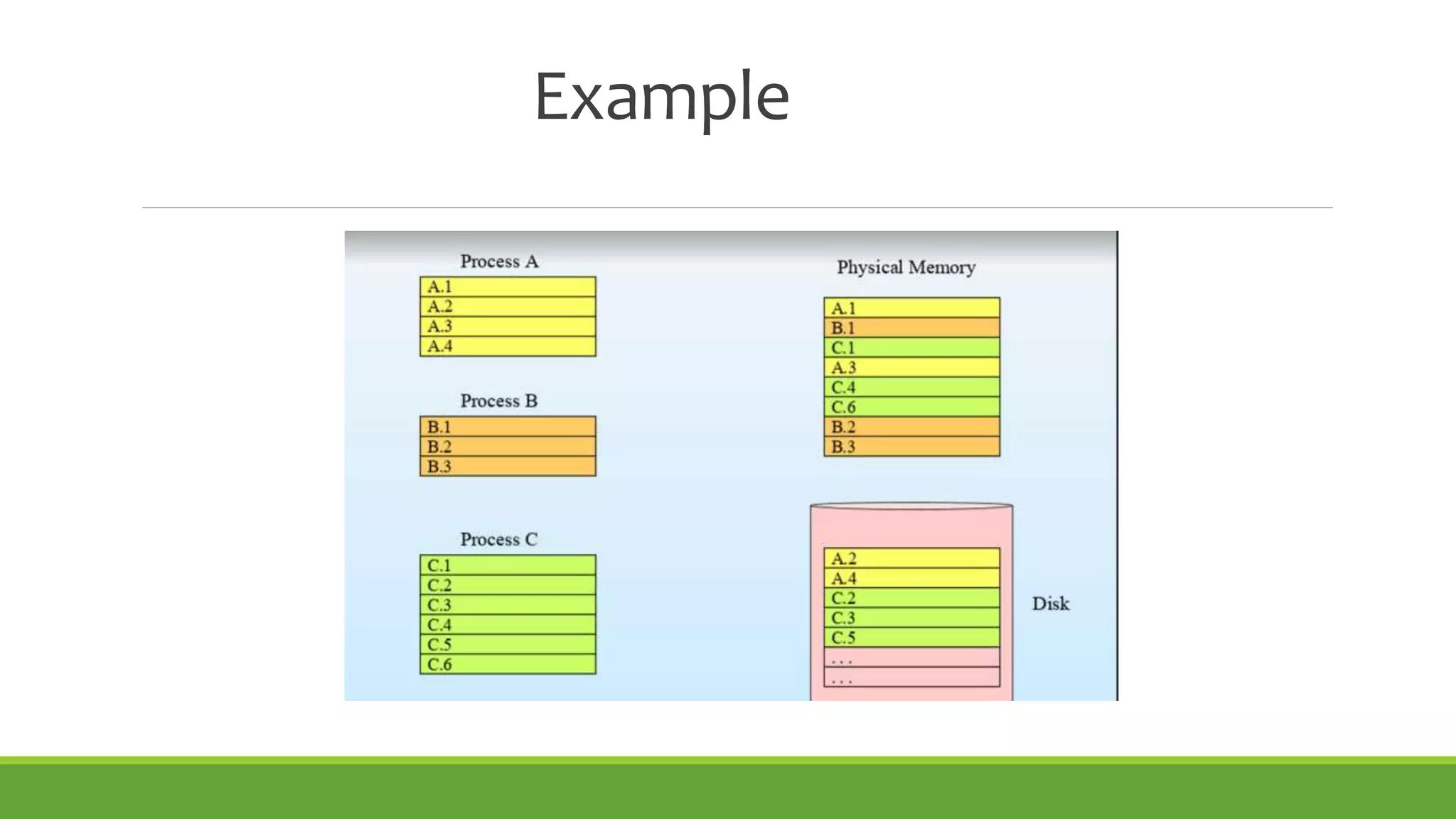
This document summarizes a presentation on virtual memory given by 5 students for their Computer Architecture and Organization course. It includes definitions of virtual memory, how it works using demand paging and segmentation, why it is used to support multitasking and large programs, the mapping and address translation processes, page tables, page size and faults, and advantages and disadvantages of virtual memory such as protection, sharing, and memory and performance overhead.