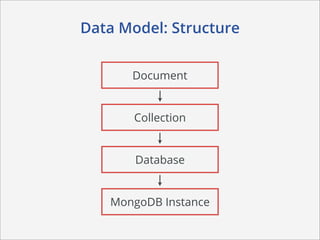
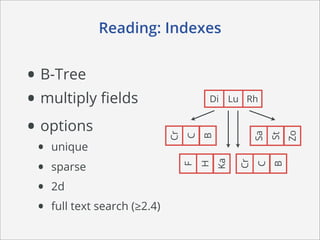
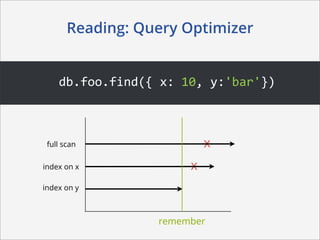
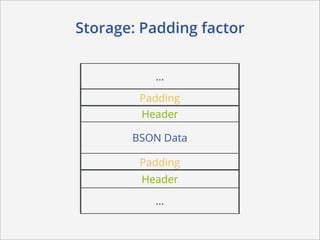
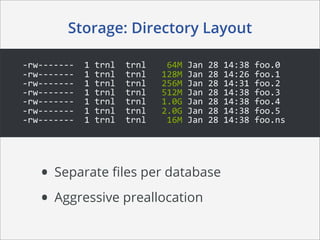
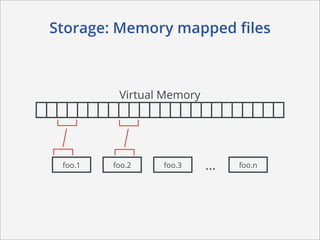
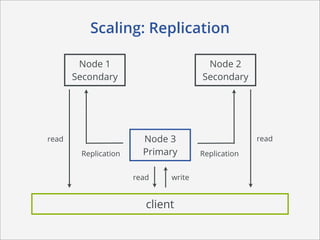
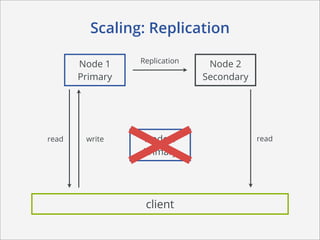
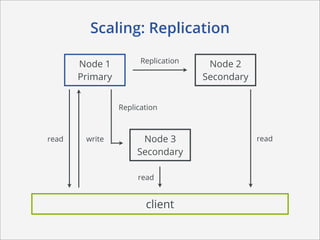
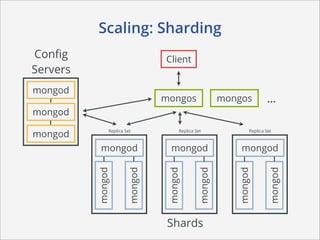
This document summarizes how MongoDB works. It discusses MongoDB's document-oriented data model using JSON-like documents and BSON format. It covers reading and querying data dynamically using conditions and projections, as well as indexing to optimize queries. Writing data with different write concerns for reliability is also summarized. Other sections discuss storage layout and memory mapping, as well as scaling MongoDB through replication and sharding across multiple nodes.

![Data Model: Document oriented
{
_id:
1,
name:
{
first:
'Michael',
last:
'Faraday'
},
birth:
new
Date('Sep
22,
1791'),
death:
new
Date('Aug
25,
1867'),
contribs:
['Chemistry',
'Electricity',
'Diamagnetism']
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howmongodbworks-130201054641-phpapp01/85/How-MongoDB-works-3-320.jpg)