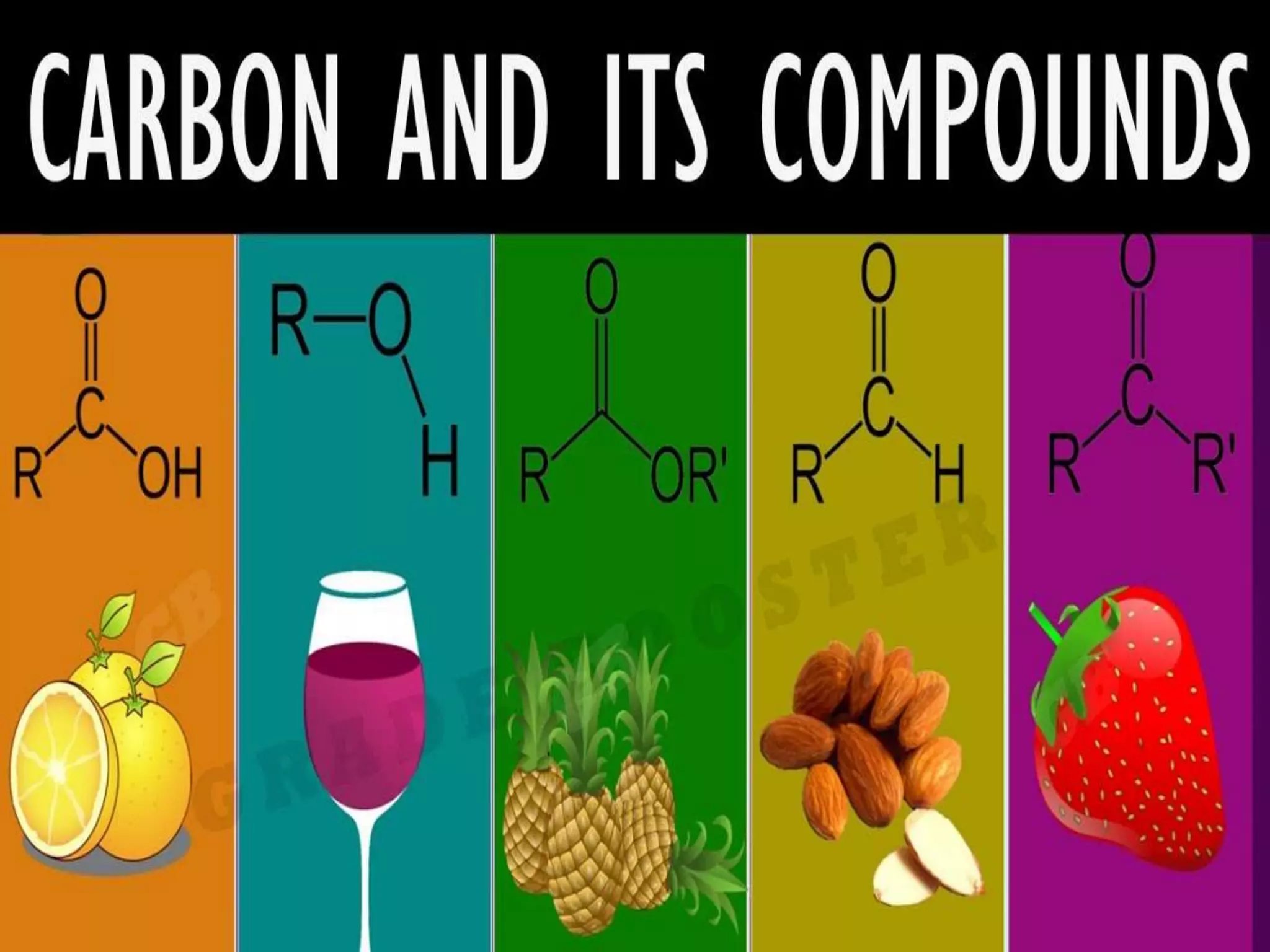
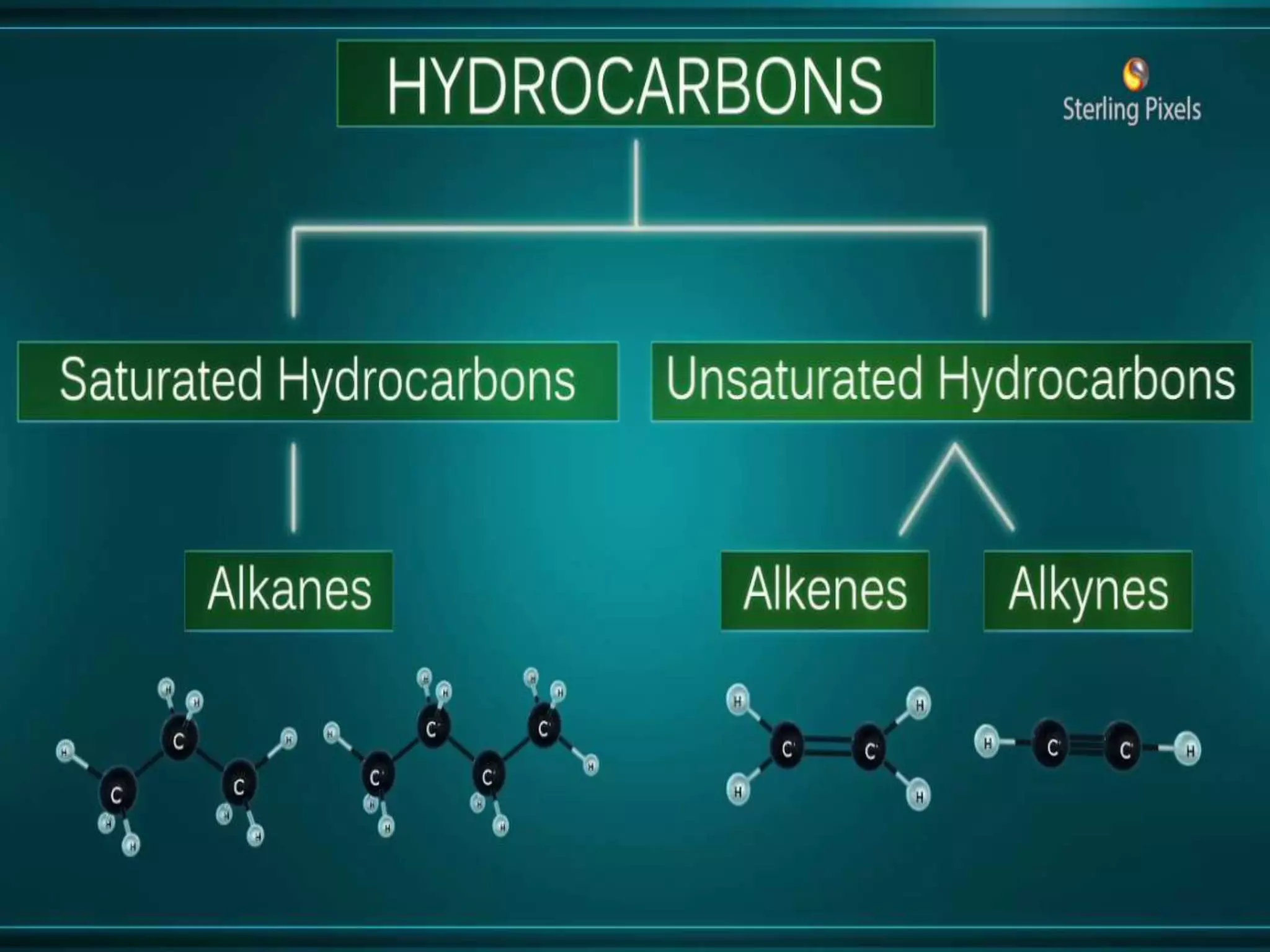
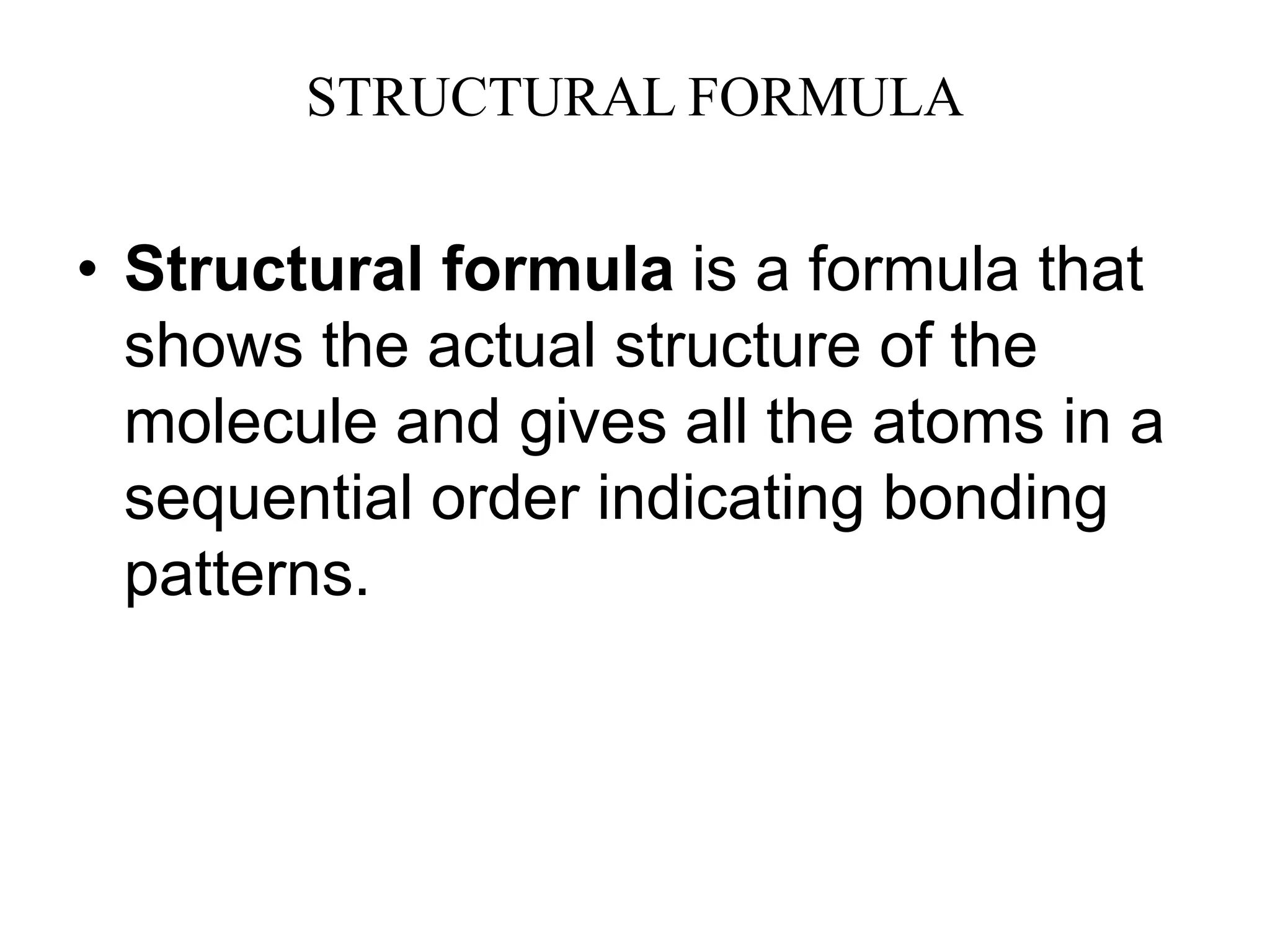
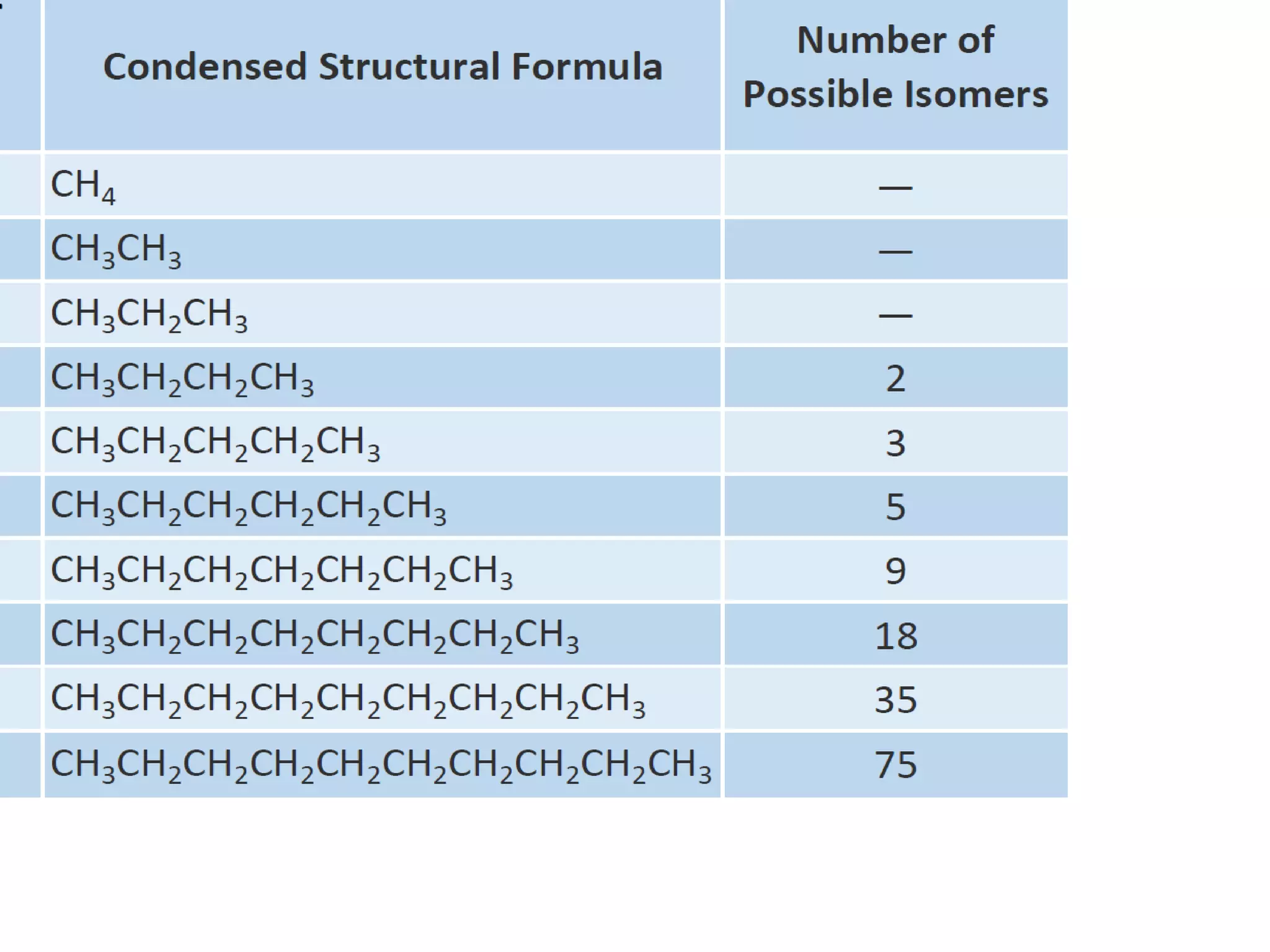
This document discusses carbon compounds and their classes. It introduces carbon catenation, which allows carbon to form chains through covalent bonds. The main classes of carbon compounds discussed are hydrocarbons, which are composed of carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons can be saturated, containing only single bonds, or unsaturated, containing double or triple bonds. Specific types of saturated hydrocarbons discussed include alkanes, which are saturated hydrocarbons with only single carbon-carbon bonds. Unsaturated hydrocarbons include alkenes with double bonds and alkynes with triple bonds. The document also discusses cyclic and aromatic hydrocarbons. It introduces molecular and structural formulas for writing formulas of organic compounds.