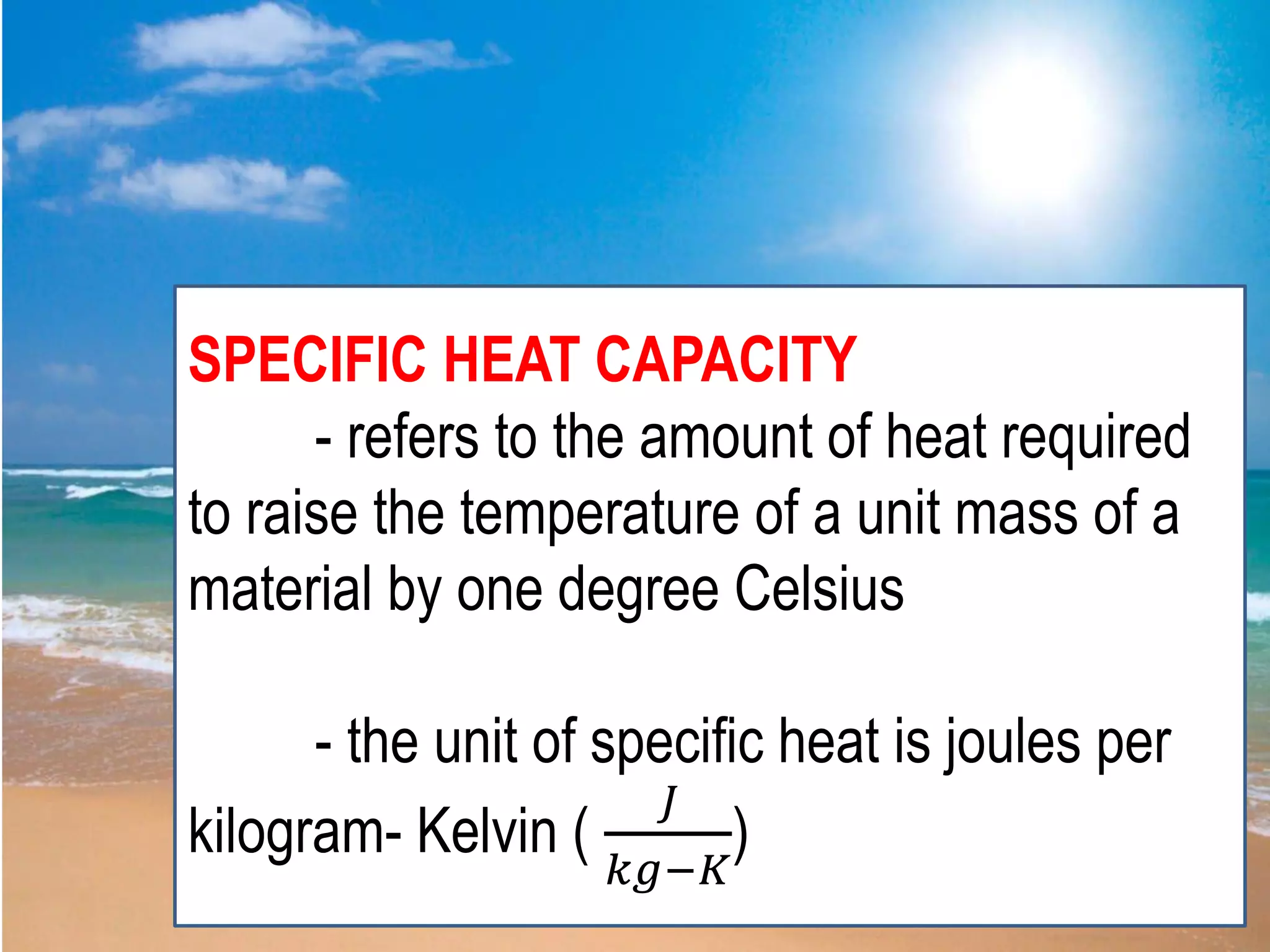
This document discusses several key concepts related to physics. It defines breeze as wind near bodies of water. It then explains specific heat capacity as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a material by one degree Celsius. Specific heat is described as how slowly an object heats up and cools down. The document also defines pressure as the ratio of force per unit area. Density is explained as the ratio of mass to volume, with denser materials sinking and less dense materials floating. Finally, it outlines the three mechanisms of heat transfer: conduction through physical contact, radiation through electromagnetic waves, and convection through fluid movement.