Embed presentation
Downloaded 46 times

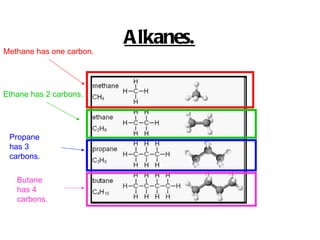
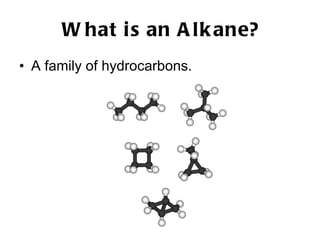


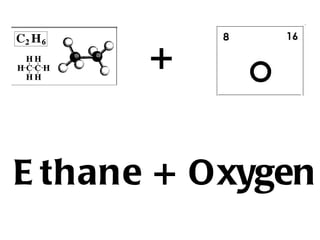
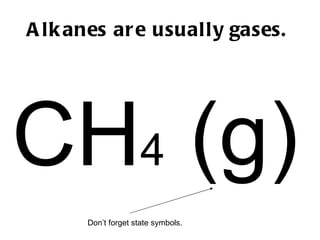



Hydrocarbons, specifically alkanes, are chains of carbon atoms surrounded by hydrogen atoms, with methane, ethane, propane, and butane being examples with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, respectively. Alkanes are generally unreactive with aqueous reagents due to the stability of their C-C and C-H bonds. The document also prompts readers to explore structural and molecular representations of alkanes and consider their reactions with oxygen.









