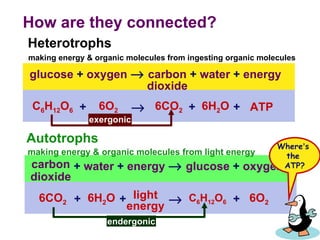
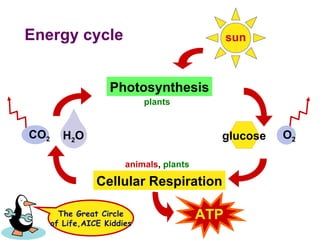
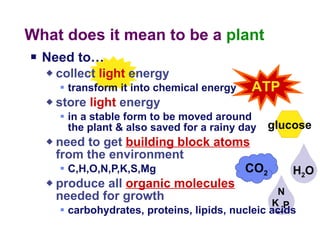
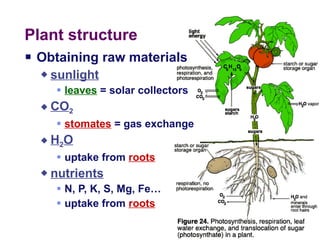
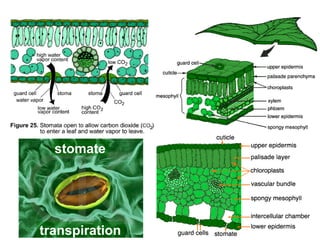
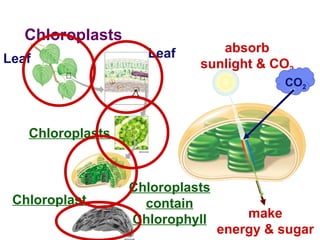
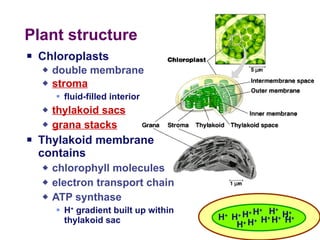
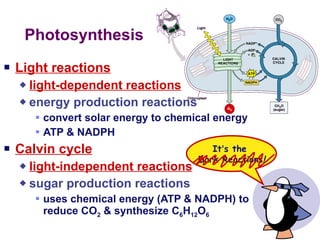
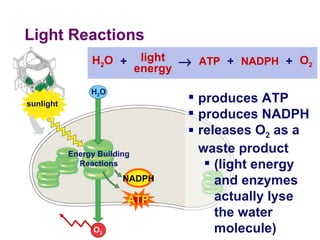
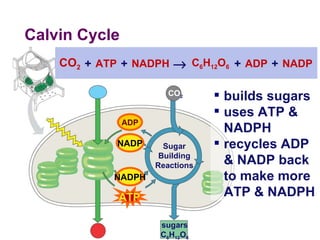
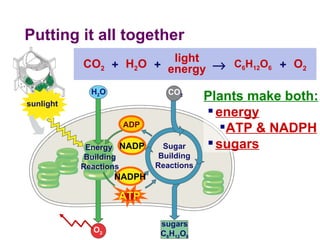
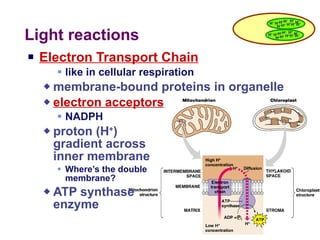
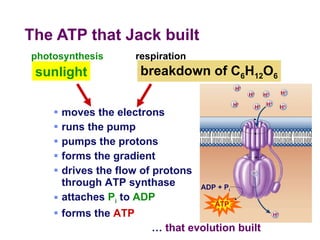
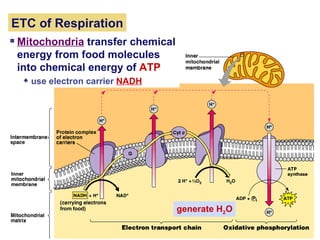
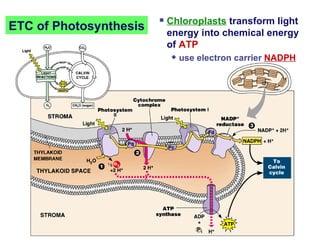
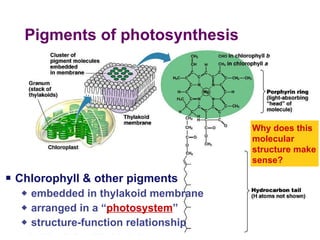
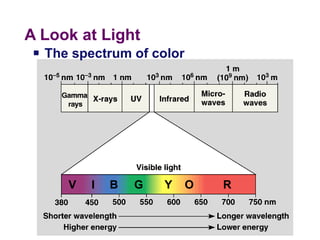
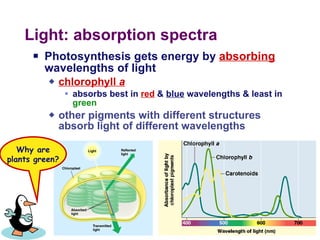
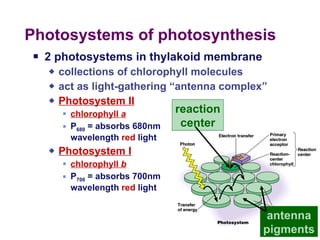
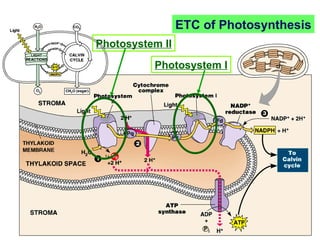
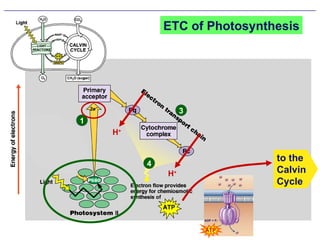
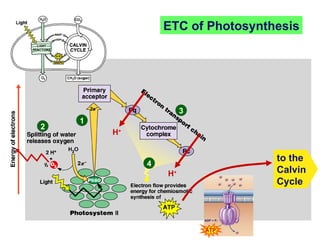
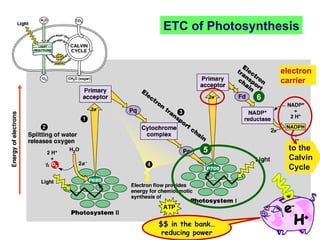
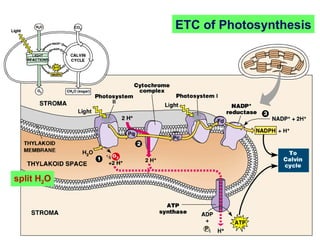
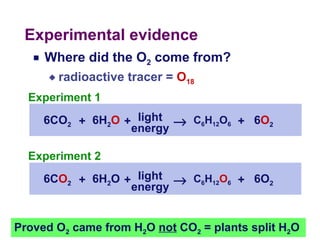
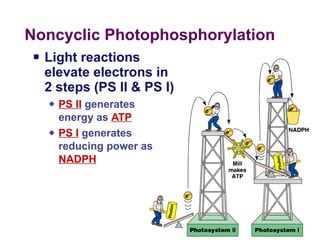
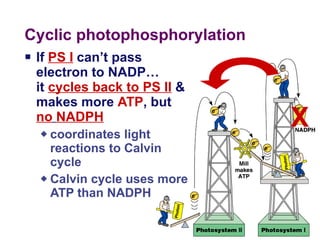
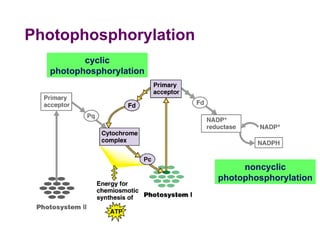
Photosynthesis uses energy from sunlight, carbon dioxide from air, and water to produce oxygen and energy-rich organic molecules like glucose. The light reactions use sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, providing energy and electrons. The Calvin cycle then uses ATP and NADPH to incorporate carbon from carbon dioxide into organic molecules like glucose. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of splitting water during the light reactions.