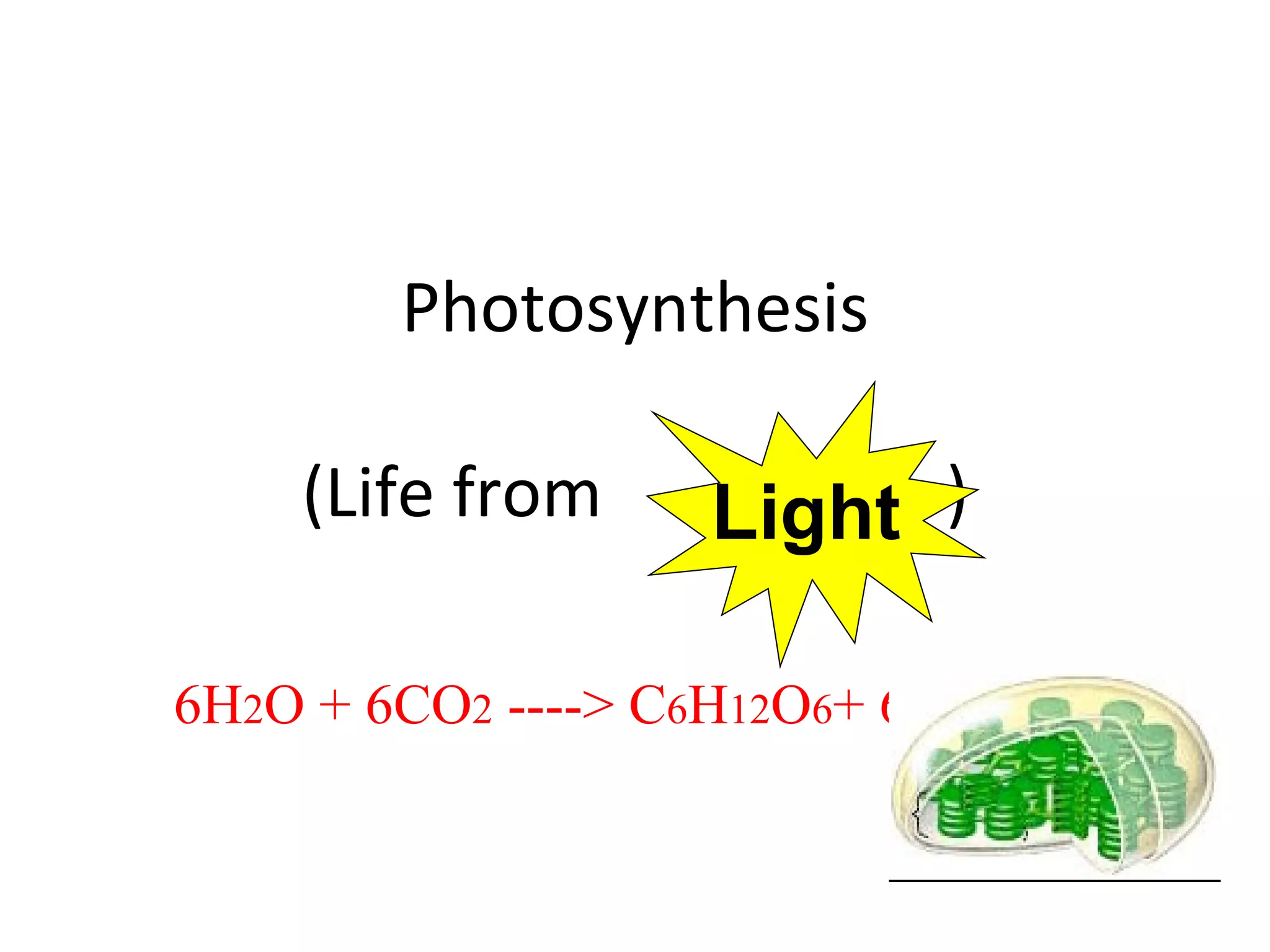
1) Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of ATP and sugars like glucose.
2) It is comprised of two stages - the light reaction which converts solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP, and the Calvin cycle which uses ATP to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars.
3) The process occurs in chloroplasts within plant cells, and relies on chlorophyll to absorb sunlight and drive the creation of ATP and oxygen from water and carbon dioxide.