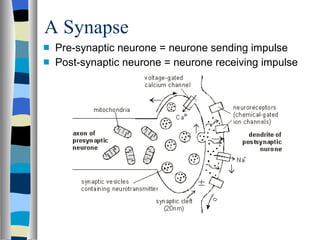
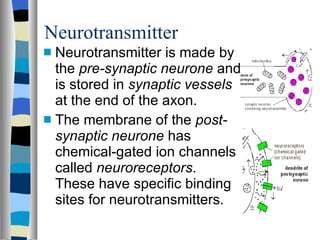
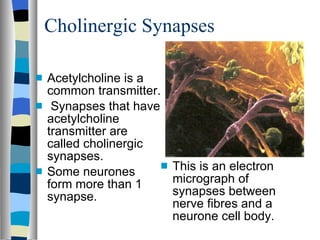
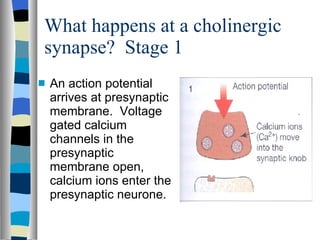
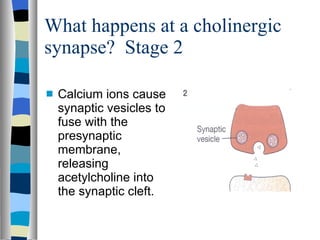
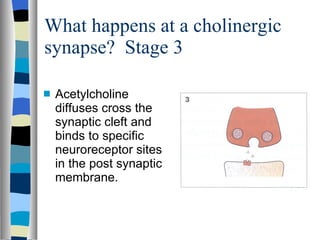
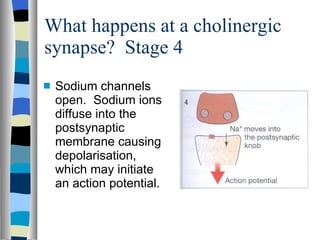
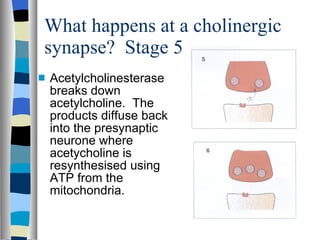
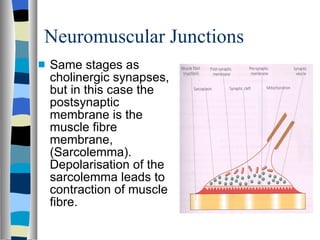
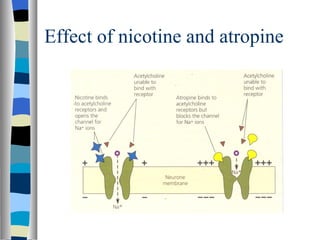
A synapse is the junction between two neurons, with a tiny gap called the synaptic cleft. Chemical neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic neuron and diffuse across the cleft to bind with receptor sites on the postsynaptic neuron, which can cause it to depolarize and generate an action potential. Neuromuscular junctions operate similarly, connecting motor neurons to muscle fibers. Drugs can mimic, stimulate, or inhibit neurotransmitters, affecting synaptic transmission in various ways.