1. The document discusses customer-driven marketing strategies, including market segmentation, targeting, differentiation, and positioning.
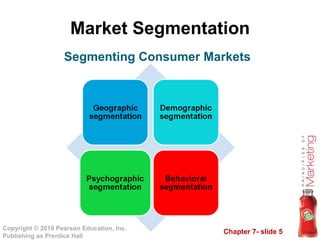
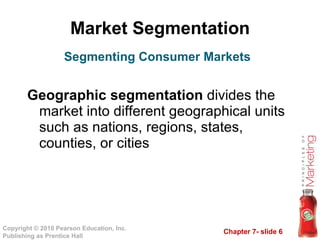
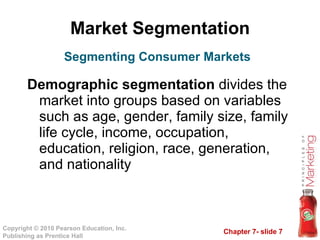
2. Market segmentation involves dividing large, heterogeneous markets into smaller segments based on geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors.
3. Targeting involves evaluating market segments and choosing specific segments to target based on size, attractiveness, and fit with company objectives.
4. Differentiation and positioning involve identifying competitive advantages to build a unique position for the product or service in customers' minds relative to competitors.