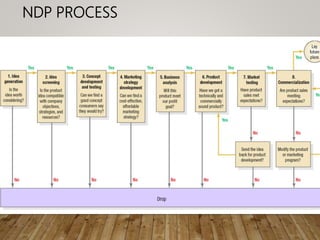
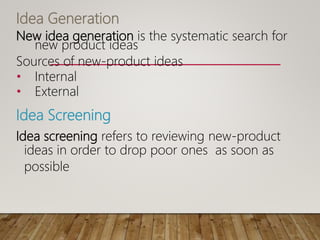
The document discusses lessons learned from failed product launches. It begins by defining new product development and explaining why companies engage in it. It then outlines the typical NPD process, including idea generation, screening, concept development, marketing strategy development, product development, market testing, and commercialization. Several examples of failed products are provided, such as the Pepsi Atom, Colgate Entrees brand extension, Apple Newton, Crystal Pepsi, Tata Nano, and Windows Vista. Key lessons from failures include specializing in a target group rather than everyone, dominating a niche rather than a small part of a large market, testing assumptions, having an adaptable product, and establishing a solid business model from the