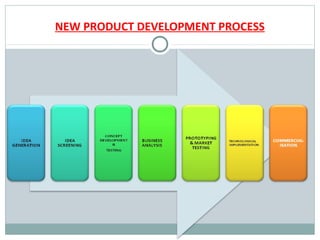
The document outlines the 7 step new product development process: [1] idea generation through techniques like brainstorming, [2] idea screening to evaluate ideas, [3] concept development and testing consumer reception, [4] business analysis of financial viability, [5] prototyping and market testing, [6] technological implementation, and [7] commercialization through marketing strategies. New product development is important for meeting changing consumer needs, making new profits, and combating threats while providing benefits like quality products, customer satisfaction, market expansion, and stable demand.