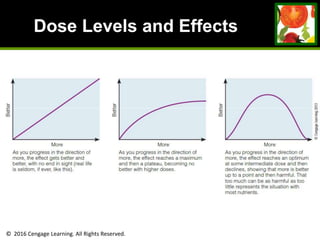
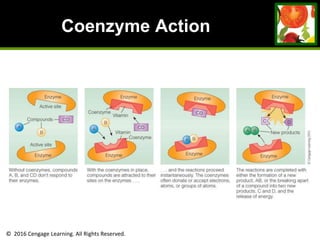
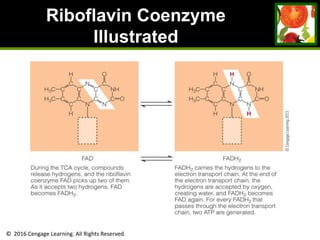
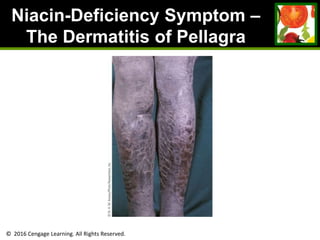
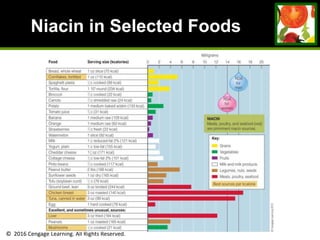
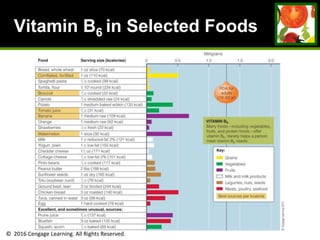
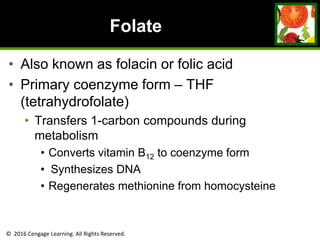
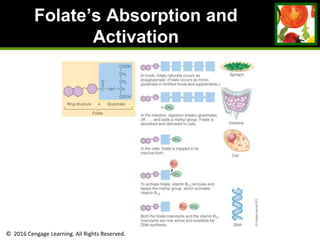
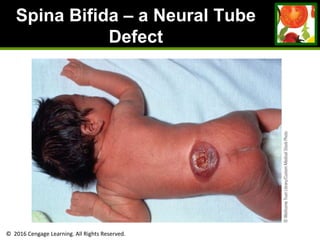
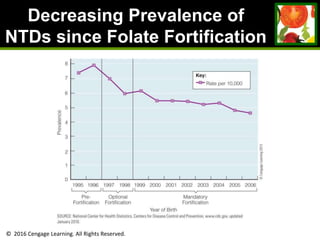
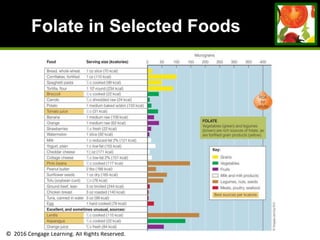
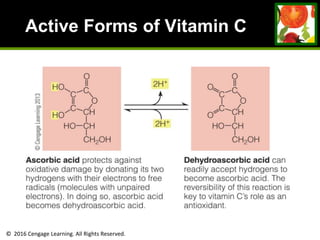
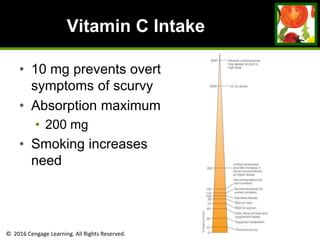
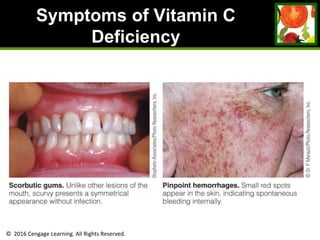
This document provides an overview of vitamin B and vitamin C. It discusses key topics such as bioavailability, precursors, dose levels and effects, coenzyme action, deficiency and toxicity for specific B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, biotin, pantothenic acid, vitamin B6, folate). Food sources for each vitamin are also presented. The purpose is to describe the water-soluble vitamins, their roles in the body, and factors that impact their absorption and function.