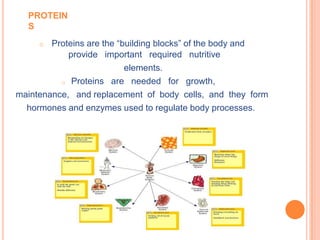
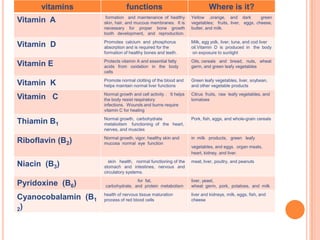
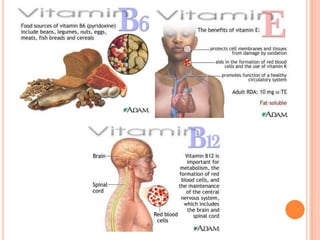
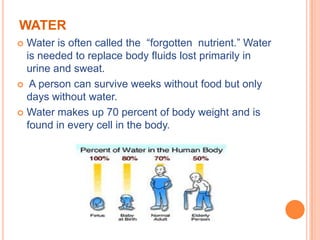
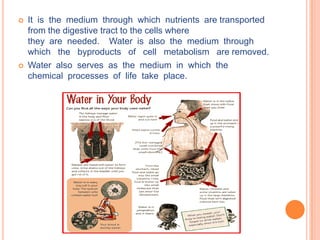
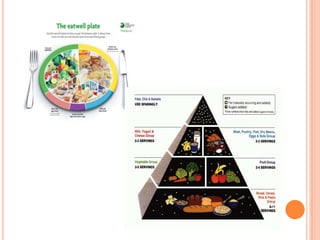
Here is an example of a typical lunch dish from my country and the food groups it contains:
Chicken sandwich:
- 2 slices whole wheat bread - Bread group
- Grilled chicken breast - Meat group
- Lettuce, tomato, cucumber - Vegetable group
- Mayonnaise - Fats group
- Apple - Fruit group
- Glass of milk - Dairy group
This chicken sandwich lunch contains components from 6 of the major food groups. The whole wheat bread provides grains and fiber. The grilled chicken offers a lean protein source. The lettuce, tomato and cucumber add vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients. Mayonnaise adds fat for flavor and to carry vitamins. The apple provides vitamins