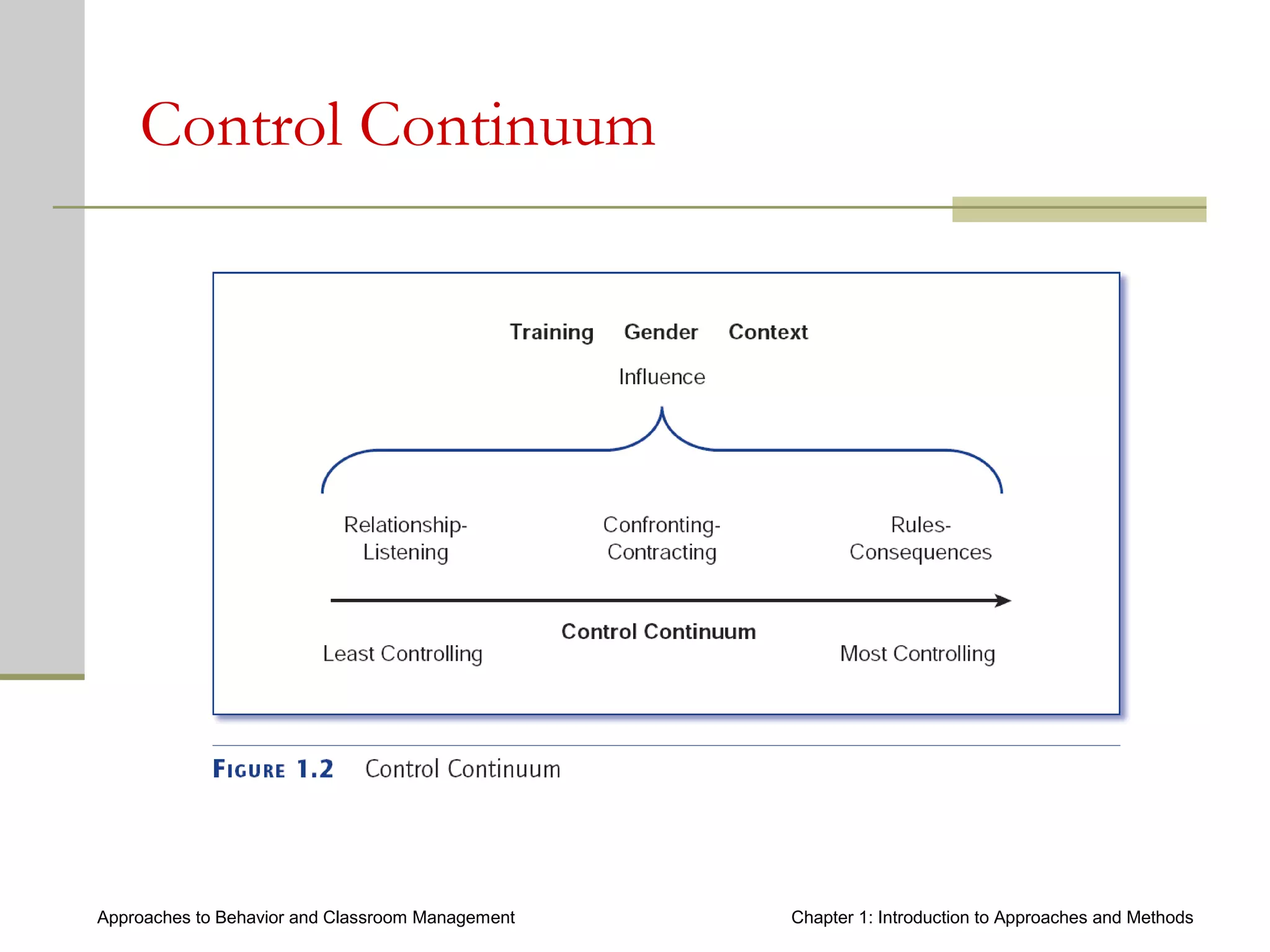
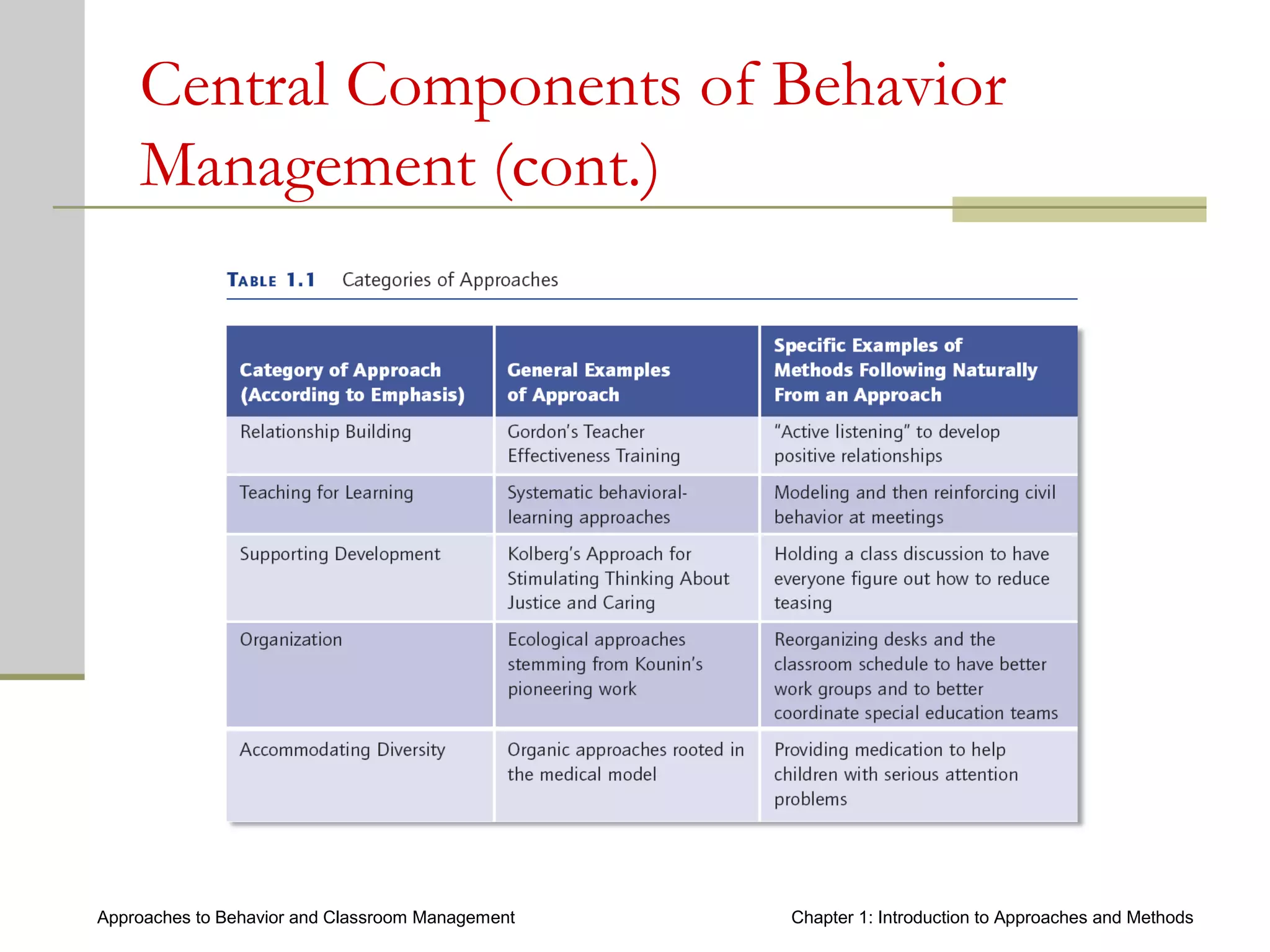
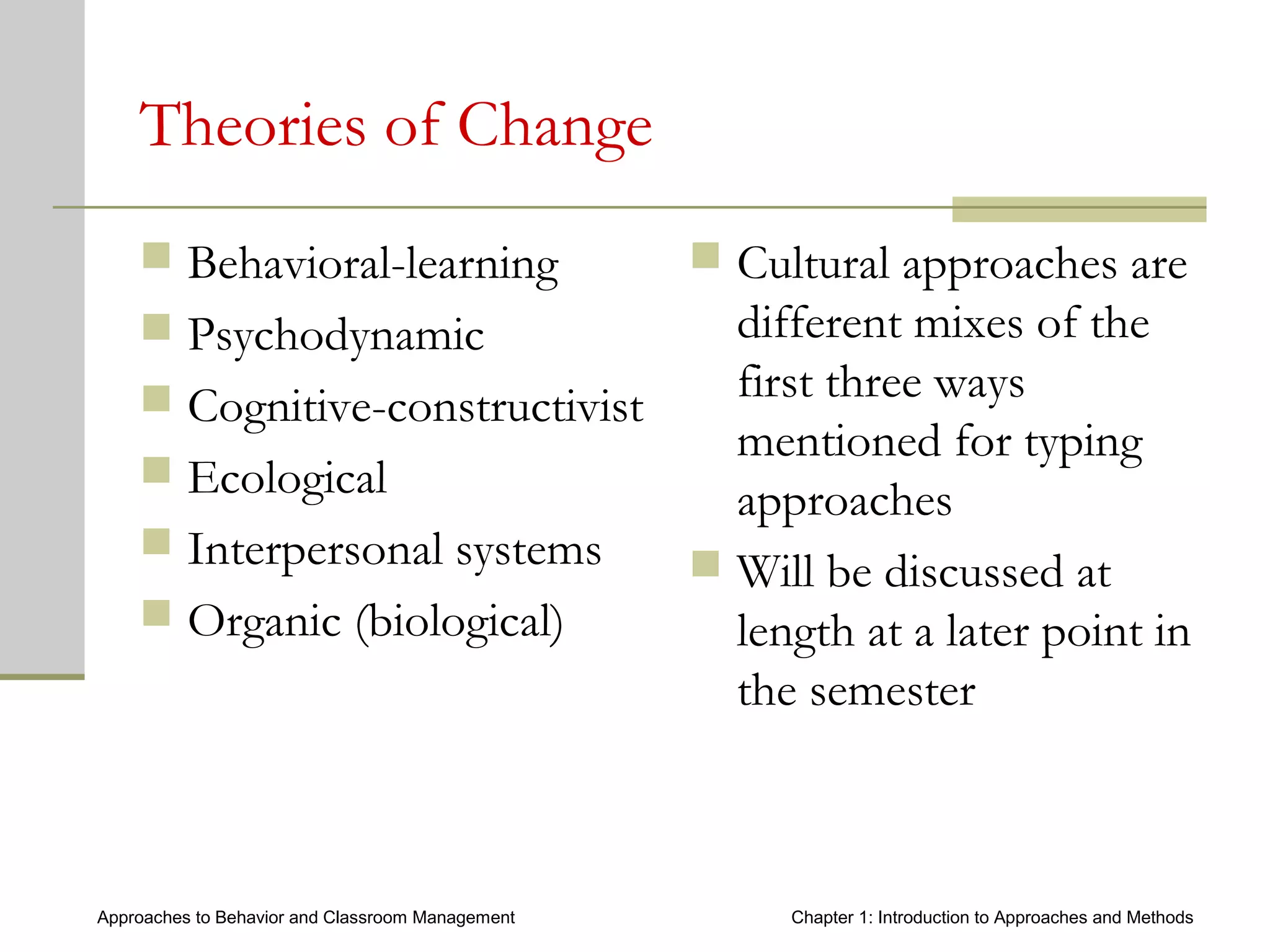
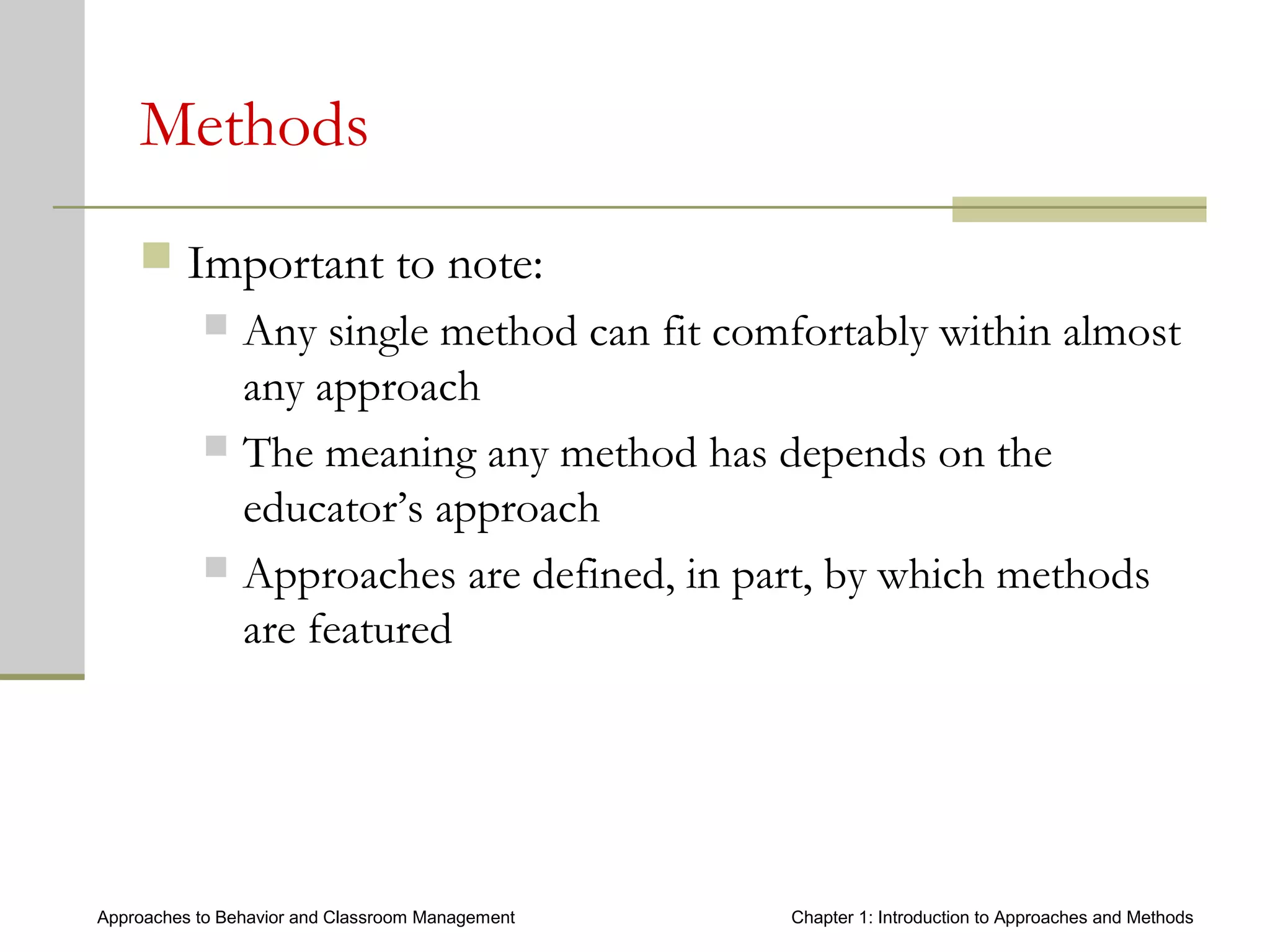
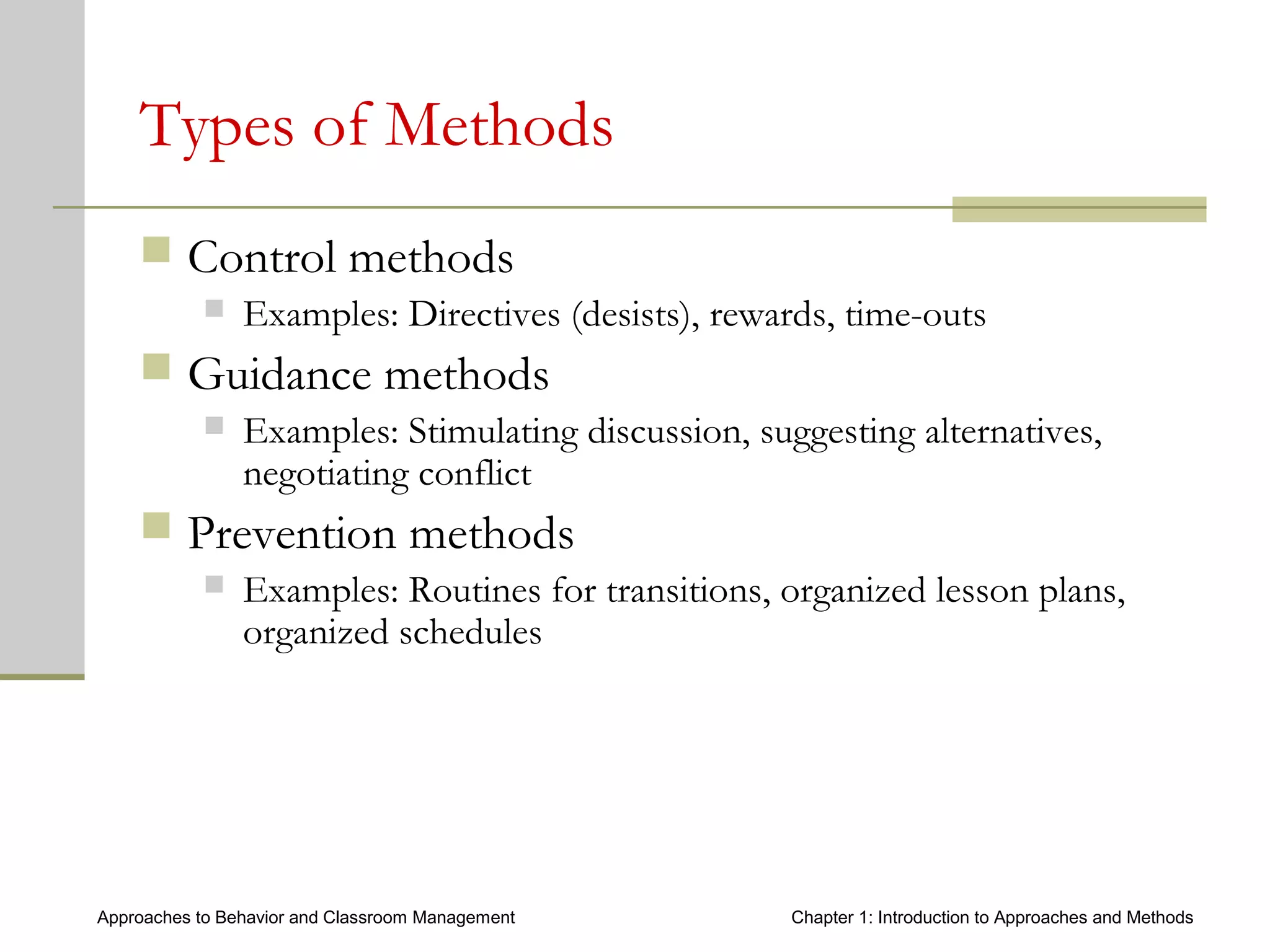
This document introduces approaches and methods for behavior and classroom management. It defines approaches as based on core concepts, values and assumptions about managing behavior effectively. Approaches can be categorized by levels of teacher control, emphasized components, theories of change and culture. The document also discusses Baumrind's parenting styles, a control continuum of teaching types, central components of behavior management, theories of change, types of methods, how methods relate to approaches, and choosing appropriate methods.