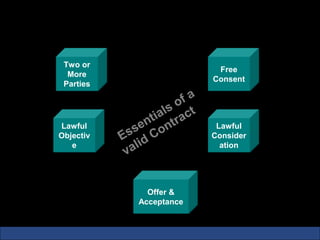
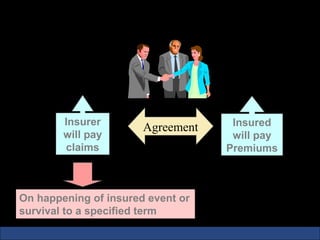
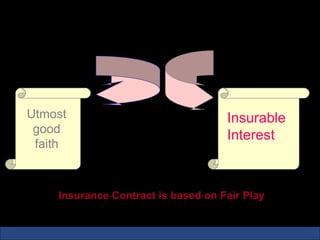
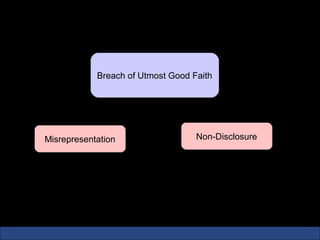
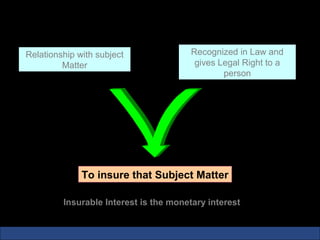
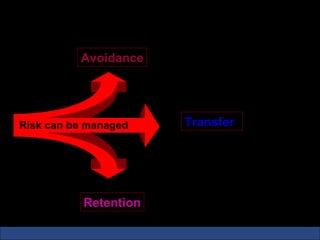
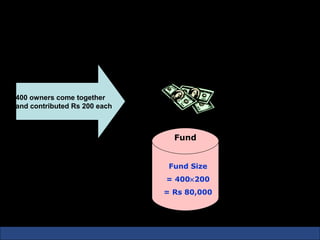
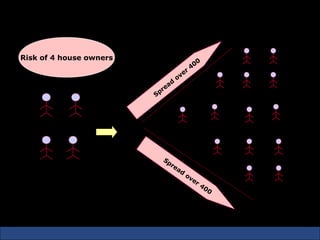
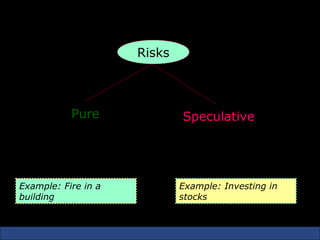
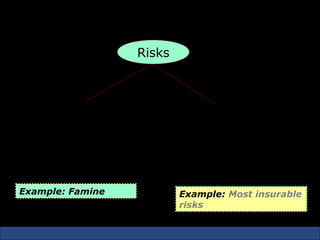
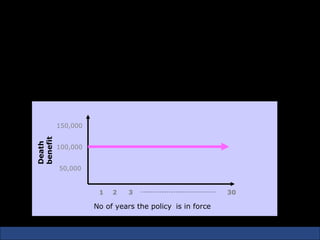
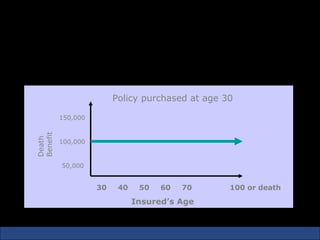
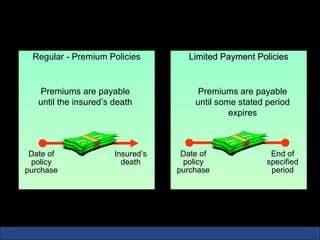
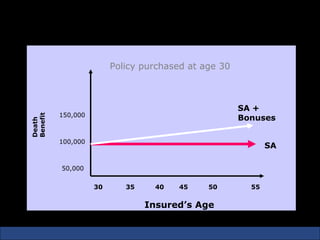
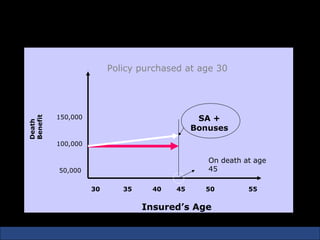
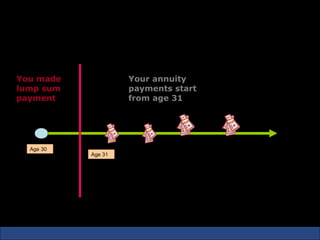
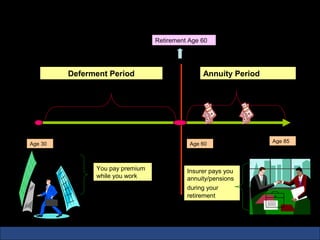
The document provides an introduction to various concepts in insurance including the life insurance contract, principles of insurance, utmost good faith, insurable interest, and different types of insurance policies like term insurance, whole life insurance, endowment policies, and annuities. It explains that a life insurance contract is a valid legal agreement between the insurer and insured where the insurer agrees to pay claims on the happening of an insured event in exchange for premiums paid by the insured.