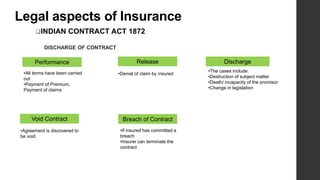
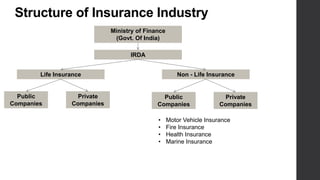
The document provides an overview of insurance concepts including the definition of insurance, features of insurance contracts, need for insurance, objectives of insurance contracts, insurable risks, legal aspects of insurance contracts, types of insurance policies, and reinsurance. It defines insurance as a contract where an individual or organization receives financial protection and reimbursement of damages from an insurer in exchange for payment of a premium. Key features of insurance include risk sharing among a large number of insured persons, payment on a contingency or insurable event, and payment of a premium. [END SUMMARY]