The document discusses key concepts in life insurance including:
1) Life insurance provides protection for dependents by ensuring continuity of income if the primary breadwinner dies. It also serves as a savings instrument and provides benefits like education funds and annuities.
2) Determining how much insurance is needed factors in immediate expenses after death, education costs of children, recurring costs of dependents, and paying off debts.
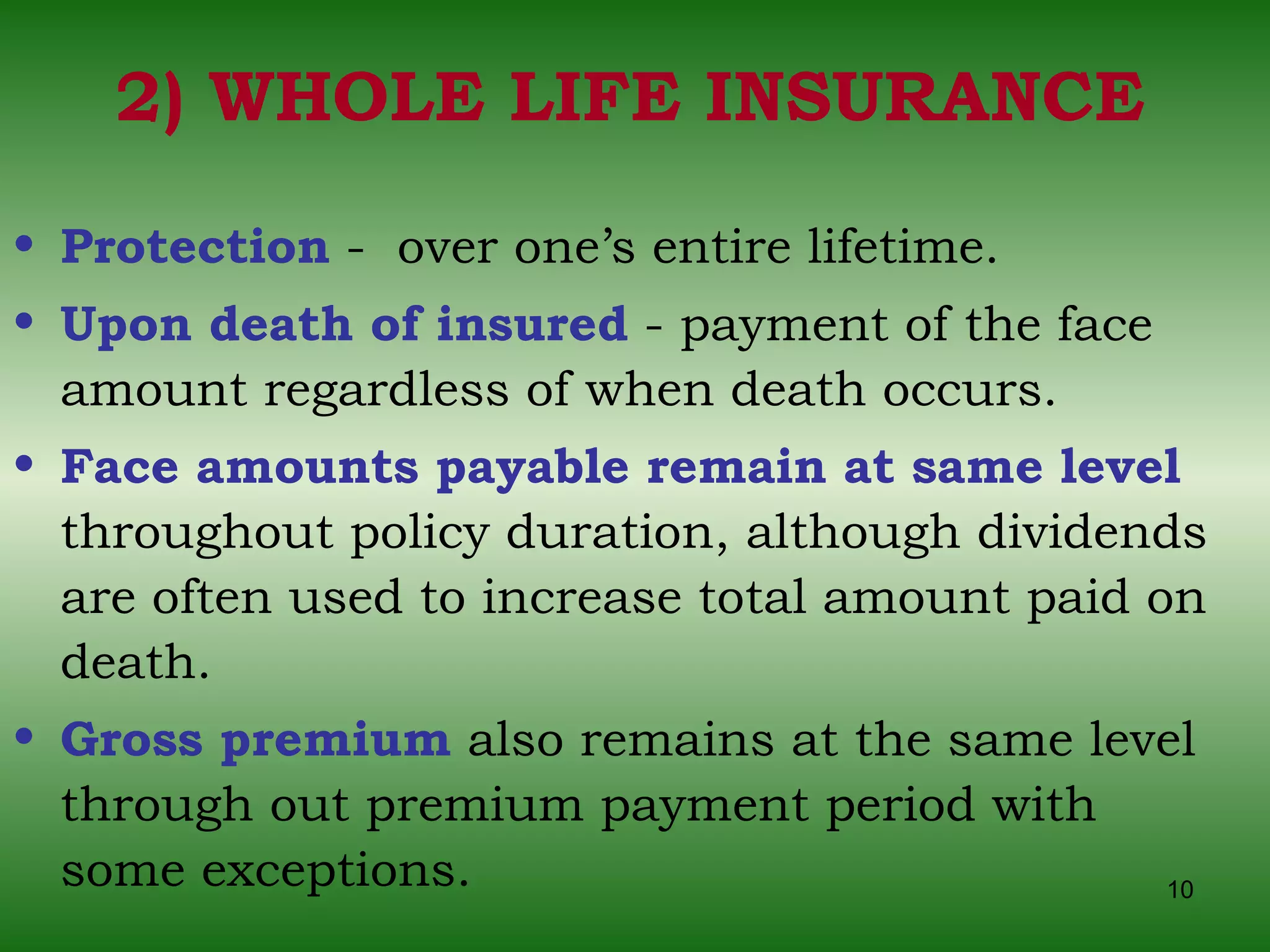
3) Popular life insurance plans include term insurance, whole life insurance, endowment insurance, and annuity contracts. Combination plans also exist to meet various policyholder needs.




![CLASSIFICATION OF LIFE AND HEALTH INSURANCE Group Insurance - A group of persons, who usually have a business or professional relationship to contract owner, are provided insurance coverage under a single contract . [ Ex – Employees, Savings account depositors, poorer sections of society, landless agricultural workers] Ordinary – individually issued policies – majority of policies fall within the ordinary category Industrial Insurance –includes life and health insurance policies issued to individuals in small amounts, premiums payable on a weekly or monthly basis. Not popular in India. Credit insurance –This is issued through lending institutions to cover debtors’ obligations if they die or become disabled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-principlesandpracticeoflifeinsurance-100629121504-phpapp02/75/Chapter-03-principles-and-practice-of-lifeinsurance-7-2048.jpg)


![3) ENDOWMENT INSURANCE PROMISE TO PAY - Policy amount on death of insured during a fixed term of years (+) Full-face amount at the end of the term if insured survives term ENDOWMENT INSURANCE = Term life insurance (+) Pure endowment [to pay face amount if insured dies during the period + to pay maturity amount only if insured is living at the end of a specific period, with nothing paid in case of prior death]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-principlesandpracticeoflifeinsurance-100629121504-phpapp02/75/Chapter-03-principles-and-practice-of-lifeinsurance-11-2048.jpg)