The document discusses various techniques for testing and troubleshooting network issues:
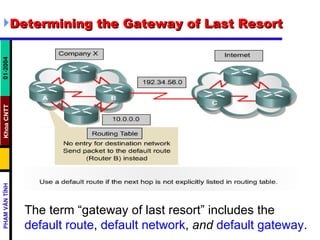
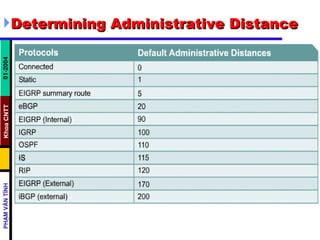
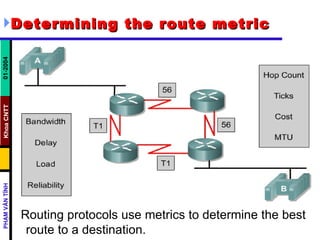
- The show ip route command displays the IP routing table containing known networks, subnetworks, and how routing information was learned. The "gateway of last resort" refers to the default route, network, or gateway.
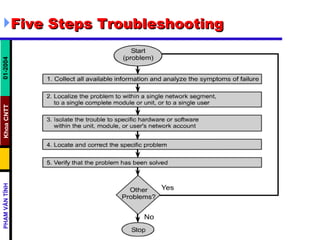
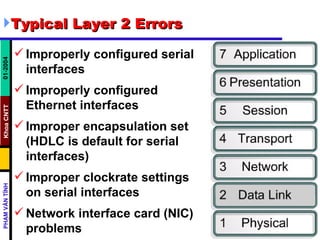
- Typical layer 1 errors include broken or disconnected cables, cables connected to the wrong ports, intermittent connections, or using the wrong cable type. Layer 2 errors include improperly configured interfaces, improper encapsulation, or NIC problems. Layer 3 errors involve incorrect routing protocol configuration, IP addresses, or subnet masks.
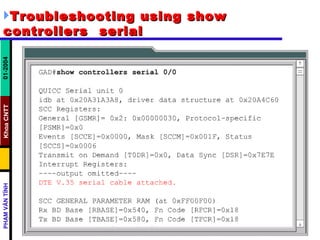
- The show interfaces command can help troubleshoot layer 1 by examining carrier transitions and resets, input errors, and hardware issues indicated by