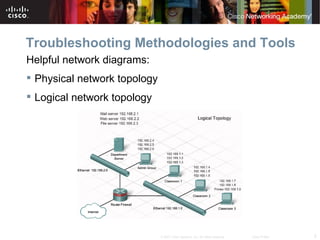
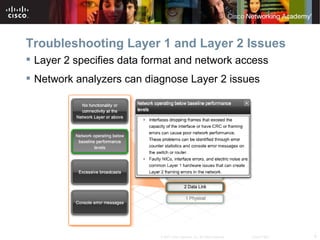
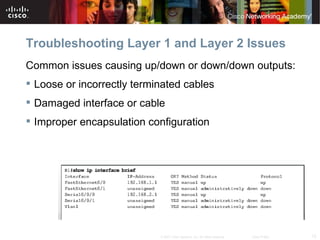
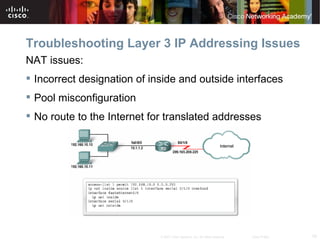
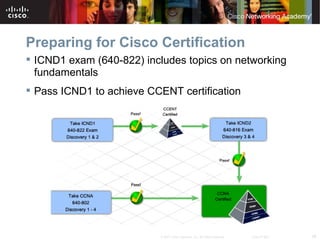
The document discusses troubleshooting network issues. It recommends using a top-down, bottom-up, or divide-and-conquer methodology. Issues are often caused by poor IP addressing schemes or firewall misconfigurations. Troubleshooting involves verifying hardware, cables, configurations, and protocols using tools like network analyzers. Preparing for Cisco certification requires a study plan to build knowledge of networking fundamentals through practice tests and labs.